一、新建一个vue项目,建立好后的相关文件
查看一下新建好的vue项目的结构:
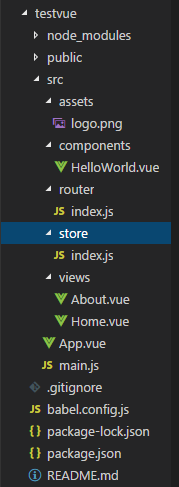
当前各个文件中的内容:
App.vue:主入口
<template> <div id="app"> <div id="nav"> <router-link to="/">Home</router-link> | <router-link to="/about">About</router-link> </div> <router-view/> </div> </template> <style> #app { font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; -moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; text-align: center; color: #2c3e50; } #nav { padding: 30px; } #nav a { font-weight: bold; color: #2c3e50; } #nav a.router-link-exact-active { color: #42b983; } </style>
main.js:Vue.config.productionTip用于切换是生产环境还是开发环境。这里创建Vue对象的时候同时关联上了App.vue中的id名为app的div标签。引入路由router的js文件以及存储数据的store。
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' import router from './router' import store from './store' Vue.config.productionTip = false new Vue({ router, store, render: h => h(App) }).$mount('#app')
router/index.js:这里定义路由对应的模板。有两种方式,一种是在开头先引入,例如Home.vue。另一种是先不引入,之后在component中引入。
import Vue from 'vue' import VueRouter from 'vue-router' import Home from '../views/Home.vue' Vue.use(VueRouter) const routes = [ { path: '/', name: 'Home', component: Home }, { path: '/about', name: 'About', // route level code-splitting // this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route // which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited. component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About.vue') } ] const router = new VueRouter({ mode: 'history', base: process.env.BASE_URL, routes }) export default router
store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { }, mutations: { }, actions: { }, modules: { } })
views/About.vue
<template> <div class="about"> <h1>This is an about page</h1> </div> </template>
views/Home.vue:这里面可以将component中的vue文件进行引入。
<template> <div class="home"> <img alt="Vue logo" src="../assets/logo.png"> <HelloWorld msg="Welcome to Your Vue.js App"/> </div> </template> <script> // @ is an alias to /src import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld.vue' export default { name: 'Home', components: { HelloWorld } } </script>
当前效果是:

点击About:
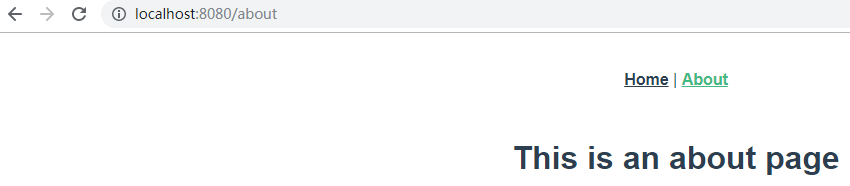
就将内容切换到了About.vue。
二、自己定义页面并进行路由
在views下新建一个Test.vue
<template> <!--只允许有一个根节点--> <div class="test"> <table> <tr> <td>编号</td> <td>姓名</td> <td>年龄</td> <td>性别</td> <td>邮箱</td> <td>爱好</td> <td>自我介绍</td> </tr> <tr v-for="(item, index) in users" :key="index"> <td>{{item.id}}</td> <td>{{item.username}}</td> <td>{{item.age}} </td> <td>{{item.gender}}</td> <td>{{item.email}}</td> <td>{{item.hobby}}</td> <td>{{item.introduce}}</td> </tr> </table> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Book", data () { return { msg: "hello world", users: {}, } }, created () { const that = this; axios.get('http://localhost:8181/user/findAll/') .then(function (response) { console.log(response); that.users = response.data; }) } } </script> <style scoped> </style>
在router/index.js中
import Vue from 'vue' import VueRouter from 'vue-router' import Home from '../views/Home.vue' import Test from '../views/Test.vue' Vue.use(VueRouter) const routes = [ { path: '/test', name: 'Test', component: Test, }, { path: '/', name: 'Home', component: Home }, { path: '/about', name: 'About', // route level code-splitting // this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route // which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited. component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About.vue') } ] const router = new VueRouter({ mode: 'history', base: process.env.BASE_URL, routes }) export default router
在App.vue中
<template> <div id="app"> <div id="nav"> <router-link to="/">Home</router-link> | <router-link to="/about">About</router-link> | <router-link to="/test">Test</router-link> </div> <router-view/> </div> </template> <style> #app { font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; -moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; text-align: center; color: #2c3e50; } #nav { padding: 30px; } #nav a { font-weight: bold; color: #2c3e50; } #nav a.router-link-exact-active { color: #42b983; } </style>
三、新建一个springboot项目,勾选上lombok、web、jpa、mysql
(1)配置连接数据库以及jpa相关:后盾使用8181端口,前端使用8080端口。
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jpa:
#控制台显示SQL
show-sql: true
properties:
hibernate:
format_sql: true
server:
port: 8181
(2)数据库相关设计
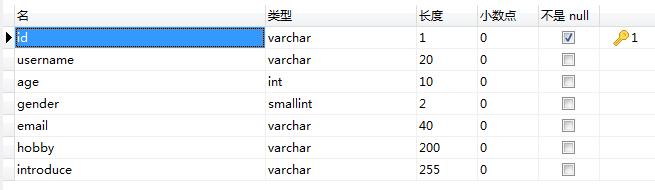
(3) 新建一个entity包用于存放实体类、一个repository包用于存放jpa类,一个config包用于存放后端和前端跨域交互配置,一个controller。
User.java
package com.gong.springbootvue.entity; import lombok.Data; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.Id; @Entity @Data public class User { @Id private Integer id; private String username; private Integer age; private Integer gender; private String email; private String hobby; private String introduce; }
Entity用于标识是一个实体类,Data用于自动生成getter和setter等方法,Id用于标识主键。
UserRepository.java
package com.gong.springbootvue.repository; import com.gong.springbootvue.entity.User; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User,Integer> { }
继承了JpaRepository之后就会有相应的增删改查方法了,不需要自己写,第一个泛型是实体类类型,第二个泛型是主键类型。
UserController.java
package com.gong.springbootvue.controller; import com.gong.springbootvue.entity.User; import com.gong.springbootvue.repository.UserRepository; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import java.util.List; @Controller @RequestMapping("/user") public class UserController { @Autowired UserRepository userRepository; @ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/findAll") public List<User> getAll(){ return userRepository.findAll(); } }
VueConfig.java
package com.gong.springbootvue.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer; @Configuration public class VueConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer{ @Override public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) { registry.addMapping("/**") .allowedOrigins("*") .allowedMethods("GET","HEAD","POST","PUT","DELETE","OPTIONS") .allowCredentials(true) .maxAge(3600) .allowedHeaders("*"); } }
四、分别启动后端服务和前端服务
先看下后端是否能正确运行:

再看下前端:
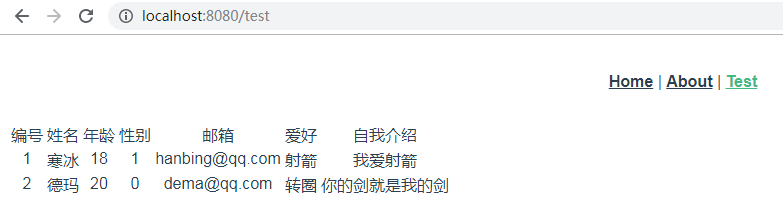
说明前端与后端交互成功。
总结:
后端中要配置与前端不同的端口,同时定义一个配置类用于配置与Vue进行交互。
前端使用axios发送请求获取后端传过来的json格式的数据,相关数据可以赋给data中的数据。使用created()方法在刷新页面时就发送请求。