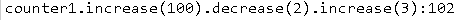一、古罗马皇帝凯撒在打仗时曾经使用过以下方法加密军事情报:

请编写一个程序,使用上述算法加密或解密用户输入的英文字串
1、设计思想
输入字符串,使用判断其字符串长度,用charAt()将它们转换为字符,然后判断当(c>='X'&&c<='Z')使c=c-23,当(c>='A'&&c<='W')c=c+3,之后即可解密。
2、程序流程图

3、源代码
1 import java.util.*; 2 public class SecretString { 3 4 public static void main(String args[]) 5 { 6 Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in); 7 System.out.println("请输入字符串:"); 8 String str=scanner.nextLine(); 9 String output=""; 10 char c = 0; 11 for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++) 12 { 13 c=(str.charAt(i)); 14 { 15 if(c>='X'&&c<='Z') 16 c-=23; 17 else if(c>='A'&&c<='W') 18 c+=3; 19 } 20 output+=c; 21 } 22 System.out.println("加密的字符串结果为: "+output); 23 } 24 } 25
4、结果截图

二、请运行以下示例代码StringPool.java,查看其输出结果。如何解释这样的输出结果?从中你能总结出什么?
public class StringPool { public static void main(String args[]) { String s0="Hello"; String s1="Hello"; String s2="He"+"llo"; System.out.println(s0==s1);//true System.out.println(s0==s2);//true System.out.println(new String("Hello")==new String("Hello"));//false } }
1.在Java中,内容相同的字串常量(“Hello”)只保存一份以节约内存,所以s0,s1,s2实际上引用的是同一个对象。
2.编译器在编译s2一句时,会去掉“+”号,直接把两个字串连接起来得一个字串(“Hello”)。这种优化工作由Java编译器自动完成。
3.当直接使用new关键字创建字符串对象时,虽然值一致(都是“Hello”),但仍然是两个独立的对象。

regionMatches:比较两字串中的某一部分是否相等参数含义如下:1.调用这个方法的字串中的起始下标2.要比较的字串3.要比较的字串的起始下标4.要比较的字串比较的字符长度比如s3.regionMatches( 0, s4, 0, 5 ),若忽略大小写使用s3.regionMatches( true, 0, s4, 0, 5 )

equals的源代码
public class StringEquals { /** * @param args the command line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) { String s1=new String("Hello"); String s2=new String("Hello"); System.out.println(s1==s2);//false System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true String s3="Hello"; String s4="Hello"; System.out.println(s3==s4); //true System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));//true } }
结果原因:s1.equals(s2)比较两个字符串的内容是否相等。使用==比较两字符串变量是否引用同一子串对象。s1,s2用new创建为不同对象,s3,s4引用同一个字符串对象。
四、字符串查找
哈希码产生的依据:哈希码并不是完全唯一的,它是一种算法,让同一个类的对象按照自己不同的特征尽量的有不同的哈希码,但不表示不同的对象哈希码完全不同。也有相同的情况,看程序员如何写哈希码的算法。
下面给出几个常用的哈希码的算法。
1:Object类的hashCode.返回对象的内存地址经过处理后的结构,由于每个对象的内存地址都不一样,所以哈希码也不一样。
2:String类的hashCode.根据String类包含的字符串的内容,根据一种特殊算法返回哈希码,只要字符串内容相同,返回的哈希码也相同。
3:Integer类,返回的哈希码就是Integer对象里所包含的那个整数的数值,例如Integer i1=new Integer(100),i1.hashCode的值就是100 。由此可见,2个一样大小的Integer对象,返回的哈希码也一样。

getChars():获取从指定位置起的子串复制到字符数组中(它有四个参数,在示例中有介绍)四个参数的含义1.被拷贝字符在字串中的起始位置2.被拷贝的最后一个字符在字串中的下标再加13.目标字符数组4.拷贝的字符放在字符数组中的起始下标
char charArray[];s1 = new String( "hello there" );charArray = new char[ 5 ];s1.getChars( 0, 5, charArray, 0 );


toUpperCase()、 toLowerCase():大小写转换









trim():去除头尾空格

toCharArray():将字符串对象转换为字符数组

charAt(i)输出第i个字符

getChars( 0, buf.length(), charArray, 0 ); //(起始下标,长度,字符数组名,起始下标)将buf中的内容赋给charArray[]。



七、
String类的方法可以连续调用:String str="abc";String result=str.trim().toUpperCase().concat("defg");
请阅读JDK中String类上述方法的源码,模仿其编程方式,编写一个MyCounter类,它的方法也支持上述的“级联”调用特性,
其调用示例为:MyCounter counter1=new MyCounter(1);MyCounter counter2=counter1.increase(100).decrease(2).increase(3);

1 public class MyCounter { 2 public int counter; 3 MyCounter(int i) 4 { 5 counter=i; 6 } 7 public MyCounter increase(int add) 8 { 9 counter=counter+add; 10 return this; 11 } 12 public MyCounter decrease(int subtraction) 13 { 14 counter=counter-subtraction; 15 return this; 16 } 17 static public void main(String args[]) 18 { 19 MyCounter counter1=new MyCounter(1); 20 MyCounter counter2=counter1.increase(100).decrease(2).increase(3); 21 System.out.println("counter1.increase(100).decrease(2).increase(3):"+counter2.counter); 22 } 23 }
执行结果: