一,需要满足的需求
1.统计文件的字符数
2.统计文件的单词书
3.统计文件的行数
4.统计文件中各单词的出现次数
5.对给定文件夹及其递归文件夹下的所有文件进行统计
6.统计两个单词(词组)在一起的频率,输出频率最高的前10个。
二,功能设计:
1.统计 ASCII码 32 到126的字符
2.根据单词定义判断两个分隔符直接是否为一个单词
3.用' '来计算行数
4.遍历文件夹
5.用命令行参数输入
6.使用unordered_map存储
6.遍历unordered_map,选出前十个单词
8.统计词组数
三.具体设计
- 利用自己编写的chuli函数来将一个字符串分解为有效部分和后缀,同时将有效部分大小写归一。
- 使用unordered_map进行统计
- 寻找词频前十的单词时,维护一个10个大小的“榜单”,线性遍历哈希表,用其中的每一个元素来更新“榜单”,时间复杂度O(N)
四,过程分析
1.遍历文件夹
使用vector 作为容器,结构体files[i]的成员file[i].c_str(),就是一个文件的绝对地址,用fopen_s打开
void Tongji(char* fp1) { vector<string> files; char * filePath = fp1; //获取该路径下的所有jpg文件 //getFiles(filePath, "jpg", files); //获取该路径下的所有文件 getFiles(filePath, "*", files); //列表文件输出路径 // FILE* fp; FILE* fp2; //fopen_s(&fp, "d:\Adobe\dir_list.txt", "w"); int size = files.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { fopen_s(&fp2, files[i].c_str(), "r"); countword(fp2); fclose(fp2); } //fclose(fp); }
void getFiles(string path, string exd, vector<string>& files) { //cout << "getFiles()" << path<< endl; //文件句柄 long hFile = 0; //文件信息 struct _finddata_t fileinfo; string pathName, exdName; if (0 != strcmp(exd.c_str(), "")) { exdName = "\*." + exd; } else { exdName = "\*"; } if ((hFile = _findfirst(pathName.assign(path).append(exdName).c_str(), &fileinfo)) != -1) { do { //cout << fileinfo.name << endl; //如果是文件夹中仍有文件夹,迭代之 //如果不是,加入列表 if ((fileinfo.attrib & _A_SUBDIR)) { if (strcmp(fileinfo.name, ".") != 0 && strcmp(fileinfo.name, "..") != 0) getFiles(pathName.assign(path).append("\").append(fileinfo.name), exd, files); } else { if (strcmp(fileinfo.name, ".") != 0 && strcmp(fileinfo.name, "..") != 0) files.push_back(pathName.assign(path).append("\").append(fileinfo.name)); } } while (_findnext(hFile, &fileinfo) == 0); _findclose(hFile); } }
2.countword
函数的功能是,读取一个文件的每个字符的同时,统计字符数,单词数,行数,利用chuli函数处理有效的单词,将其封装成一个结构体,送入uordered_map中。
1 int countword(FILE* stream) 2 { 3 4 char ch; 5 char word_stream[1024] = { '� ' }; 6 char word_[1024] = { '�' }; 7 char houzhui[1024] = { '�' }; 8 char *key ; 9 int word = 0;// 字符串长度 10 int word1 = 1;//word1为0则一定不是单词 11 int K = 0; 12 WordNode WN; 13 unordered_map<char*, WordNode>::iterator iter; 14 do 15 { 16 ch = fgetc(stream); 17 if (ch >= 32 && ch <= 126) 18 char_num++; 19 if (ch == ' ') 20 line_num++; 21 if (panduan(ch) == 2) 22 { 23 //if (word1 == 1)//前面没出现在前四个字符的数字 24 word_stream[word] = ch; 25 word++; 26 27 } 28 29 else if (panduan(ch) == 3)// 是分隔符 30 { 31 if (word >= 4 && word<=1024 && word1 == 1) 32 { 33 word_stream[word] = '�'; 34 word_num++; 35 //cout << word_stream << endl; 36 chuli(word_stream, word, word_, houzhui, key);//cout << word_stream <<endl;//把字符串分解为有效部分和后缀,计算出哈希值,送到哈希函数里去储存; 37 //cout << "!!!" << word_ << key << endl; 38 iter = wordmap.find(key); 39 40 if (iter!=wordmap.end()) 41 { 42 wordmap.at(key).geshu++; 43 if (wordmap.at(key).word > word_) 44 wordmap.at(key).word = word_; 45 if (wordmap.at(key).houzhui > word_) 46 wordmap.at(key).houzhui = word_; 47 48 } 49 else 50 { 51 WN.geshu = 1; 52 WN.word = word_; 53 WN.houzhui = houzhui; 54 pair<char*, WordNode>myword(key, WN); 55 wordmap.insert(myword); 56 57 } 58 59 60 61 //charu(word_, houzhui, K); 62 } 63 //if (word) 64 // strcpy_s(word_stream, word, "�"); 65 word = 0; 66 word1 = 1; 67 68 69 } 70 else if ((panduan(ch) == 1)) 71 { 72 if (word < 4)// 数字出现在前4个 73 word1 = 0; 74 word_stream[word] = ch; 75 word++; 76 } 77 } while (ch != EOF); 78 79 return 0; 80 }
void chuli(char word_stream[], int word, char word_[], char houzhui[],char* &key) { int i = 0; for (i = word - 1; panduan(word_stream[i]) == 1; i--); substring_sq(word_, word_stream, 0, i + 1); substring_sq(houzhui, word_stream, i + 1, word - i - 1); Biaozhunhua(key, word_, i + 1); }
void substring_sq(char* Sub, char* S, int pos, int len) { int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < len; i++) Sub[i] = S[pos + i]; Sub[len] = '�'; } void Biaozhunhua( char* &key ,char *S, int len) { int i = 0; char Sub[1024]; for (i = 0; i < len;i++) if (S[i] >= 'a' && S[i] <= 'z') Sub[i] = S[i] - 32; else Sub[i] = S[i]; Sub[i] = '�'; key = Sub; }
3.遍历unordered_map 。自己写了个榜单,遍历过程中,每读出一个单词,更新一下榜单,最后读出前十个单词
void Select_Word() { unordered_map<char*, WordNode>::iterator iter; for (iter = wordmap.begin(); iter != wordmap.end(); iter++) { Charu_Out_Word(iter->second.word, iter->second.houzhui, iter->second.geshu); } }
void Charu_Out_Word(char* word, char* houzhui, int geshu) { int i, j; for (i = 0; i < 10 && Out_Word[i].geshu >= geshu; i++); if (i < 10)// That means Out_Word[i] < geshu; { for (j = 9; j>i; j--) { Out_Word[j].geshu = Out_Word[j - 1].geshu; Out_Word[j].word = Out_Word[j - 1].word; Out_Word[j].houzhui = Out_Word[j - 1].houzhui; } Out_Word[j].geshu = geshu; Out_Word[j].word = word; Out_Word[j].houzhui = houzhui; } }
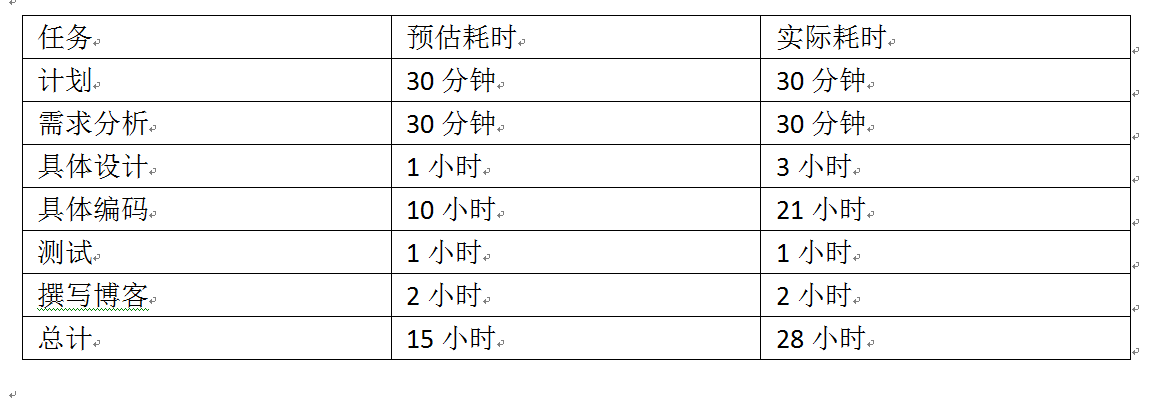
六,PSP 表格
五,代码质量和性能分析
1)质量分析
没有错误和警告
2)用vs自带的性能分析
我的vs一性能分析,电脑就死机了····我也很无奈啊。
七。心得体会
这次个人作业,我个人感觉还是有很多收获的,但也有很多经验教训。
经验教训:
一个是我在网上寻找解决方案的能力不够。我缺少看懂一个需要自学的东西的悟性和耐心,所以在别人博客上学新东西的时候我往往感觉蛮痛苦的。
二是我排查错误的能力不够,主要是不会用VS进行debug。
三是心态还不够强大。ddl对于很多同学来说是生产力,但是对于我来说,这次个人作业实际上只有四天的时间,ddl常常使我的阵脚大乱,我觉得心态上我也有很多需要改进的。
具体收获:
一是掌握一门面向对象的语言的重要性,如果不会面向对象的语言,在使用unordered_map等操作的时候看不懂,还很容易出错。
二是锻炼了自己的动手能力,尤其是使用vs进行debug的能力吧。
最重要的就是认识到应该实事求是,认识到自己和其他同学在工程能力上确实有差距。我虽然成绩还可以,但是软件工程能力和其他同学相比确实相对比较弱。
投入了将近30小时的时间,得到的结果却比很多话费不到20小时的同学还差,能力上的差距确实客观存在,但是,虽然我现在很菜,但是还是要不断努力啊。
唯有一个会受伤,会害怕的人,拼尽全力地去做一件事,那才是真正的英雄罢,加油加油。
八,源代码附录

// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include <string> #include <io.h> #include <vector> #include <iostream> //#include <conio.h> #include<math.h> #include"string.h" #include <unordered_map> using namespace std; #define N 1000000 typedef struct WordNode { char* word; char* houzhui; int geshu; }WordNode, *Word, *Wordpt; typedef unordered_map<char*, WordNode> wmap; wmap wordmap; typedef struct WNode { char* word; char* houzhui; int geshu; }WNode; WNode Out_Word[10]; int char_num = 0, word_num = 0, line_num = 0; void initial_Out_Word() { int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Out_Word[i].geshu = 0; Out_Word[i].word = "a"; Out_Word[i].houzhui = "1"; } } void Charu_Out_Word(char* word, char* houzhui, int geshu) { int i, j; for (i = 0; i < 10 && Out_Word[i].geshu >= geshu; i++); if (i < 10)// That means Out_Word[i] < geshu; { for (j = 9; j>i; j--) { Out_Word[j].geshu = Out_Word[j - 1].geshu; Out_Word[j].word = Out_Word[j - 1].word; // 这里可能有问题 Out_Word[j].houzhui = Out_Word[j - 1].houzhui; } Out_Word[j].geshu = geshu; Out_Word[j].word = word; Out_Word[j].houzhui = houzhui; } } int panduan(char ch) { if (ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9') return 1; else if ((ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z') || (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z')) return 2; else return 3; } void substring_sq(char* Sub, char* S, int pos, int len) { int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < len; i++) Sub[i] = S[pos + i]; Sub[len] = '�'; } void Biaozhunhua( char* &key ,char *S, int len) { int i = 0; char Sub[1024]; for (i = 0; i < len;i++) if (S[i] >= 'a' && S[i] <= 'z') Sub[i] = S[i] - 32; else Sub[i] = S[i]; Sub[i] = '�'; key = Sub; } void chuli(char word_stream[], int word, char word_[], char houzhui[],char* &key) { int i = 0; for (i = word - 1; panduan(word_stream[i]) == 1; i--); substring_sq(word_, word_stream, 0, i + 1); substring_sq(houzhui, word_stream, i + 1, word - i - 1); Biaozhunhua(key, word_, i + 1); } void Select_Word() { unordered_map<char*, WordNode>::iterator iter; for (iter = wordmap.begin(); iter != wordmap.end(); iter++) { Charu_Out_Word(iter->second.word, iter->second.houzhui, iter->second.geshu); } } int count_char_line(FILE* stream) { char ch; do { /* read a char from the file */ ch = fgetc(stream); if (ch >= 32 && ch <= 126) char_num++; if (ch == ' ') line_num++; } while (ch != EOF); return 0; } int countword(FILE* stream) { char ch; char word_stream[1024] = { '� ' }; char word_[1024] = { '�' }; char houzhui[1024] = { '�' }; char *key ; int word = 0;// 字符串长度 int word1 = 1;//word1为0则一定不是单词 int K = 0; WordNode WN; unordered_map<char*, WordNode>::iterator iter; do { ch = fgetc(stream); if (ch >= 32 && ch <= 126) char_num++; if (ch == ' ') line_num++; if (panduan(ch) == 2) { //if (word1 == 1)//前面没出现在前四个字符的数字 word_stream[word] = ch; word++; } else if (panduan(ch) == 3)// 是分隔符 { if (word >= 4 && word<=1024 && word1 == 1) { word_stream[word] = '�'; word_num++; //cout << word_stream << endl; chuli(word_stream, word, word_, houzhui, key);//cout << word_stream <<endl;//把字符串分解为有效部分和后缀,计算出哈希值,送到哈希函数里去储存; //cout << "!!!" << word_ << key << endl; iter = wordmap.find(key); if (iter!=wordmap.end()) { wordmap.at(key).geshu++; if (wordmap.at(key).word > word_) wordmap.at(key).word = word_; if (wordmap.at(key).houzhui > word_) wordmap.at(key).houzhui = word_; } else { WN.geshu = 1; WN.word = word_; WN.houzhui = houzhui; pair<char*, WordNode>myword(key, WN); wordmap.insert(myword); } //charu(word_, houzhui, K); } //if (word) // strcpy_s(word_stream, word, "�"); word = 0; word1 = 1; } else if ((panduan(ch) == 1)) { if (word < 4)// 数字出现在前4个 word1 = 0; word_stream[word] = ch; word++; } } while (ch != EOF); return 0; } void getFiles(string path, string exd, vector<string>& files) { //cout << "getFiles()" << path<< endl; //文件句柄 long hFile = 0; //文件信息 struct _finddata_t fileinfo; string pathName, exdName; if (0 != strcmp(exd.c_str(), "")) { exdName = "\*." + exd; } else { exdName = "\*"; } if ((hFile = _findfirst(pathName.assign(path).append(exdName).c_str(), &fileinfo)) != -1) { do { //cout << fileinfo.name << endl; //如果是文件夹中仍有文件夹,迭代之 //如果不是,加入列表 if ((fileinfo.attrib & _A_SUBDIR)) { if (strcmp(fileinfo.name, ".") != 0 && strcmp(fileinfo.name, "..") != 0) getFiles(pathName.assign(path).append("\").append(fileinfo.name), exd, files); } else { if (strcmp(fileinfo.name, ".") != 0 && strcmp(fileinfo.name, "..") != 0) files.push_back(pathName.assign(path).append("\").append(fileinfo.name)); } } while (_findnext(hFile, &fileinfo) == 0); _findclose(hFile); } } void Tongji(char* fp1) { vector<string> files; char * filePath = fp1; //获取该路径下的所有jpg文件 //getFiles(filePath, "jpg", files); //获取该路径下的所有文件 getFiles(filePath, "*", files); //列表文件输出路径 // FILE* fp; FILE* fp2; //fopen_s(&fp, "d:\Adobe\dir_list.txt", "w"); int size = files.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { fopen_s(&fp2, files[i].c_str(), "r"); countword(fp2); fclose(fp2); } //fclose(fp); } int main(int agrc, char * agrv[]) { int i; char * fp1 = agrv[1]; initial_Out_Word(); Tongji(fp1); Select_Word(); FILE* fp; fopen_s(&fp, "D:/test1/result.txt", "w"); fprintf(fp, "%d", word_num); fputs(" ", fp); fprintf(fp, "%d", char_num); fputs(" ", fp); fprintf(fp, "%d", line_num); fputs(" ", fp); for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { fputs(Out_Word[i].word, fp); fputs(Out_Word[i].houzhui, fp); fputs(":", fp); fprintf(fp, "%d", Out_Word[i].geshu); fputs(" ", fp); } fclose(fp); system("pause"); }
