实验内容
1.已知字符串:"this is a test of java".按要求执行以下操作:(要求源代码、结果截图。)
统计该字符串中字母s出现的次数。
统计该字符串中子串“is”出现的次数。
统计该字符串中单词“is”出现的次数。
实现该字符串的倒序输出。
统计该字符串中字母s出现的次数
实验代码
public class Dome1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String r = "this is a test of java";
int sum = 0;
char[] c = r.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
if (c[i] == 's') {
sum++;
}}
System.out.println("S的个数为"+sum);
}
}
实验截图

统计该字符串中子串“is”出现的次数。
实验代码:
public class Dome2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String c = "this is a test of java";
int sun = 0;
char[] r = c.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) {
if (r[i] == 'i' && r[i + 1] == 's') {
sun++;
}
}
System.out.println("is的个数为"+sun);
}
}
实验截图
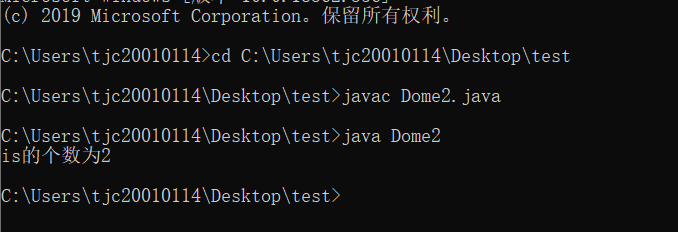
统计该字符串中单词“is”出现的次数。
实验代码:
public class Dome3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String r = "this is a test java";
String t[] = r.split(" ");
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < t.length; i++) {
if (t[i].equals("is")) {
sum++;
}
}
System.out.println("is的个数为"+sum);
}
}
实验截图
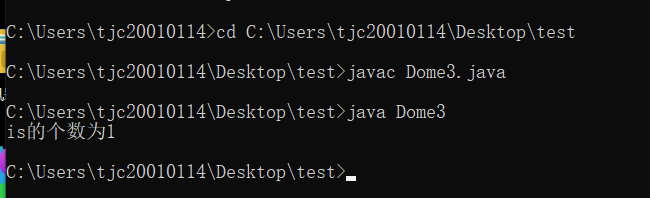
实现this is the text of java 倒序输出。
实验代码:
public class Dome4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String c = "this is a test of java";
int i;
char[] r = c.toCharArray();
for (i = r.length-1; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.print(r[i]);
}
}
}
实验截图
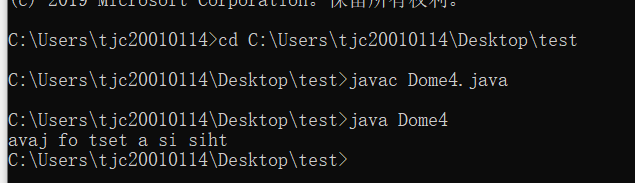
2.请编写一个程序,使用下述算法加密或解密用户输入的英文字串。要求源代码、结果截图.
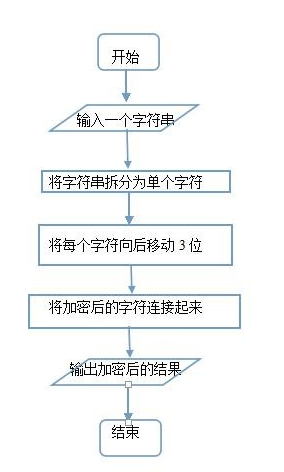
实验代码
import java.util.*;
public class Dome5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
String str=sc.nextLine();
char c[] = str.toCharArray();
char b;
for(int i=0;i<c.length;i++) {
b=(char)(c[i]+3);
System.out.print(""+b);
}
}
}
实验截图
3.已知字符串“ddejidsEFALDFfnef2357 3ed”。输出字符串里的大写字母数,小写英文字母数,非英文字母数
实验代码:
public class Dome6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int big=0,small=0,count=0;
String str="ddejidsEFALDFfnef2357 3ed";
char s[]=str.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i<s.length;i++) {
if(s[i]>='a'&&s[i]<='z') {
small++;
}else if(s[i]>='A'&&s[i]<='Z') {
big++;
}else {
count++;
}
}
System.out.println("大写字母个数为:"+big);
System.out.println("小写字母个数为:"+small);
System.out.println("非字母个数为:"+count);
}
}
实验截图

学习总结
1.构造方法可以为类中的属性初始化,构造方法与类名称相同,无返回值类型声明,在类中没有明确地定义构造方法,
则会自动生成一个无参数的随机构造方法,在一个类中的构造方法可以重载,但是每个类都至少有一个构造方法。
2.String类在Java中较特殊,String使用直接赋值的方式或者通过构造方法进行实例化。
在String中比较内容时使用equals方法,而“==”比较的只是两个字符串的地址值。字符串的内容一旦声明则不可改变。
3.在Java中使用this关键字可以表示当前的对象,通过“this.属性”可以调用本类中的属性,
通过“this.方法()”可以调用本类中的其他方法,通过this()调用本类的构造方法。
4.对象数组的使用要分为声明数组和为数组开辟空间,开辟空间后数组中的每个元素的内容都是null。在Java中使用extends关键字完成类的继承关系
5.访问限制:子类是不能直接访问父类中的私有成员的,但是子类可以调用父类中的非私有方法
6.子类对象实例化过程:子类对象在实例化之前必须首先调用父类中的构造方法之后再调用子类自己的构造方法。
7.方法的覆写:在继承的关系中也存在着方法覆写的概念,即在子类中定义与父类中同名的方法。
方法覆写时必须考虑到权限,被子类覆写的方法不能拥有比父类方法更加严格的访问权限。
8.final:使用final声明的类不能有子类;使用final声明的方法不能被子类所覆写;使用final声明的变量及成为常量