(匿名)管道:一种进程间通信形式。把从一个进程连接到另一个进程的一个数据流成为一个管道(固定大小内核缓冲区)。
管道的限制:1、半双工(数据只能在一个方向流动)需要双方通信时,要建立两个管道;
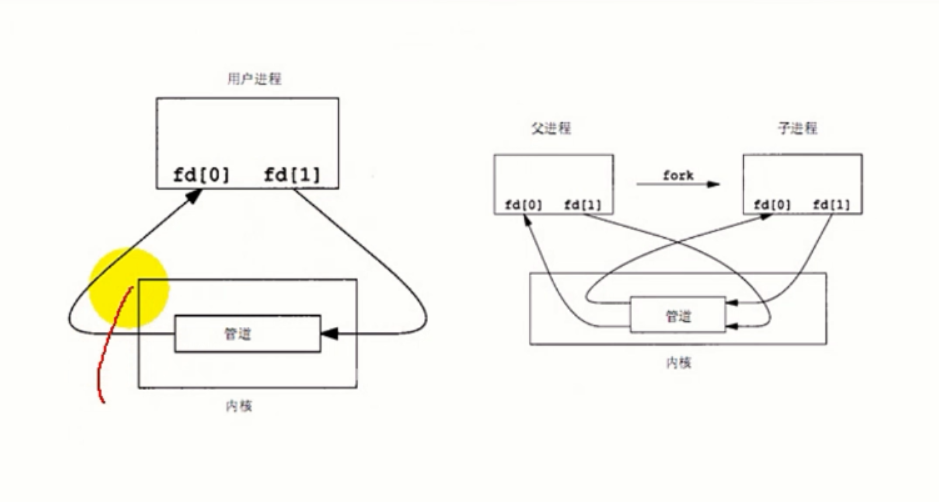
2、只能用于共同祖先进程(具有亲缘关系的进程)通信,通常一个管道由一个进程创建,然后调用fork。
例如:ls | wc -w : ls进程将输出写到管道,wc进程从管道获取数据.
#include<unistd.h>
int pipe(int fd[2]); // 创建管道,返回两个文件描述符,fd[0]表示读端,fd[1]表示写端.成功返回0,失败返回-1
具体状态可以如下图:父进程创建管道后,调用fork,子进程的fd0 fd1 也指向了管道读写端
1 #include<unistd.h> 2 #include<sys/types.h> 3 #include<sys/stat.h> 4 #include<fcntl.h> 5 #include<stdlib.h> 6 #include<stdio.h> 7 #include<errno.h> 8 #include<string.h> 9 10 #include<signal.h> 11 #define ERR_EXIT(m) 12 do 13 { 14 perror(m); 15 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 16 }while(0) //宏要求一条语句 17 int main(int argc,char*argv[]) 18 { 19 int pipefd[2]; 20 //创建管道 21 if(pipe(pipefd)==-1) 22 ERR_EXIT("pipe error"); 23 pid_t pid; 24 if((pid=fork())==-1) 25 ERR_EXIT("fork error"); 26 else if(pid==0){//子进程发送数据给父进程 27 close(pipefd[0]); 28 write(pipefd[1],"hello",5); 29 close(pipefd[1]); 30 exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); 31 } 32 close(pipefd[1]); 33 char buf[10]; 34 read(pipefd[0],buf,10); 35 printf("buf=%s ",buf); 36 close(pipefd[0]); 37 return 0; 38 }
下面这个例子用pipe来模拟 ls | wc -w :运行两个进程 ls进程 、 wc -w进程。 用子进程运行ls,写数据到管道。 父进程运行wc 从管道读数据
正常情况,ls输出到标准输出,因而需要先进行重定向(到管道写端)。输出到管道。 同理 wc也一样
1 #include<unistd.h> 2 #include<sys/types.h> 3 #include<sys/stat.h> 4 #include<fcntl.h> 5 #include<stdlib.h> 6 #include<stdio.h> 7 #include<errno.h> 8 #include<string.h> 9 10 #include<signal.h> 11 #define ERR_EXIT(m) 12 do 13 { 14 perror(m); 15 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 16 }while(0) //宏要求一条语句 17 int main(int argc,char*argv[]) 18 { 19 int pipefd[2]; 20 if(pipe(pipefd)==-1) 21 ERR_EXIT("pipe error"); 22 pid_t pid; 23 if((pid=fork())==-1) 24 ERR_EXIT("fork error"); 25 else if(pid==0){ 26 close(pipefd[0]);//关闭管道读端 27 dup2(pipefd[1],STDOUT_FILENO);//1指向pipefd[1], 1指向管道写端。 标准输出,输出到1;不管1指向哪,都记住输出到 1 .等效于close(oldfd); fcntl(oldfd, F_DUPFD, newfd); 28 close(pipefd[1]); 29 execlp("ls","ls",(char*)0,NULL);//若果调用失败将执行以下内容,ls 输出到管道写端 30 fprintf(stderr,"error ececutr ls "); 31 exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); 32 } 33 close(pipefd[1]);//关闭管道写端 34 dup2(pipefd[0],STDIN_FILENO); 35 close(pipefd[0]);//标准输入是管道读端 36 execlp("wc","wc","-w",(char*)0,NULL);//从标准输入获取 37 fprintf(stderr,"error ececutr ls "); 38 return 0; 39 }
补充一个例子来说明文件描述符拷贝。
1 #include<unistd.h> 2 #include<sys/types.h> 3 #include<sys/stat.h> 4 #include<fcntl.h> 5 #include<stdlib.h> 6 #include<stdio.h> 7 #include<errno.h> 8 #include<string.h> 9 10 #include<signal.h> 11 #define ERR_EXIT(m) 12 do 13 { 14 perror(m); 15 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 16 }while(0) //宏要求一条语句 17 int main(int argc,char*argv[]) 18 { 19 close(0);//0和标准输入断开,0指向Makefile 20 open("Makefile",O_RDONLY);//Makefile作为标准输入 21 close(1); 22 open("Makefile2",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0644);//Makefile2作为标准输出 23 //拷贝makefile 24 execlp("cat","cat",(char*)0,NULL);//cat不带参数,表示将标准输入获取数据写入标准输出 25 return 0; 26 }