spring循环依赖
本章需要解决的问题
- 什么是循环依赖
- 如何解决循环依赖
- 为何需要三级缓存
- 为何需要二级缓存
- 如何拓展
- spring是否解决构造器的循环依赖
- spring是否解决多例下的循环依赖
问题1,什么是循环依赖
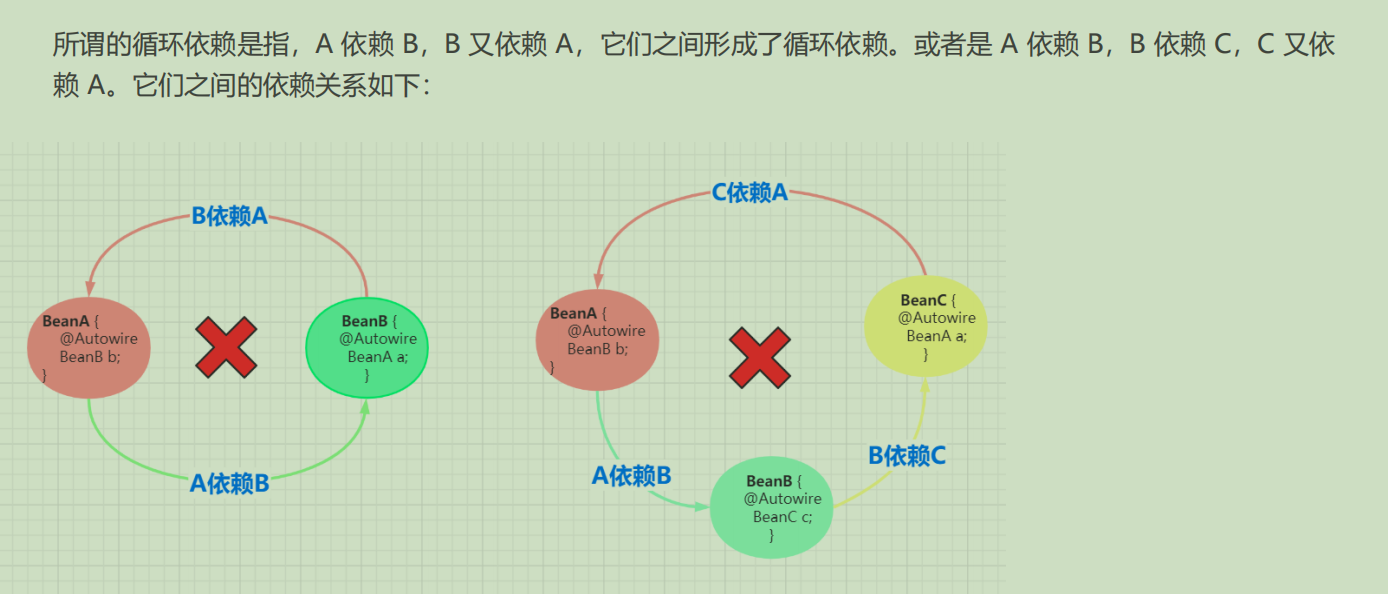
问题2 如何解决循环依赖-三级缓存
- 注意看每一级缓存的类型,尤其是value类型
-
为什么需要二级缓存
一级缓存和二级缓存相比:二级缓存是为了分离成熟bean和未注入属性bean的存放,防止多线程在bean还未创建完成时读取到,所以也是为了保证我们getbean是完整的bean
还有一个作用是为了存储三级缓存创建出来的早期bean,防止三级缓存重复执行
-
为什么需要三级缓存(当面试题看,不要深究)
bean的aop动态代理创建是在初始化之后,但是循环依赖的bean如果使用了动态代理,那无法等到解决完循环依赖在来创建动态代理,这个时候属性已经注入,所以需要提前创建aop,那么提前创建的位置在哪里?正常的bean是在初始化创建的,可以通过判断是否是循环依赖,如果是就实例化之后调用。没有就初始化后调用。
-
如何判断当前bean是否是循环依赖
看是否有二级缓存,有就是循环依赖
-
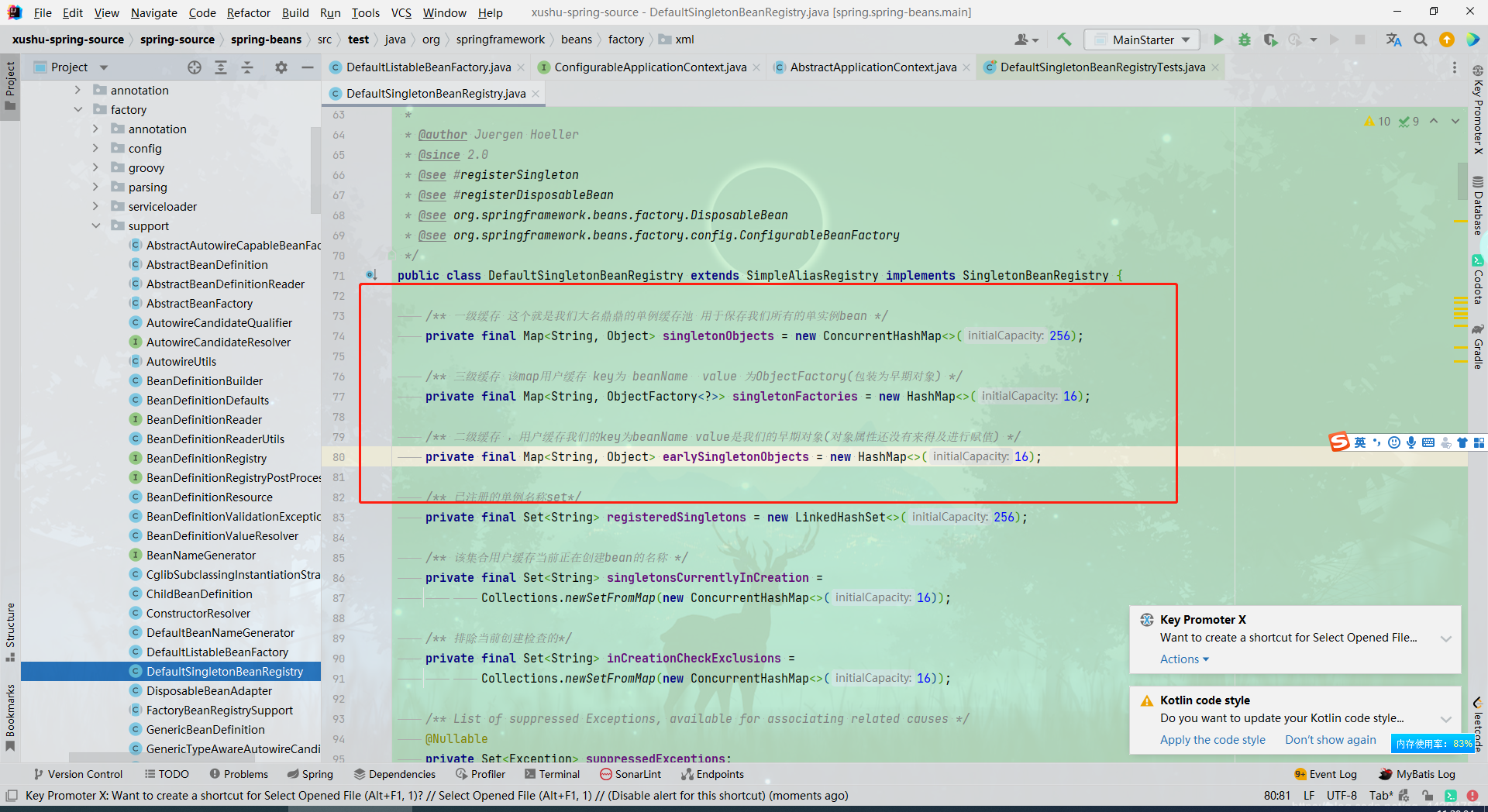
三级缓存那个关于aop的判断怎么加?这里有几个例子,挨个分析其原理,为什么可行,为什么不可行

-
看上面这个位置,这个是不可行的,实例化最终是放在二级缓存,不管是否是循环依赖都会在实例化后创建动态代理,而且创建本身的时候是没法判断是否是循环依赖,只有b引用a,这种情况才能判断是否是循环依赖。所以判断要在getSingleton方法中
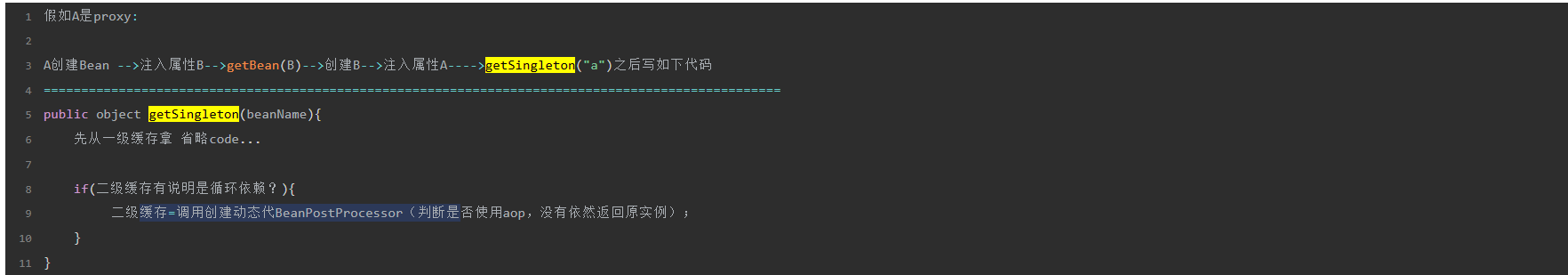
-
看上面这个位置,这里是可行的(注意,二级魂村完全可以解决循环依赖,包括扩展能力,(扩展能力指调用beanpostprocessor,aop也是基于beanpostprocessor,也是可以解决的))。那三级缓存的是干嘛的?(非要找一个理由:)spring的方法都是单一职责,getBean只是为了获取bean,但是调用创建动态代理beanPostProcessor是属于create的过程中,如果判断代码在这里写会显得耦合。为了解耦,将调用创建动态代理beanPostProcessor放在creatBean中。

所以判断当前是否是循环依赖放在getSingleton里吗?并不是,看上面三级缓存的结构,三级缓存存的是一个函数接口,函数接口实现创建动态代理调用beanPostProcessor,为了避免重复创建,调用吧返回的动态里对象或者原实力放到二级缓存中。
总结:三级缓存实现了接口,扩展,性能,代码阅读性。
-
-
为什么spring不能解决构造器的循环依赖
看上图,构造器实例化之前,一二三级缓存并没有bean的任何信息,实例化之后才放入三级缓存中。
-
为什么多例不能解决循环依赖
解决循环依赖的核心是利用缓存。多例没有使用缓存所以无法解决
-
如何关闭循环依赖
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); applicationContext.setAllowCircularReferences(false); applicationContext.register(AppConfig.class); applicationContext.refresh(); } } -
如何进行扩展
bean可以通过实现SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口,对getEarlyBeanReference进行扩展,看下面这个例子
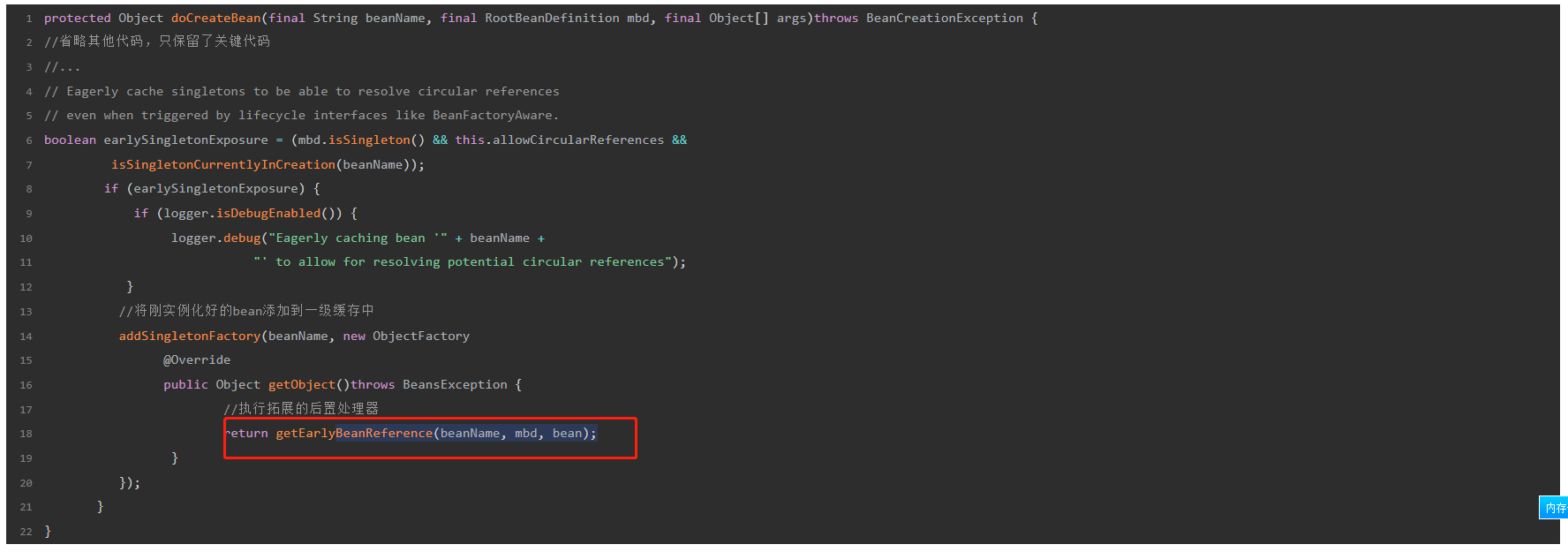
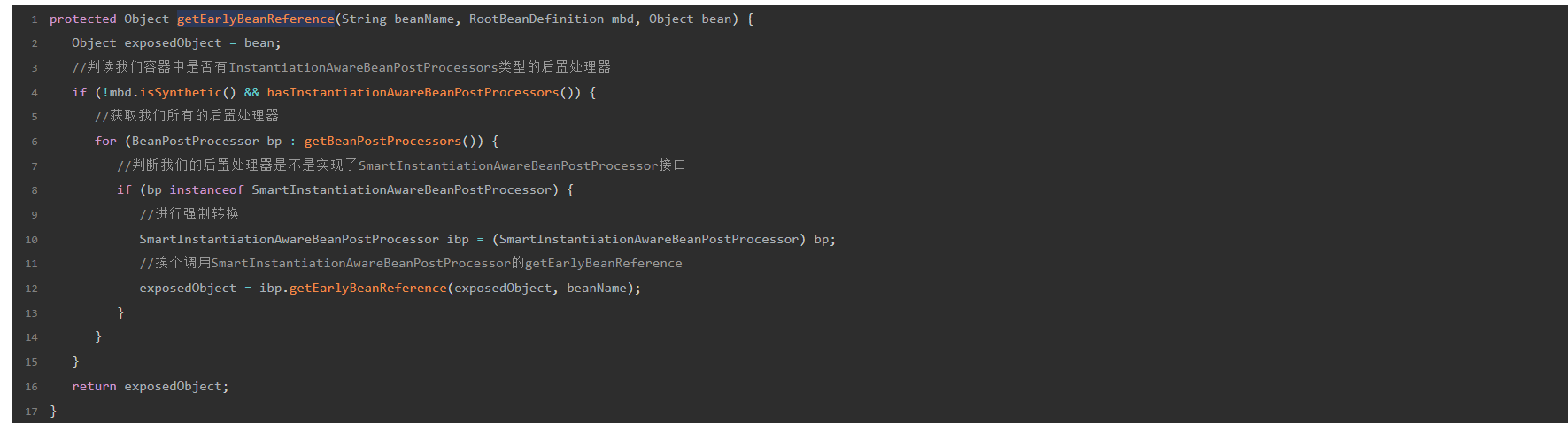
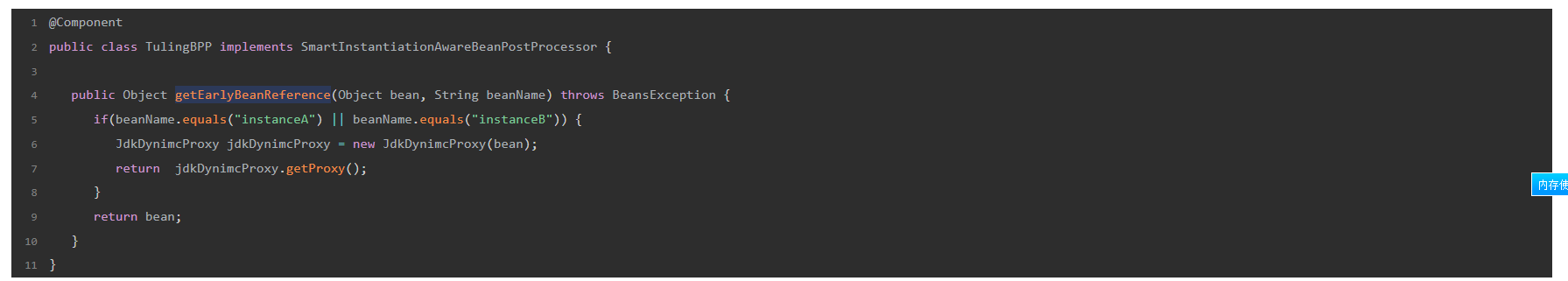
-
最后附上三级缓存这个类DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry,把注释好好读一下
/* * Copyright 2002-2018 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.beans.factory.support; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.LinkedHashSet; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationNotAllowedException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCurrentlyInCreationException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean; import org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.SingletonBeanRegistry; import org.springframework.core.SimpleAliasRegistry; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; import org.springframework.util.Assert; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; /** * Generic registry for shared bean instances, implementing the * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.SingletonBeanRegistry}. * Allows for registering singleton instances that should be shared * for all callers of the registry, to be obtained via bean name. * * <p>Also supports registration of * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean} instances, * (which might or might not correspond to registered singletons), * to be destroyed on shutdown of the registry. Dependencies between * beans can be registered to enforce an appropriate shutdown order. * * <p>This class mainly serves as base class for * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory} implementations, * factoring out the common management of singleton bean instances. Note that * the {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory} * interface extends the {@link SingletonBeanRegistry} interface. * * <p>Note that this class assumes neither a bean definition concept * nor a specific creation process for bean instances, in contrast to * {@link AbstractBeanFactory} and {@link DefaultListableBeanFactory} * (which inherit from it). Can alternatively also be used as a nested * helper to delegate to. * * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 2.0 * @see #registerSingleton * @see #registerDisposableBean * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory */ public class DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry extends SimpleAliasRegistry implements SingletonBeanRegistry { /** 一级缓存 这个就是我们大名鼎鼎的单例缓存池 用于保存我们所有的单实例bean */ private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256); /** 三级缓存 该map用户缓存 key为 beanName value 为ObjectFactory(包装为早期对象) */ private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap<>(16); /** 二级缓存 ,用户缓存我们的key为beanName value是我们的早期对象(对象属性还没有来得及进行赋值) */ private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new HashMap<>(16); /** 已注册的单例名称set*/ private final Set<String> registeredSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<>(256); /** 该集合用户缓存当前正在创建bean的名称 */ private final Set<String> singletonsCurrentlyInCreation = Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16)); /** 排除当前创建检查的*/ private final Set<String> inCreationCheckExclusions = Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16)); /** List of suppressed Exceptions, available for associating related causes */ @Nullable private Set<Exception> suppressedExceptions; /** Flag that indicates whether we're currently within destroySingletons */ private boolean singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = false; /** 用户缓存记录实现了DisposableBean 接口的实例 */ private final Map<String, Object> disposableBeans = new LinkedHashMap<>(); /** 缓存bean的属性关系的映射<tulingServce,<tulingDao,tulingDao2> --> Set of bean names that the bean contains */ private final Map<String, Set<String>> containedBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16); /** * Map between dependent bean names: bean name to Set of dependent bean names. * * 保存的是依赖 beanName 之间的映射关系:beanName - > 依赖 beanName 的集合 */ private final Map<String, Set<String>> dependentBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64); /** * Map between depending bean names: bean name to Set of bean names for the bean's dependencies. * * 保存的是依赖 beanName 之间的映射关系:依赖 beanName - > beanName 的集合 */ private final Map<String, Set<String>> dependenciesForBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64); @Override public void registerSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) throws IllegalStateException { Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null"); Assert.notNull(singletonObject, "Singleton object must not be null"); synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { Object oldObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName); if (oldObject != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Could not register object [" + singletonObject + "] under bean name '" + beanName + "': there is already object [" + oldObject + "] bound"); } addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject); } } /** * 把对象加入到单例缓存池中(所谓的一级缓存 并且考虑循环依赖和正常情况下,移除二三级缓存) * @param beanName bean的名称 * @param singletonObject 创建出来的单实例bean */ protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) { synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { //加入到单例缓存池中 this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject); //从三级缓存中移除(针对的不是处理循环依赖的) this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName); //从二级缓存中移除(循环依赖的时候 早期对象存在于二级缓存) this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName); //用来记录保存已经处理的bean this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName); } } /** * 该方法用于把早期对象包装成一个ObjectFactory 暴露到三级缓存中 用于将解决循环依赖... * @param beanName the name of the bean * @param singletonFactory the factory for the singleton object */ protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) { Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null"); //同步加锁 synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { //单例缓存池中没有包含当前的bean if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) { //加入到三级缓存中,,,,,暴露早期对象用于解决循环依赖 this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory); this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName); this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName); } } } /** * 该方法是一个空壳方法 * @param beanName bean的名称 * @return 缓存中的对象(有可能是一个单例完整对象,也有可能是一个早期对象(用于解决循环依赖)) */ @Override @Nullable public Object getSingleton(String beanName) { //在这里 系统一般是允许早期对象引用的 allowEarlyReference通过这个参数可以控制解决循环依赖 return getSingleton(beanName, true); } /** * 在网上很多很多写源码的大佬或者是<spring源码深度解析>一书上,也没有说清楚为啥要使用三级缓存(二级缓存可不可以能够 * 解决) 答案是:可以, 但是没有很好的扩展性为啥这么说....... * 原因: 获取三级缓存-----getEarlyBeanReference()经过一系列的后置处理来给我们早期对象进行特殊化处理 * //从三级缓存中获取包装对象的时候 ,他会经过一次后置处理器的处理对我们早期对象的bean进行 * 特殊化处理,但是spring的原生后置处理器没有经过处理,而是留给了我们程序员进行扩展 * singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject(); * 把三级缓存移植到二级缓存中 * this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject); * //删除三级缓存中的之 * this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName); * @param beanName bean的名称 * @param allowEarlyReference 是否允许暴露早期对象 通过该参数可以控制是否能够解决循环依赖的. * @return * 这里可能返回一个null(IOC容器加载单实例bean的时候,第一次进来是返回null) * 也有可能返回一个单例对象(IOC容器加载了单实例了,第二次来获取当前的Bean) * 也可能返回一个早期对象(用于解决循环依赖问题) */ @Nullable protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) { /** * 第一步:我们尝试去一级缓存(单例缓存池中去获取对象,一般情况从该map中获取的对象是直接可以使用的) * IOC容器初始化加载单实例bean的时候第一次进来的时候 该map中一般返回空 */ Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName); /** * 若在第一级缓存中没有获取到对象,并且singletonsCurrentlyInCreation这个list包含该beanName * IOC容器初始化加载单实例bean的时候第一次进来的时候 该list中一般返回空,但是循环依赖的时候可以满足该条件 */ if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { /** * 尝试去二级缓存中获取对象(二级缓存中的对象是一个早期对象) * 何为早期对象:就是bean刚刚调用了构造方法,还来不及给bean的属性进行赋值的对象(纯净态) * 就是早期对象 */ singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName); /** * 二级缓存中也没有获取到对象,allowEarlyReference为true(参数是有上一个方法传递进来的true) */ if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) { /** * 直接从三级缓存中获取 ObjectFactory对象 这个对接就是用来解决循环依赖的关键所在 * 在ioc后期的过程中,当bean调用了构造方法的时候,把早期对象包裹成一个ObjectFactory * 暴露到三级缓存中 */ ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName); //从三级缓存中获取到对象不为空 if (singletonFactory != null) { /** * 在这里通过暴露的ObjectFactory 包装对象中,通过调用他的getObject()来获取我们的早期对象 * 在这个环节中会调用到 getEarlyBeanReference()来进行后置处理 */ singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject(); //把早期对象放置在二级缓存, this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject); //ObjectFactory 包装对象从三级缓存中删除掉 this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName); } } } } return singletonObject; } /** * 获取单例对象(该流程用于触发构建bean) * @param beanName the name of the bean * @param singletonFactory the ObjectFactory to lazily create the singleton * with, if necessary * @return the registered singleton object */ public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) { Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null"); //加锁 synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { //尝试从单例缓存池中获取对象 Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName); if (singletonObject == null) { if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction) { throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(beanName, "Singleton bean creation not allowed while singletons of this factory are in destruction " + "(Do not request a bean from a BeanFactory in a destroy method implementation!)"); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'"); } /** * 标记当前的bean马上就要被创建了 * singletonsCurrentlyInCreation 在这里会把beanName加入进来,若第二次循环依赖(构造器注入会抛出异常) */ beforeSingletonCreation(beanName); boolean newSingleton = false; boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null); if (recordSuppressedExceptions) { this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>(); } try { //<3> 初始化 bean // 这个过程其实是调用 createBean() 方法 singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject(); newSingleton = true; } catch (IllegalStateException ex) { //回调我们singletonObjects的get方法,进行正在的创建bean的逻辑 singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName); if (singletonObject == null) { throw ex; } } catch (BeanCreationException ex) { if (recordSuppressedExceptions) { for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) { ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException); } } throw ex; } finally { if (recordSuppressedExceptions) { this.suppressedExceptions = null; } // <4> 后置处理 //主要做的事情就是把singletonsCurrentlyInCreation标记正在创建的bean从集合中移除 afterSingletonCreation(beanName); } if (newSingleton) { // <5> 加入缓存中 addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject); } } return singletonObject; } } /** * Register an Exception that happened to get suppressed during the creation of a * singleton bean instance, e.g. a temporary circular reference resolution problem. * @param ex the Exception to register */ protected void onSuppressedException(Exception ex) { synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { if (this.suppressedExceptions != null) { this.suppressedExceptions.add(ex); } } } /** * Remove the bean with the given name from the singleton cache of this factory, * to be able to clean up eager registration of a singleton if creation failed. * @param beanName the name of the bean * @see #getSingletonMutex() */ protected void removeSingleton(String beanName) { synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { this.singletonObjects.remove(beanName); this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName); this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName); this.registeredSingletons.remove(beanName); } } @Override public boolean containsSingleton(String beanName) { return this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName); } @Override public String[] getSingletonNames() { synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { return StringUtils.toStringArray(this.registeredSingletons); } } @Override public int getSingletonCount() { synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { return this.registeredSingletons.size(); } } public void setCurrentlyInCreation(String beanName, boolean inCreation) { Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null"); if (!inCreation) { this.inCreationCheckExclusions.add(beanName); } else { this.inCreationCheckExclusions.remove(beanName); } } public boolean isCurrentlyInCreation(String beanName) { Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null"); return (!this.inCreationCheckExclusions.contains(beanName) && isActuallyInCreation(beanName)); } protected boolean isActuallyInCreation(String beanName) { return isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName); } /** * Return whether the specified singleton bean is currently in creation * (within the entire factory). * @param beanName the name of the bean */ public boolean isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(String beanName) { return this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.contains(beanName); } /** * Callback before singleton creation. * <p>The default implementation register the singleton as currently in creation. * @param beanName the name of the singleton about to be created * @see #isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation */ protected void beforeSingletonCreation(String beanName) { //若singletonsCurrentlyInCreation 没添加成功 if (!this.inCreationCheckExclusions.contains(beanName) && !this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.add(beanName)) { throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName); } } /** * Callback after singleton creation. * <p>The default implementation marks the singleton as not in creation anymore. * @param beanName the name of the singleton that has been created * @see #isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation */ protected void afterSingletonCreation(String beanName) { if (!this.inCreationCheckExclusions.contains(beanName) && !this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.remove(beanName)) { throw new IllegalStateException("Singleton '" + beanName + "' isn't currently in creation"); } } /** * Add the given bean to the list of disposable beans in this registry. * <p>Disposable beans usually correspond to registered singletons, * matching the bean name but potentially being a different instance * (for example, a DisposableBean adapter for a singleton that does not * naturally implement Spring's DisposableBean interface). * @param beanName the name of the bean * @param bean the bean instance */ public void registerDisposableBean(String beanName, DisposableBean bean) { synchronized (this.disposableBeans) { this.disposableBeans.put(beanName, bean); } } /** * Register a containment relationship between two beans, * e.g. between an inner bean and its containing outer bean. * <p>Also registers the containing bean as dependent on the contained bean * in terms of destruction order. * @param containedBeanName the name of the contained (inner) bean * @param containingBeanName the name of the containing (outer) bean * @see #registerDependentBean */ public void registerContainedBean(String containedBeanName, String containingBeanName) { synchronized (this.containedBeanMap) { Set<String> containedBeans = this.containedBeanMap.computeIfAbsent(containingBeanName, k -> new LinkedHashSet<>(8)); if (!containedBeans.add(containedBeanName)) { return; } } registerDependentBean(containedBeanName, containingBeanName); } /** * 注册bean之间的依赖关系 * to be destroyed before the given bean is destroyed. * @param beanName the name of the bean * @param dependentBeanName the name of the dependent bean */ public void registerDependentBean(String beanName, String dependentBeanName) { //获取原始的beanName String canonicalName = canonicalName(beanName); // 添加 <canonicalName, <dependentBeanName>> 到 dependentBeanMap 中 synchronized (this.dependentBeanMap) { Set<String> dependentBeans = this.dependentBeanMap.computeIfAbsent(canonicalName, k -> new LinkedHashSet<>(8)); if (!dependentBeans.add(dependentBeanName)) { return; } } // 添加 <dependentBeanName, <canonicalName>> 到 dependenciesForBeanMap 中 synchronized (this.dependenciesForBeanMap) { Set<String> dependenciesForBean = this.dependenciesForBeanMap.computeIfAbsent(dependentBeanName, k -> new LinkedHashSet<>(8)); dependenciesForBean.add(canonicalName); } } /** * Determine whether the specified dependent bean has been registered as * dependent on the given bean or on any of its transitive dependencies. * @param beanName the name of the bean to check * @param dependentBeanName the name of the dependent bean * @since 4.0 */ protected boolean isDependent(String beanName, String dependentBeanName) { synchronized (this.dependentBeanMap) { return isDependent(beanName, dependentBeanName, null); } } private boolean isDependent(String beanName, String dependentBeanName, @Nullable Set<String> alreadySeen) { // alreadySeen 已经检测的依赖 bean if (alreadySeen != null && alreadySeen.contains(beanName)) { return false; } // 获取原始 beanName String canonicalName = canonicalName(beanName); //获取创建当前bean 所依赖的bean的名称集合 Set<String> dependentBeans = this.dependentBeanMap.get(canonicalName); //不依赖任何前置Bean 直接返回 if (dependentBeans == null) { return false; } // 存在,则证明存在已经注册的依赖 if (dependentBeans.contains(dependentBeanName)) { return true; } // 递归检测依赖 for (String transitiveDependency : dependentBeans) { if (alreadySeen == null) { alreadySeen = new HashSet<>(); } // 添加到 alreadySeen 中 alreadySeen.add(beanName); //递归检查依赖 if (isDependent(transitiveDependency, dependentBeanName, alreadySeen)) { return true; } } return false; } /** * Determine whether a dependent bean has been registered for the given name. * @param beanName the name of the bean to check */ protected boolean hasDependentBean(String beanName) { return this.dependentBeanMap.containsKey(beanName); } /** * Return the names of all beans which depend on the specified bean, if any. * @param beanName the name of the bean * @return the array of dependent bean names, or an empty array if none */ public String[] getDependentBeans(String beanName) { Set<String> dependentBeans = this.dependentBeanMap.get(beanName); if (dependentBeans == null) { return new String[0]; } synchronized (this.dependentBeanMap) { return StringUtils.toStringArray(dependentBeans); } } /** * Return the names of all beans that the specified bean depends on, if any. * @param beanName the name of the bean * @return the array of names of beans which the bean depends on, * or an empty array if none */ public String[] getDependenciesForBean(String beanName) { Set<String> dependenciesForBean = this.dependenciesForBeanMap.get(beanName); if (dependenciesForBean == null) { return new String[0]; } synchronized (this.dependenciesForBeanMap) { return StringUtils.toStringArray(dependenciesForBean); } } public void destroySingletons() { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Destroying singletons in " + this); } synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = true; } String[] disposableBeanNames; synchronized (this.disposableBeans) { disposableBeanNames = StringUtils.toStringArray(this.disposableBeans.keySet()); } for (int i = disposableBeanNames.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { destroySingleton(disposableBeanNames[i]); } this.containedBeanMap.clear(); this.dependentBeanMap.clear(); this.dependenciesForBeanMap.clear(); clearSingletonCache(); } /** * Clear all cached singleton instances in this registry. * @since 4.3.15 */ protected void clearSingletonCache() { synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { this.singletonObjects.clear(); this.singletonFactories.clear(); this.earlySingletonObjects.clear(); this.registeredSingletons.clear(); this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = false; } } /** *发生移除,销毁当前bean的所有信息 * @param beanName bean的名称 * @see #destroyBean */ public void destroySingleton(String beanName) { //从缓存中移除当前bean的相关信息,由于不知道在哪里发生异常,所以我们把跟当前bean的所有缓存记录都清除 removeSingleton(beanName); //创建一个变量用于接受 实现了DisposableBean接口的对象变量 DisposableBean disposableBean; synchronized (this.disposableBeans) { disposableBean = (DisposableBean) this.disposableBeans.remove(beanName); } //进行bean的销毁 destroyBean(beanName, disposableBean); } /** * 销毁bean的依赖关系 * @param beanName the name of the bean * @param bean the bean instance to destroy */ protected void destroyBean(String beanName, @Nullable DisposableBean bean) { //销毁dependentBeanMap中保存的是当前bean和依赖bean之间的映射 Set<String> dependencies; synchronized (this.dependentBeanMap) { //把当前创建dependon 依赖的bean从缓存中移除并且返回处理 dependencies = this.dependentBeanMap.remove(beanName); } if (dependencies != null) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Retrieved dependent beans for bean '" + beanName + "': " + dependencies); } //递归销毁bean for (String dependentBeanName : dependencies) { destroySingleton(dependentBeanName); } } // 真正的调用bean的destory()方法 if (bean != null) { try { bean.destroy(); } catch (Throwable ex) { logger.error("Destroy method on bean with name '" + beanName + "' threw an exception", ex); } } // Trigger destruction of contained beans... Set<String> containedBeans; synchronized (this.containedBeanMap) { // Within full synchronization in order to guarantee a disconnected Set containedBeans = this.containedBeanMap.remove(beanName); } if (containedBeans != null) { for (String containedBeanName : containedBeans) { destroySingleton(containedBeanName); } } //销毁dependentBeanMap 中 synchronized (this.dependentBeanMap) { for (Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Set<String>>> it = this.dependentBeanMap.entrySet().iterator(); it.hasNext();) { Map.Entry<String, Set<String>> entry = it.next(); Set<String> dependenciesToClean = entry.getValue(); dependenciesToClean.remove(beanName); if (dependenciesToClean.isEmpty()) { it.remove(); } } } //dependenciesForBeanMap集合 this.dependenciesForBeanMap.remove(beanName); } /** * Exposes the singleton mutex to subclasses and external collaborators. * <p>Subclasses should synchronize on the given Object if they perform * any sort of extended singleton creation phase. In particular, subclasses * should <i>not</i> have their own mutexes involved in singleton creation, * to avoid the potential for deadlocks in lazy-init situations. */ public final Object getSingletonMutex() { return this.singletonObjects; } }