本文详细说明,如何使用 tensorrt python API搭建MLP网络,实现推理,帮助与我类似的小白更快上手python版本的方法,我将介绍内容为: 简单介绍、linux如何配置tensorRT、MLP网络搭建步骤及详细说明、原始代码与改编代码。
同篇关联C++ API文章为:https://www.cnblogs.com/tangjunjun/p/16127634.html
一.简单介绍
TensorRT是英伟达针对自家平台做的一个加速包,可以认为 TensorRT 是一个只有前向传播的深度学习框架,这个框架可以将 Caffe,TensorFlow 的网络模型解析,然后与 TensorRT 中对应的层进行一一映射,把其他框架的模型统一全部转换到 TensorRT 中,然后在 TensorRT 中可以针对 NVIDIA 自家 GPU 实施优化策略,并进行部署加速。根据官方文档,使用TensorRT,在CPU或者GPU模式下其可提供10X乃至100X的加速。
TensorRT主要做了这么两件事情,来提升模型的运行速度:
- TensorRT支持INT8和FP16的计算。深度学习网络在训练时,通常使用 32 位或 16 位数据。TensorRT则在网络的推理时选用不这么高的精度,达到加速推断的目的
- TensorRT对于网络结构进行了重构,把一些能够合并的运算合并在了一起,针对GPU的特性做了优化
二.Linux系統配置tensorrt环境/pycharm如何使用配置环境
简单介绍visual studio的环境配置,前提条件你已经将tensorrt库相应放在cuda文件夹下了:
①官网下载tensorrt对应cuda版本,下载地址:https://developer.nvidia.com/nvidia-tensorrt-8x-download;
②添加环境路径:
执行: vim ~/.bashrc
添加: export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/home/soft/TensorRT-8.2.1.8/lib
执行:source ~/.bashrc
③虚拟环境安装对应环境
pycuda安装:pip install pycuda
tensorrt安装:
cd /home/soft/TensorRT-8.2.1.8/python
pip install tensorrt-8.2.1.8**省略****.whl #下载tensorrt包自带
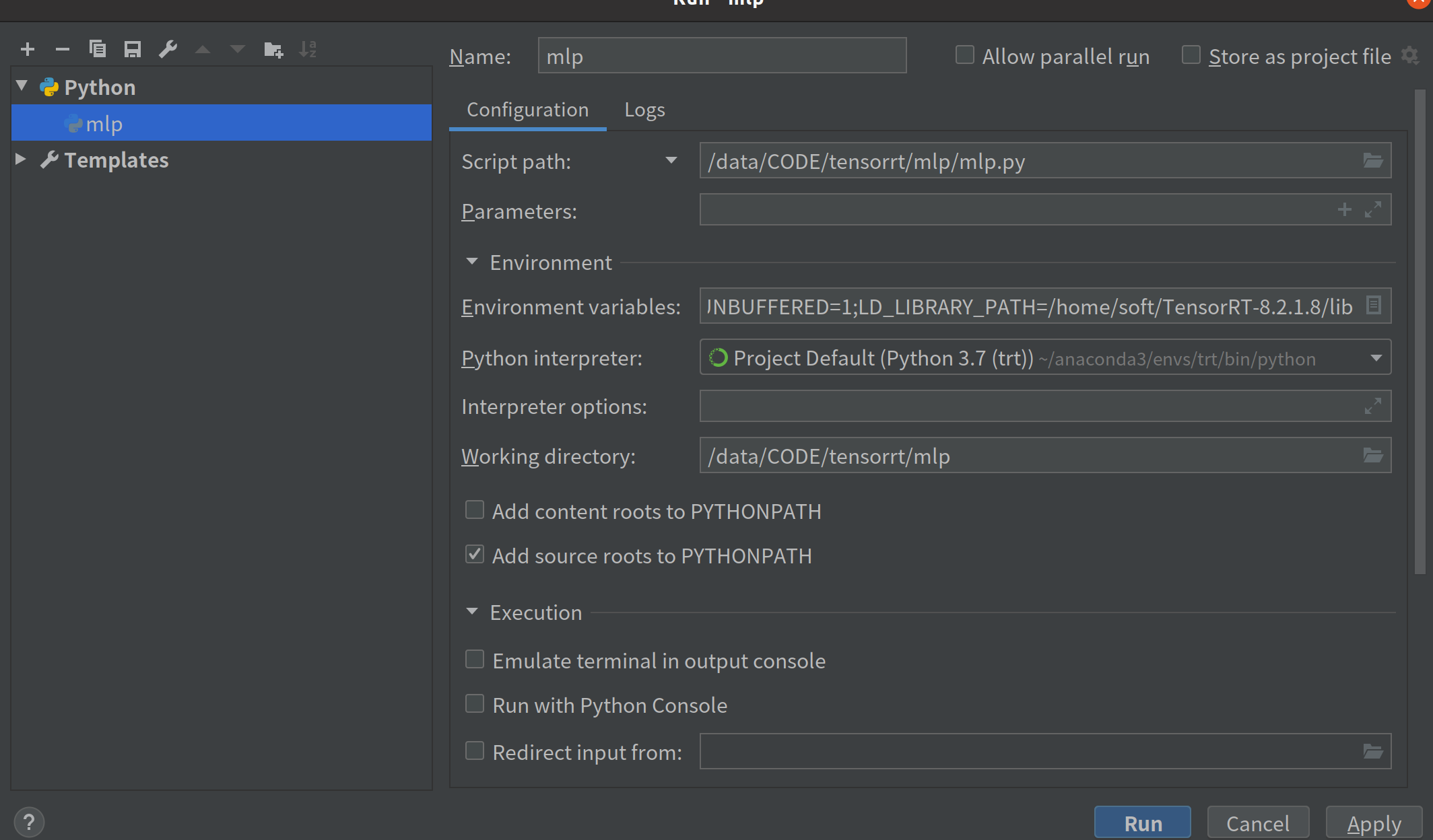
④若pycharm出现找不到libnvonnxparser.so.8库等报错,需
选择Run——>Edit Configurations——>Environment variables——>输入:LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/home/soft/TensorRT-8.2.1.8/lib
三.tensorrt python API 以搭建MLP网络结构,详细说明步骤:
需引用头文件如下:
import os import numpy as np import struct import tensorrt as trt # required for the inference using TRT engine import pycuda.driver as cuda
建引擎engine,并将其保存为文件形式
①构建glogging,为创建builder做准备,简单创建代码如下:
# A logger provided by NVIDIA-TRT gLogger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.INFO)
②创建builder,使用gLogger
# Create Builder with logger provided by TRT builder = trt.Builder(gLogger)
③构建网络
# build an empty network using builder network = builder.create_network()
网络构建完毕后,需为网络添加结构,可以使用onnx/caffe/uft解析添加网络,但本篇博客使用C++ API 构建网络,如下:
# add an input to network using the *input-name data = network.add_input('data', dt, (1, 1,INPUT_SIZE )) # add the layer with output-size (number of outputs) linear = network.add_fully_connected(input=data, num_outputs=OUTPUT_SIZE, kernel=weight_map['linear.weight'], bias=weight_map['linear.bias']) # set the name for output layer linear.get_output(0).name = OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME # mark this layer as final output layer network.mark_output(linear.get_output(0))
其中weightMap为权重保存变量,类似一个字典
④设置网络参数
调用TensorRT的builder来创建优化的runtime。 builder的其中一个功能是搜索其CUDA内核目录以获得最快的实现,因此用来构建优化的engine的GPU设备和实际跑的GPU设备一定要是相同的才行,这也是为什么无法适应其它环境原因。
builder具有许多属性,可以通过设置这些属性来控制网络运行的精度,以及自动调整参数。还可以查询builder以找出硬件本身支持的降低的精度类型。
有个特别重要的属性,最大batch size :大batch size指定TensorRT将要优化的batch大小。在运行时,只能选择比这个值小的batch。
# Create configurations from Engine Builder config = builder.create_builder_config() # set the batch size of current builder builder.max_batch_size = max_batch_size
⑤创建引擎engine
# create the engine with model and hardware configs engine = builder.build_engine(network, config)
⑥引擎engine序列化并保存
# Write the engine into binary file print("[INFO]: Writing engine into binary...") with open(ENGINE_PATH, "wb") as f: # write serialized model in file f.write(engine.serialize())
其中file_engine为保存engine的地址,如:"/home/mlp/mlp.engine"
⑦释放内存
# free the memory del engine del builder # free captured memory del network del weight_map
以上为tensorrt C++ API 将网络编译成engine,并保存的全部流程,若后续更改不同网络,主要更改步骤③构建网络模块。
重载引擎文件,并实现推理:
①读取引擎engine,并反序列化
# create a runtime (required for deserialization of model) with NVIDIA's logger runtime = trt.Runtime(gLogger) assert runtime # read and deserialize engine for inference with open(ENGINE_PATH, "rb") as f: engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
其中ENGINE_PATH为:ENGINE_PATH = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\code\\tensorrt-code\\mlp\\mlp.engine"
其中gLogger来源创建引擎构建的glogging
② ④设置输入输出
# create input as array data = np.array([input_data], dtype=np.float32) # capture free memory for input in GPU host_in = cuda.pagelocked_empty((INPUT_SIZE), dtype=np.float32) # copy input-array from CPU to Flatten array in GPU np.copyto(host_in, data.ravel()) # capture free memory for output in GPU host_out = cuda.pagelocked_empty(OUTPUT_SIZE, dtype=np.float32)
③调用推理
# do inference using required parameters do_inference(context, host_in, host_out)
推理函数为:
def do_inference(inf_context, inf_host_in, inf_host_out): """ Perform inference using the CUDA context :param inf_context: context created by engine :param inf_host_in: input from the host :param inf_host_out: output to save on host :return: """ inference_engine = inf_context.engine # Input and output bindings are required for inference assert inference_engine.num_bindings == 2 # allocate memory in GPU using CUDA bindings device_in = cuda.mem_alloc(inf_host_in.nbytes) device_out = cuda.mem_alloc(inf_host_out.nbytes) # create bindings for input and output bindings = [int(device_in), int(device_out)] # create CUDA stream for simultaneous CUDA operations stream = cuda.Stream() # copy input from host (CPU) to device (GPU) in stream cuda.memcpy_htod_async(device_in, inf_host_in, stream) # execute inference using context provided by engine inf_context.execute_async(bindings=bindings, stream_handle=stream.handle) ################# key step ########### # copy output back from device (GPU) to host (CPU) cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(inf_host_out, device_out, stream) # synchronize the stream to prevent issues # (block CUDA and wait for CUDA operations to be completed) stream.synchronize()
以上为tensorrt实现推理过程
执行结果如下:

四.完整代码

import argparse import os import numpy as np import struct # required for the model creation import tensorrt as trt # required for the inference using TRT engine import pycuda.autoinit import pycuda.driver as cuda # Sizes of input and output for TensorRT model INPUT_SIZE = 1 OUTPUT_SIZE = 1 # path of .wts (weight file) and .engine (model file) # input and output names are must for the TRT model # INPUT_BLOB_NAME = 'data' OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME = 'out' # A logger provided by NVIDIA-TRT gLogger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.INFO) ################################ # DEPLOYMENT RELATED ########### ################################ def load_weights(file_path): """ Parse the .wts file and store weights in dict format :param file_path: :return weight_map: dictionary containing weights and their values """ print(f"[INFO]: Loading weights: {file_path}") assert os.path.exists(file_path), '[ERROR]: Unable to load weight file.' weight_map = {} with open(file_path, "r") as f: lines = [line.strip() for line in f] # count for total # of weights count = int(lines[0]) assert count == len(lines) - 1 # Loop through counts and get the exact num of values against weights for i in range(1, count + 1): splits = lines[i].split(" ") name = splits[0] cur_count = int(splits[1]) # len of splits must be greater than current weight counts assert cur_count + 2 == len(splits) # loop through all weights and unpack from the hexadecimal values values = [] for j in range(2, len(splits)): # hex string to bytes to float values.append(struct.unpack(">f", bytes.fromhex(splits[j]))) # store in format of { 'weight.name': [weights_val0, weight_val1, ..] } weight_map[name] = np.array(values, dtype=np.float32) return weight_map def create_mlp_engine(max_batch_size, builder, config, dt, WEIGHT_PATH): """ Create Multi-Layer Perceptron using the TRT Builder and Configurations :param max_batch_size: batch size for built TRT model :param builder: to build engine and networks :param config: configuration related to Hardware :param dt: datatype for model layers :return engine: TRT model """ print("[INFO]: Creating MLP using TensorRT...") # load weight maps from the file weight_map = load_weights(WEIGHT_PATH) # build an empty network using builder network = builder.create_network() # add an input to network using the *input-name data = network.add_input('data', dt, (1, 1,INPUT_SIZE )) # add the layer with output-size (number of outputs) linear = network.add_fully_connected(input=data, num_outputs=OUTPUT_SIZE, kernel=weight_map['linear.weight'], bias=weight_map['linear.bias']) # set the name for output layer linear.get_output(0).name = OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME # mark this layer as final output layer network.mark_output(linear.get_output(0)) # set the batch size of current builder builder.max_batch_size = max_batch_size # create the engine with model and hardware configs engine = builder.build_engine(network, config) # free captured memory del network del weight_map # return engine return engine def api2model(max_batch_size,dt=trt.float32, WEIGHT_PATH=None,ENGINE_PATH=None): """ Create engine using TensorRT APIs :param max_batch_size: for the deployed model configs :return: """ # Create Builder with logger provided by TRT builder = trt.Builder(gLogger) # Create configurations from Engine Builder config = builder.create_builder_config() # Create MLP Engine engine = create_mlp_engine(max_batch_size, builder, config, dt, WEIGHT_PATH) assert engine # Write the engine into binary file print("[INFO]: Writing engine into binary...") with open(ENGINE_PATH, "wb") as f: # write serialized model in file f.write(engine.serialize()) # free the memory del engine del builder ################################ # INFERENCE RELATED ############ ################################ def inite_engine(ENGINE_PATH): # create a runtime (required for deserialization of model) with NVIDIA's logger runtime = trt.Runtime(gLogger) assert runtime # read and deserialize engine for inference with open(ENGINE_PATH, "rb") as f: engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read()) assert engine return engine def do_inference(inf_context, inf_host_in, inf_host_out): """ Perform inference using the CUDA context :param inf_context: context created by engine :param inf_host_in: input from the host :param inf_host_out: output to save on host :return: """ inference_engine = inf_context.engine # Input and output bindings are required for inference assert inference_engine.num_bindings == 2 # allocate memory in GPU using CUDA bindings device_in = cuda.mem_alloc(inf_host_in.nbytes) device_out = cuda.mem_alloc(inf_host_out.nbytes) # create bindings for input and output bindings = [int(device_in), int(device_out)] # create CUDA stream for simultaneous CUDA operations stream = cuda.Stream() # copy input from host (CPU) to device (GPU) in stream cuda.memcpy_htod_async(device_in, inf_host_in, stream) # execute inference using context provided by engine inf_context.execute_async(bindings=bindings, stream_handle=stream.handle) ################# key step ########### # copy output back from device (GPU) to host (CPU) cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(inf_host_out, device_out, stream) # synchronize the stream to prevent issues # (block CUDA and wait for CUDA operations to be completed) stream.synchronize() def perform_inference(input_data,ENGINE_PATH): """ Get inference using the pre-trained model :param input_val: a number as an input :return: """ engine=inite_engine(ENGINE_PATH) # create execution context -- required for inference executions context = engine.create_execution_context() assert context # create input as array data = np.array([input_data], dtype=np.float32) # capture free memory for input in GPU host_in = cuda.pagelocked_empty((INPUT_SIZE), dtype=np.float32) # copy input-array from CPU to Flatten array in GPU np.copyto(host_in, data.ravel()) # capture free memory for output in GPU host_out = cuda.pagelocked_empty(OUTPUT_SIZE, dtype=np.float32) # do inference using required parameters do_inference(context, host_in, host_out) print(f'\n[INFO]: Predictions using pre-trained model..\n\tInput:\t{input_data}\n\tOutput:\t{host_out[0]:.4f}') if __name__ == "__main__": args=2 weight_path = "./mlp.wts" output_engine_path = "./mlp.engine" if args==1: api2model(max_batch_size=1, WEIGHT_PATH=weight_path,ENGINE_PATH=output_engine_path) print("[INFO]: Successfully created TensorRT engine...") print("\n\tRun inference using `python mlp.py -d`\n") else: data=4.0 perform_inference(input_data=data,ENGINE_PATH=output_engine_path)
