shell中条件测试的三种格式:
格式1: test 条件表达式
格式2: [ 条件表达式 ]
格式3: [[ 条件表达式 ]]
使用test: [root@host-131 ~]# test -f file && echo true || echo false false [root@host-131 ~]# touch file [root@host-131 ~]# test -f file && echo true || echo false true [root@host-131 ~]# man test #可以查看帮助 -z 测试如果字符串长度是否为零: [root@host-131 ~]# test -z "yanglt" && echo 1 || echo 0 0 [root@host-131 ~]# char="yanglt" [root@host-131 ~]# test -z "$char" && echo 1 || echo 0 0 [root@host-131 ~]# char="" [root@host-131 ~]# test -z "$char" && echo 1 || echo 0 1
使用[]: [root@host-131 tmp]# touch yanglt.txt [root@host-131 tmp]# [ -f /tmp/yanglt.txt ] && echo 1 || echo 0 1 判断逻辑表达式写法: [root@host-131 tmp]# [ -f /tmp/yanglt.txt ] && echo 1 #成功输出1 1 [root@host-131 tmp]# [ -f /tmp/yanglt.txt ] || echo 0 #不成功输出0 [root@host-131 tmp]# [ -f /tmp/yanglt123.txt ] || echo 0 0 []命令和test命令的选项时通用的,所以[] 也可以用 man test 命令获取帮助
使用[[]]: [root@host-131 tmp]# [[ -f /tmp/yanglt.txt ]] && echo 1 || echo 0 1
注:[[]] 表达式和 []和test 测试表达式区别:
[[]]:可以使用通配符进行模式匹配,可以使用&& 、 || 、> 、< 等操作符
但不能用于[]中,[]中一般使用-a 、-o 、-gt(用于整数) 、-lt(用于整数)
查看帮助:
test、[]、[[]]这些操作符的用法,通过help test 或 man test查询得到帮助,完整的[]、[[]] 用法可以通过man bash来获得帮助。
一、文件测试表达
常用的文件测试操作符:
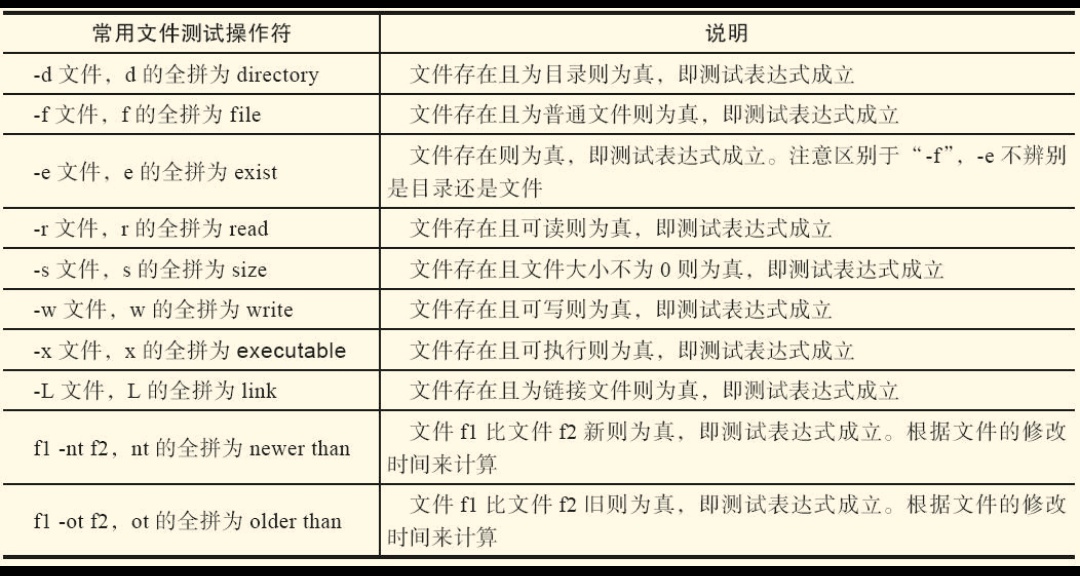
(1) 普通文件(测试文件类型) [root@host-131 ~]# touch yanglt [root@host-131 ~]# ls -l |grep "yanglt$" -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2592 6月 20 21:00 yanglt [root@host-131 ~]# [ -f yanglt ] && echo 1 || echo 0 1 (2)目录文件 (测试目录类型) [root@host-131 ~]# mkdir yanglt01 [root@host-131 ~]# [ -f yanglt01 ] && echo 1|| echo 0 #测试是否为普通文件 是为1,不是为0 0 [root@host-131 ~]# [ -e yanglt01 ] && echo 1|| echo 0 #测试yanglt001是否存在 1 [root@host-131 ~]# [ -d yanglt01 ] && echo 1|| echo 0 #测试是否为目录 1 [root@host-131 ~]# [ -d yanglt ] && echo 1|| echo 0 0 [root@host-131 ~]# (2)测试文件属性 [root@host-131 ~]# ls -l yanglt -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2592 6月 20 21:00 yanglt [root@host-131 ~]# ls -l yanglt01 总用量 0 [root@host-131 ~]# [ -r yanglt ] && echo 1||echo 0 1 [root@host-131 ~]# [ -w yanglt ] && echo 1 || echo 0 1 [root@host-131 ~]# [ -x yanglt ] && echo 1 || echo 0 0 [root@host-131 ~]# chmod 001 yanglt [root@host-131 ~]# ls -l yanglt ---------x 1 root root 2592 6月 20 21:00 yanglt #我们发现用户权限没有读写,但是下边依然可以返回1,这就是root用户比较特殊的地方 [root@host-131 ~]# echo 'text' > yanglt [root@host-131 ~]# cat yanglt text [root@host-131 ~]# [ -w yanglt ] && echo 1 || echo 0 1 [root@host-131 ~]# [ -x yanglt ] && echo 1 || echo 0 1 [root@host-131 ~]# [ -r yanglt ] && echo 1||echo 0 1 当我们切换用户后按照以上方法再次操作: [root@host-131 ~]# su - yanglt1 [yanglt1@host-131 ~]$ touch yanglt001 [yanglt1@host-131 ~]$ ls -l yanglt001 -rw-rw-r-- 1 yanglt1 yanglt1 0 6月 20 21:14 yanglt001 [yanglt1@host-131 ~]$ [ -x yanglt001 ] && echo 1 || echo 0 0 [yanglt1@host-131 ~]$ [ -w yanglt001 ] && echo 1 || echo 0 1 [yanglt1@host-131 ~]$ [ -r yanglt001 ] && echo 1 || echo 0 1 [yanglt1@host-131 ~]$ chmod 001 yanglt001 [yanglt1@host-131 ~]$ [ -x yanglt001 ] && echo 1 || echo 0 0 [yanglt1@host-131 ~]$ ls -l 总用量 0 ---------x 1 yanglt1 yanglt1 0 6月 20 21:14 yanglt001 #我们可以看到没有该用户读写执行权限,下边的测试结果可见 [yanglt1@host-131 ~]$ [ -x yanglt001 ] && echo 1 || echo 0 0 #因为文件所属主没有执行权限 [yanglt1@host-131 ~]$ [ -w yanglt001 ] && echo 1 || echo 0 0 [yanglt1@host-131 ~]$ [ -r 4yanglt001 ] && echo 1 || echo 0 0 [yanglt1@host-131 ~]$ 测试文件的读写执行属性,不仅要看rwx,还要看当前用户是否有操作该文件的对应权限
二、字符串测试表达式
对于字符串的测试,一定要将字符串加双引号之后在进行比较
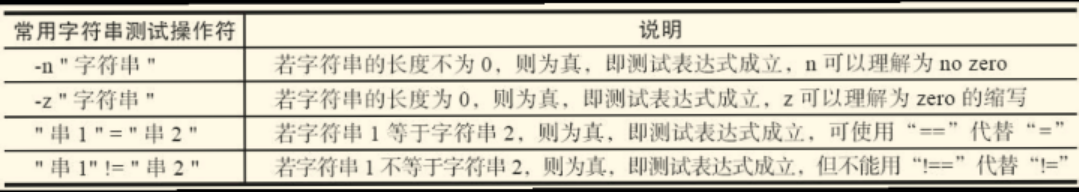
比较符号“!=”和“=”两端要有空格,比较两个字符串是否相同
[root@host-131 ~]# [ -n "abc" ]&& echo 1 || echo 0 #字符串长度不为零 1 [root@host-131 ~]# test -n "abc" && echo 1 || echo 0 1 [root@host-131 ~]# var="yanglt" [root@host-131 ~]# test -z "$var" && echo 1 || echo 0 #字符串长度为零的时候为真,现在不为真返回0 0 [root@host-131 ~]# [ "abc" = "abc"] #括号两边需要加空格 -bash: [: 缺少 `]' [root@host-131 ~]# [ "abc" = "abc" ] [root@host-131 ~]# [ "abc" = "abc" ] && echo 1 1 [root@host-131 ~]# [ "abc" != "abc" ] && echo 1 #成立返回1,不成立返回0 [root@host-131 ~]# [ "$var" != "abc" ] && echo 1 1 [root@host-131 ~]# [ "$var" = "abc" ] && echo 1 等号两边没有空格会出现以下判断错误: [root@host-131 ~]# [ "abc" = "1" ] && echo 1 || echo 0 0 [root@host-131 ~]# [ "abc"="1" ] && echo 1 || echo 0 1 [root@host-131 ~]#
字符串不加双引号出现逻辑的错误:
[root@host-131 ~]# var=""
[root@host-131 ~]# [ -n "$var" ] && echo 1 || echo 0
0
[root@host-131 ~]# [ -n $var ] && echo 1 || echo 0
1
[root@host-131 ~]# [ -z $var ] && echo 1 || echo 0
1
[root@host-131 ~]# [ -z "$var" ] && echo 1 || echo 0
1
[root@host-131 ~]#
三、数值测试表达式

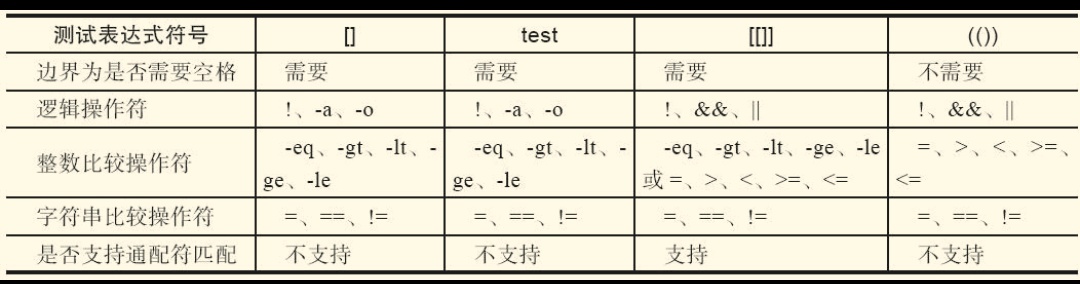
有关[]、[[]]、(())用法的小结:
- 整数加双引号的比较是对的。
- [[]]中用类似-eq等的写法是对的,[[]]中用类似>、<的写法也可能不对,有可能会只比较第一位,逻辑结果不对。
- []中用类似>、<的写法在语法上虽然可能没错,但逻辑结果不对,可以使用=、!=正确比较。
- (())中不能使用类似-eq等的写法,可以使用类似>、<的写法。
参考文件:跟老男孩学shell