1、* 查询出表中所有字段的数据
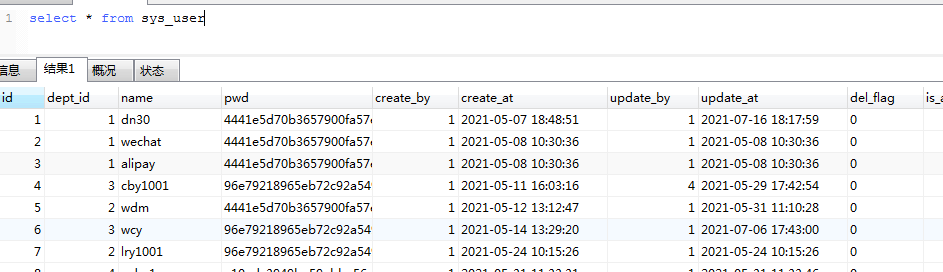
2、 as 给字段取别名

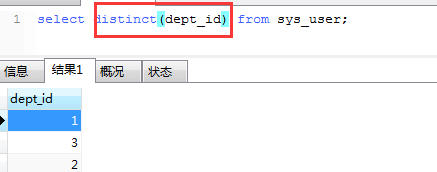
3、disticnct 查询时过滤掉重复的数据
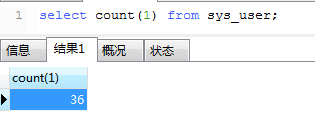
4、count 统计条数,比如统计表里有多少条数据,可用count(1)也可用count(*)

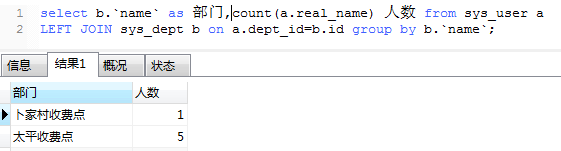
6、 group by 分组 一般跟count,sums() 结合起来用,比如统计每个部门有多少人
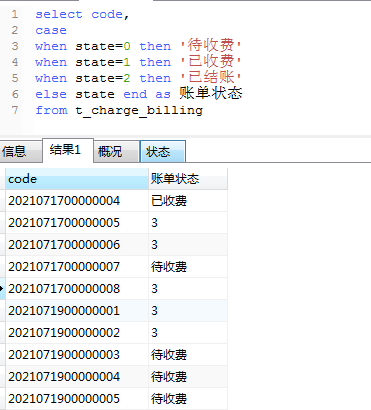
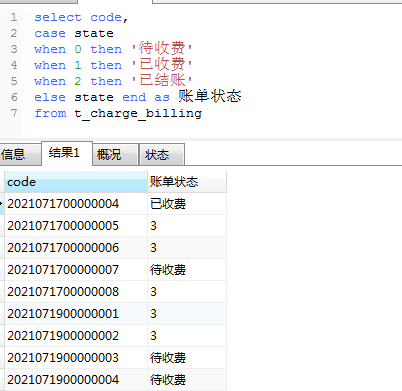
7、case when...then ...else 使用 ,比如数据库中有字段state为账单状态分表值为0,1,2,分别代表:0:待收费 1:已收费 2:已结账
count(case when members.gender=0 then gender END) 女顾客数,
count(case when members.gender=1 then gender END) 男顾客数
from members,shops where shops.id=members.shop_id GROUP BY shops.shop_name
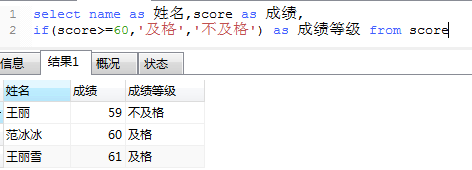
8、if用法 比如查询成绩大于等于60分及格,否则不及格
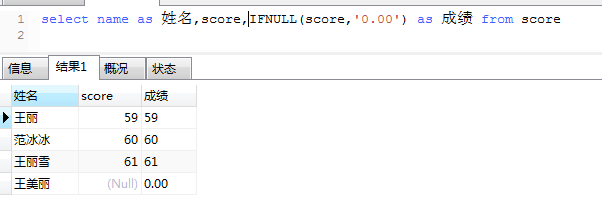
9、ifnull当字段对应的值为null时可默认一个值
and gender=0 and balance<(select max(balance) from a where shop_id=36 and gender=1)
11、having WHERE 关键字无法与聚合函数一起使用,having 一般都是跟group by一起使用 比如 统计分数重复条数大于1的数据。

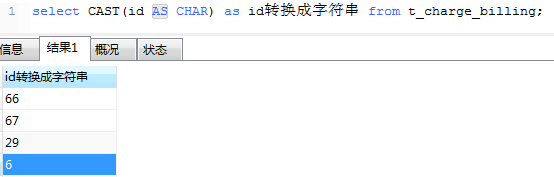
12、MySQL数字类型转换函数cast)将Int转为char类型。语法:CAST(expr AS type)
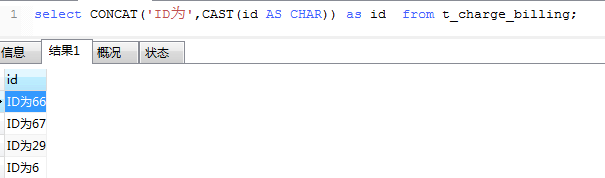
13、MySQL可通过concat 也可把两个字符合并显示。语法:CONCAT(str1,str2,...)
14、union联合查询 连接的两个sql语句字段名和字段长度和顺序需保持一致
select shops.shop_name as 店铺名,a.card_type_id as 卡种,a.balance/100 as 卡金,a.point/100 as 赠金
from a,shops where a.shop_id=shops.id
and a.mobile_phone=18780010265 and a.deleted_at is null and a.card_type_id=0
UNION ALL
select shops.shop_name as 店铺名,card_types.card_type as 卡种,a.balance/100 as 卡金,a.point/100 as 赠金
from a,shops,card_types where a.shop_id=shops.id
and a.mobile_phone=18780010265 and a.deleted_at is null and a.card_type_id=card_types.id
u联合查询 union会过滤掉重复的数据,union all不会去重,
16、获取当前时间 now()

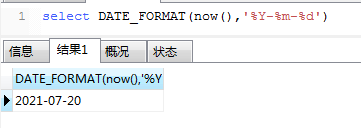
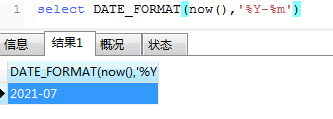
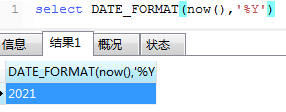
17、DATE_FORMAT时间格式化
‘’
18、sum()、avg()等的使用