一、springboot项目中有两种配置文件
springboot项目中有两种配置文件 bootstrap 和 application
bootstrap是应用程序的父上下文,由父Spring ApplicationContext加载。所以加载顺序优先于application。
bootstrap 里面的属性不能被覆盖。
应用场景
- bootstrap
- 使用 Spring Cloud Config 配置中心时,这时需要在bootstrap 配置文件中添加连接到配置中心的配置属性,来加载外部配置中心的配置信息
- 一些固定的不能被覆盖的属性
- 一些加密/解密的场景
- application
- 主要用于 Spring Boot 项目的自动化配置
二、配置文件的使用
1、配置文件的书写小技巧
spring: application: name: @artifactId@ cloud: nacos: discovery: server-addr: nacoshost:8848 config: server-addr: ${spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.server-addr} file-extension: yml shared-dataids: application-${spring.profiles.active}.${spring.cloud.nacos.config.file-extension} autoconfigure: exclude: org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayAutoConfiguration,org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayClassPathWarningAutoConfiguration profiles: active: @profiles.active@
这段是配置文件内容:@artifactId@ 可以定位到pom 文件中的 <artifactId>pipe-server</artifactId>
@profiles.active@ 可以定位到pom文件中的 <profiles.active>test</profiles.active>
server-addr: ${spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.server-addr}
这种写法 ${}定位的值就是本yml文件:server-addr: nacoshost:8848 这个地方
2、外部配置文件的引用以及多配置文件切换
把外部链接地址放在bootstrap 文件里面 然后去读取文件 外部文件或者在服务器上,或者在git 通过nacos、spring cloud config、apollo 等等去找到外部文件然后读取。
1.多配置文件
profile是Spring对不同环境提供不同配置功能的支持,可以通过激活不同的环境版本,实现快速切换环境;在主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是 application-{profile}.properties/yml , 用来指定多个环境版本;
例如:application-test.properties 代表测试环境配置 application-dev.properties 代表开发环境配置,但是Springboot并不会直接启动这些配置文件,它默认使用application.properties主配置文件;
我们需要通过一个配置来选择需要激活的环境:在bootstrap中使用:spring.profiles.active=dev
3、读取配置文件内容
写个yml文件:
anything: isok: true sout: im.peizhi.wenjian
/* @ConfigurationProperties作用: 将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中; 告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定 参数 prefix = “person” : 将配置文件中的person下面的所有属性一一对应 只有这个组件是容器中的组件,才能使用容器提供的@ConfigurationProperties功能 */ @Component //注册bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "anything") public class Anything{ private Boolean isok;
private String sout ; }
除了@ConfigurationProperties以外还可以使用@Value进行读取:
@Component //注册bean public class Person { //直接使用@value @Value("${anything.isok}") //从配置文件中取值
private Boolean isok;
@ConfigurationProperties是支持松散绑定的 松散绑定:比如我的yml中写的last-name,这个和lastName是一样的, - 后面跟着的字母默认是大写的。这就是松散绑定 ,@Value 不支持
@Value的其他使用方法:应该可以猜的看懂吧 不赘述了
@Component("role2") public class Role2 { //赋值long型 @Value("#{2}") private Long id; //字符串赋值 @Value("#{'role_name_2'}") private String roleName; //字符串赋值 @Value("#{'note_2'}") private String note; }
@Component("elBean") public class ElBean { //通过beanName获取bean,然后注入 @Value("#{role2}") private Role2 role2; //获取bean的属性id @Value("#{role2.id}") private Long id; //调用bean的getNote方法,获取角色名称 // @Value("#{role.getNote().toString()}") @Value("#{role2.getNote()?.toString()}") private String note; @Value("#{T(Math).PI}") private double pi; @Value("#{T(Math).random()}") private double random; @Value("#{role.id+1}") private int num; }
@PropertySource :加载指定的配置文件;
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:bootstrap.yml") @Component //注册bean public class Anything{ @Value("${anything.isok}") private String name; }
三、自动自动配置的原理
1.SpringBoot启动的时候加载主配置类,开启自动配置功能@EnableAutoConfig
2.@EnableAutoConfig作用:
- 利用EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector给容器中导入一些组件,导入了哪些组件呢?
- 可以查看这个类selectImports()方法的内容,他返回了一个 autoConfigurationEntry , 来自 this.getAutoConfigurationEntry(autoConfigurationMetadata, annotationMetadata); 这个方法。我们继续跟踪;
- 这个方法中有一个值 : List<String> configurations = this.getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes); 叫做获取候选的配置 , 我们点击去继续跟踪;
-
这里里面有一个 SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames() ,我们继续进去看 , 它又调用了 loadSpringFactories 方法;继续跟踪。发现它去获得了一个资源文件:"META-INF/spring.factories"
-
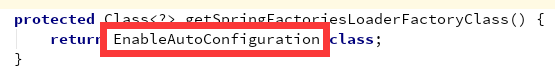
继续阅读源码 , 它将读取到的资源封装在url中,然后遍历url , 将这些url文件封装在Properties文件中;最后返回封装好的结果;他的那个ClassLoader参数,我们追踪回去,看到他就是 EnableAutoConfiguration ;
-
说明了这个逻辑就是 从properties中获取到EnableAutoConfiguration.class类(类名)对应的值,然后把他们添加在容器中
- 总结一句话就是:将类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 里面配置的所有EnableAutoConfiguration的值加入到了容器中;每一个 xxxAutoConfiguration类都是容器中的一个组件,最后都加入到容器中;用他们来做自动配置;
3.每一个自动配置类可以进行自动配置功能;
4.我们
@ConfigurationProperties( prefix = "spring.http" ) //从配置文件中获取指定的值和bean的属性进行绑定 在一次工作中我的书写是这样的(prefix = "tlyh.restUrl")报错格式不规范 应该改为:tlyh.rest-url public class HttpProperties { private boolean logRequestDetails; private final HttpProperties.Encoding encoding = new HttpProperties.Encoding(); public HttpProperties() { } public boolean isLogRequestDetails() { return this.logRequestDetails; } public void setLogRequestDetails(boolean logRequestDetails) { this.logRequestDetails = logRequestDetails; } public HttpProperties.Encoding getEncoding() { return this.encoding; } public static class Encoding { public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET; private Charset charset; private Boolean force; private Boolean forceRequest; private Boolean forceResponse; private Map<Locale, Charset> mapping; } }
5. 下面是自己写的组件
@Configuration //表示这是一个配置类,以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件
//启动指定类的ConfigurationProperties功能;
//进入这个HttpProperties查看,将配置文件中对应的值和HttpProperties绑定起来;
//并把HttpProperties加入到ioc容器中
@EnableConfigurationProperties({HttpProperties.class})
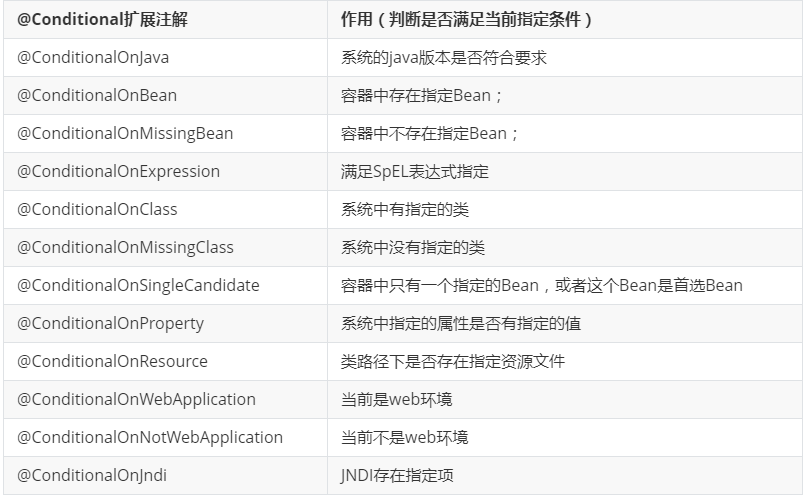
//Spring底层@Conditional注解
//根据不同的条件判断,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置就会生效;
//这里的意思就是判断当前应用是否是web应用,如果是,当前配置类生效
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(
type = Type.SERVLET
)
//判断当前项目有没有这个类CharacterEncodingFilter;SpringMVC中进行乱码解决的过滤器;
@ConditionalOnClass({CharacterEncodingFilter.class})
//判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置:spring.http.encoding.enabled;
//如果不存在,判断也是成立的
//即使我们配置文件中不配置pring.http.encoding.enabled=true,也是默认生效的;
@ConditionalOnProperty(
prefix = "spring.http.encoding",
value = {"enabled"},
matchIfMissing = true
)
public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {
//他已经和SpringBoot的配置文件映射了
private final Encoding properties;
//只有一个有参构造器的情况下,参数的值就会从容器中拿
public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties.getEncoding();
}
//给容器中添加一个组件,这个组件的某些值需要从properties中获取
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean //判断容器没有这个组件?
public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() {
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name());
filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpProperties.Encoding.Type.REQUEST));
filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpProperties.Encoding.Type.RESPONSE));
return filter;
}
}
一句话总结 : 根据当前不同的条件判断,决定这个配置类是否生效!
一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件;这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的;
这就是自动装配的原理!
1)、SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
2)、我们看我们需要的功能有没有在SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类当中;
3)、我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件存在在其中,我们就不需要再手动配置了)
4)、给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们只需要在配置文件中指定这些属性的值即可;
xxxxAutoConfigurartion:自动配置类;给容器中添加组件
了解完自动装配的原理后,我们来关注一个细节问题 ,自动配置类必须在一定的条件下才能生效;
作用:必须是@Conditional指定的条件成立,才给容器中添加组件,配置配里面的所有内容才生效;
那么多的自动配置类,必须在一定的条件下才能生效;也就是说,我们加载了这么多的配置类,但不是所有的都生效了。
我们怎么知道哪些自动配置类生效;我们可以通过启用 debug=true属性;来让控制台打印自动配置报告,这样我们就可以很方便的知道哪些自动配置类生效;