选代器:是遍历集合的一种方式。迭代器是依赖于集合而存在的。
我有一个集合: Collection c = new ArrayList();
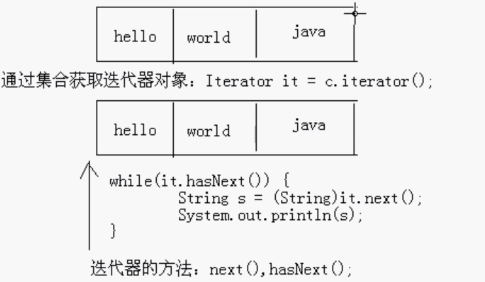
我们给集合中添加元素: c. add("hello' );c. add( "world”);c. add("java");
集合的使用步骤:
A:创建集合对象B:创建元素对象
C:把元素添加到集合D:遍历集合
a:通过集合对象获取迭代器对象
b:通过迭代器对象的hasNext (方法判断是否有元素
c:通过迭代器对象的next ()方法获取元素并移动到下一个位置
例子:
1 package com.wyh.Iterator; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 import java.util.Iterator; 6 7 8 9 public class IteratorTest2 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 //创建集合容器 12 Collection c = new ArrayList(); 13 14 //实例化5个对象 15 Student s1 = new Student("王友虎",22); 16 Student s2 = new Student("李宏灿",21); 17 Student s3 = new Student("赵以浩",23); 18 Student s4 = new Student("李先锋",24); 19 Student s5 = new Student("齐博源",25); 20 21 //将对象放进结合中 22 c.add(s1); 23 c.add(s2); 24 c.add(s3); 25 c.add(s4); 26 c.add(s5); 27 28 29 //将集合转换成一个迭代器 30 Iterator it = c.iterator(); 31 32 33 //while循环输出 34 //hasNext(),判断迭代器里是否有值,有返回true,无返回false 35 while(it.hasNext()) { 36 //System.out.println(it.next()); 37 //向下转型 38 Student st = (Student)it.next(); 39 System.out.println("姓名"+st.getName()+" 年龄:"+st.getAge()); 40 41 } 42 43 44 45 46 } 47 48 }