swagger提供开发者文档
========================================================
作用:想使用swagger的同学,一定是想用它来做前后台分离,后台开发为前台提供API,以供前台的同学调用和调试。
那么swagger的作用就是上面这句话。
具体swagger包含了哪些,swagger官网展示的很齐全
本篇只表达swagger2+spring boot怎么用,也是给想用swagger但是无从下手的同学们带带路!!!!
========================================================
本篇需要准备的东西:
InterllJ Idea/JDK1.8/spring boot 项目一个
========================================================
在这开始之前,你要自己去搭建一个spring boot项目,至于使用maven管理架包或者gradle管理架包,看你自己。
参考地址:
http://www.cnblogs.com/sxdcgaq8080/p/7712874.html. maven+spring boot
http://www.cnblogs.com/sxdcgaq8080/p/8717914.html gradle+spring boot
1.添加依赖
gradle添加依赖
// https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger-ui compile group: 'io.springfox', name: 'springfox-swagger-ui', version: '2.8.0' // https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger2 compile group: 'io.springfox', name: 'springfox-swagger2', version: '2.8.0'
maven添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0</version>
</dependency>
2.swagger配置类
其实这个配置类,只要了解具体能配置哪些东西就好了,毕竟这个东西配置一次之后就不用再动了。
【注意1】:特别要注意的是里面配置了api文件也就是controller包的路径,你要生成API接口文档的controller文件都是放在这个包路径下的,不然生成的文档扫描不到接口。
【注意2】:这个swagger配置类,是要放在你Application类同级,也就是Springboot项目的启动类的同级

package com.sxd.sweeping; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder; import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors; import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors; import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo; import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType; import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket; import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2; @Configuration @EnableSwagger2 public class Swagger2 { @Bean public Docket createRestApi() { return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo()) .select() .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.sxd.sweeping.controller")) .paths(PathSelectors.any()) .build(); } private ApiInfo apiInfo() { return new ApiInfoBuilder() .title("Spring Boot中使用Swagger2构建RESTful APIs") .description("更多精彩博客请关注:http://www.cnblogs.com/sxdcgaq8080/") .termsOfServiceUrl("http://www.cnblogs.com/sxdcgaq8080/") .contact("Angel挤一挤") .version("1.0") .build(); } }
3.然后 就是最简单的controller的swagger的表达了
【注意1】:@ApiImplicitParam 和 @ApiParam 方式均能指定参数规则。
【注意2】:使用@ApiImplicitParam的时候,需要指定paramType。

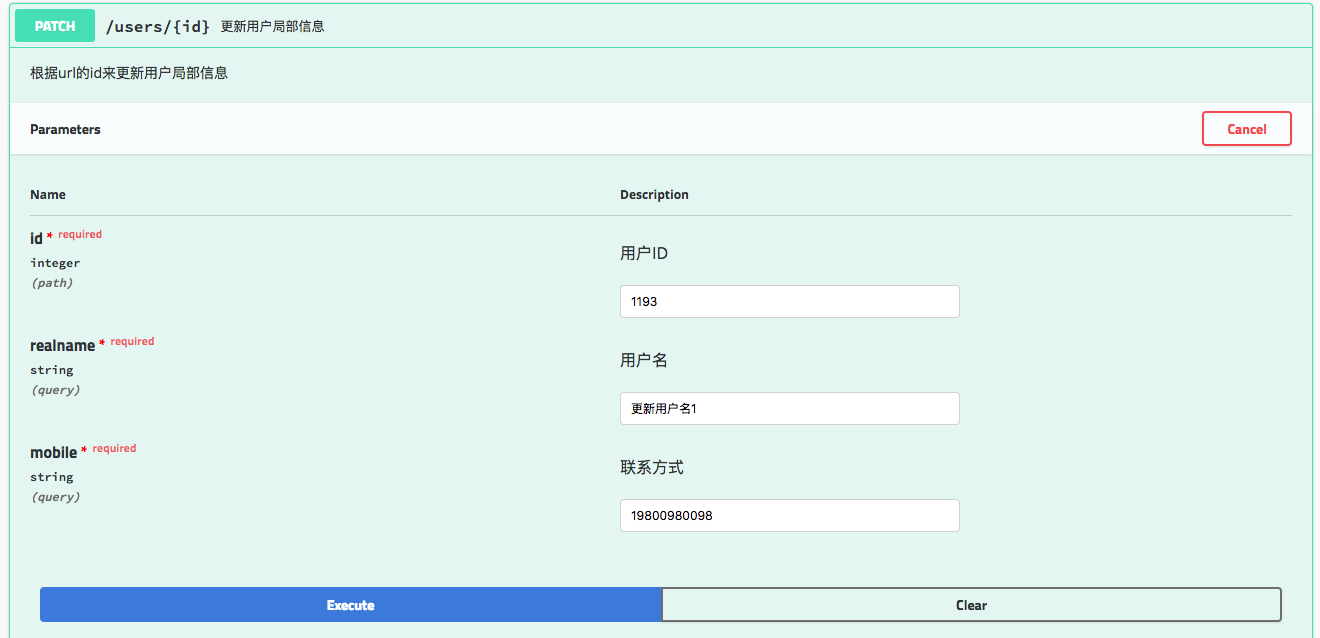
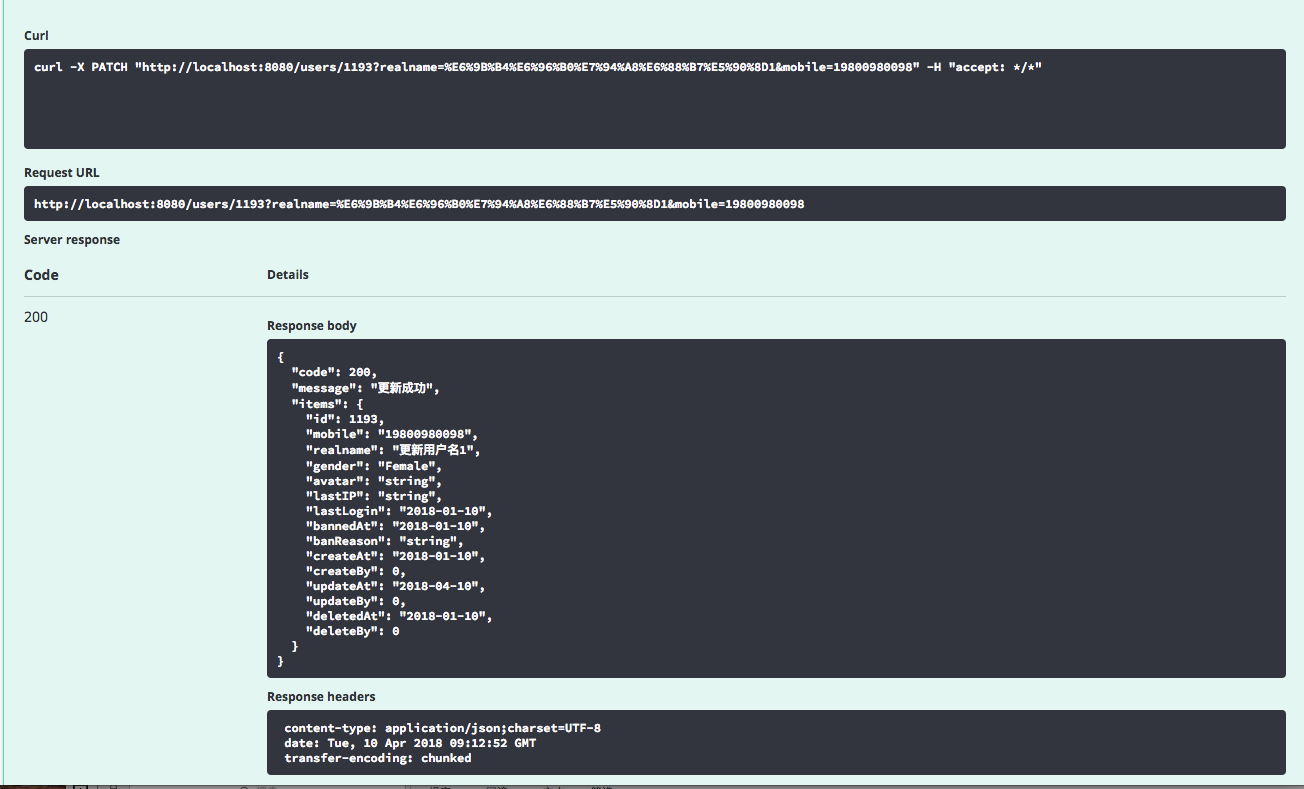
package com.sxd.sweeping.controller; import com.sxd.sweeping.entity.User; import com.sxd.sweeping.repository.UserRepository; import com.sxd.sweeping.response.GenericResponse; import io.swagger.annotations.Api; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; import java.sql.Date; import java.util.UUID; @Api(value = "userController",description = "用户相关操作",tags = {"用户"}) @RestController @RequestMapping("users") public class UserController { @Autowired private UserRepository userRepository; @ApiOperation(value = "获取用户详细信息", notes = "根据url的id来获取用户的详细信息") @ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = true,dataType = "Long",paramType = "path") // @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET) @GetMapping(value = "/{id}") public GenericResponse<User> get(@PathVariable Long id){ User user = userRepository.findUserById(id); GenericResponse<User> genericResponse = new GenericResponse<>(); genericResponse.setItems(user); genericResponse.setCode(200); if(user != null){ genericResponse.setMessage("查询成功"); }else{ genericResponse.setMessage("暂无此人"); } return genericResponse; } @ApiOperation(value = "增加用户", notes = "根据user对象创建用户") @ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "用户详细信息User", required = true,dataType = "User") // @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST) @PostMapping() public GenericResponse<User> add(@RequestBody User user){ String password = UUID.randomUUID().toString(); user.setPassword(password); user = userRepository.save(user); GenericResponse<User> genericResponse = new GenericResponse<>(); genericResponse.setItems(user); genericResponse.setCode(200); if(user != null){ genericResponse.setMessage("新增成功"); }else{ genericResponse.setMessage("新增失败"); } return genericResponse; } @ApiOperation(value = "删除用户", notes = "根据url的id来删除用户") @ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = true,dataType = "Long",paramType = "path") // @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE) @DeleteMapping(value = "/{id}") @ResponseBody public GenericResponse<User> delete(@PathVariable Long id){ userRepository.deleteById(id); GenericResponse<User> genericResponse = new GenericResponse<>(); genericResponse.setCode(200); genericResponse.setMessage("删除成功"); return genericResponse; } @ApiOperation(value = "更新用户", notes = "根据url的id来更新用户信息") @ApiImplicitParams({ @ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = true, dataType = "Long", paramType = "path"), @ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "用户实体user", required = true,dataType = "User") }) // @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.PUT) @PutMapping(value = "/{id}") public GenericResponse<User> update(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody User user){ User user1 = userRepository.findUserById(id); user1.setGender(user.getGender()); user1.setMobile(user.getMobile()); user1.setRealname(user.getRealname()); user1.setUpdateAt(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis())); GenericResponse<User> genericResponse = new GenericResponse<>(); genericResponse.setCode(200); genericResponse.setMessage("更新成功"); genericResponse.setItems(userRepository.saveAndFlush(user1)); return genericResponse; } @ApiOperation(value = "更新用户局部信息", notes = "根据url的id来更新用户局部信息") @ApiImplicitParams({ @ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = true, dataType = "Long", paramType = "path"), @ApiImplicitParam(name = "realname", value = "用户名", required = true,dataType = "String"), @ApiImplicitParam(name = "mobile", value = "联系方式", required = true,dataType = "String") }) // @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.PATCH) @PatchMapping(value = "/{id}") public GenericResponse<User> patch(@PathVariable Long id, String realname, String mobile){ User user = userRepository.findUserById(id); user.setRealname(realname); user.setMobile(mobile); GenericResponse<User> genericResponse = new GenericResponse<>(); genericResponse.setCode(200); genericResponse.setMessage("更新成功"); genericResponse.setItems(userRepository.saveAndFlush(user)); return genericResponse; } }
4.项目启动后,就可以访问地址:
http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html#
访问你的api接口了。
展示API页面如下:

==============================================================================
常用注解详情:
swagger通过注解表明该接口会生成文档,包括接口名、请求方法、参数、返回信息的等等。
@Api:作用在controller类上,修饰整个类,描述Controller的作用
@ApiOperation:作用在controller类的方法上,描述一个类的一个方法,或者说一个接口的功能
@ApiParam:单个参数描述
@ApiModel:用在返回对象类上,用对象来接收参数
@ApiModelProperty:用在参数对象的字段上
@ApiProperty:用对象接收参数时,描述对象的一个字段
@ApiResponse:用在@ApiResponses里面,HTTP响应其中1个描述
@ApiResponses:用在controller方法上,HTTP响应整体描述
@ApiIgnore:使用该注解忽略这个API
@ApiError :发生错误返回的信息
@ApiImplicitParam:用在@ApiImplicitParams中,一个请求参数
@ApiImplicitParams:用在controller方法上,多个请求参数
各个注解中属性值的解析:
@ApiImplicitParam:用在 @ApiImplicitParams 注解中,指定一个请求参数的各个方面
paramType:参数放在哪个地方
· header --> 请求参数的获取:@RequestHeader
· query -->请求参数的获取:@RequestParam
· path(用于restful接口)--> 请求参数的获取:@PathVariable
· body(不常用)
· form(不常用)
name:参数名
dataType:参数类型
required:参数是否必须传
value:参数的意思
defaultValue:参数的默认值
@Api:作用在controller类上,修饰整个类,描述Controller的作用 属性名称 备注 value url的路径值 tags 如果设置这个值、value的值会被覆盖 description 对api资源的描述 basePath 基本路径可以不配置 position 如果配置多个Api 想改变显示的顺序位置 produces For example, "application/json, application/xml" consumes For example, "application/json, application/xml" protocols Possible values: http, https, ws, wss. authorizations 高级特性认证时配置 hidden 配置为true 将在文档中隐藏
@ApiOperation:作用在controller类的方法上,描述一个类的一个方法,或者说一个接口的功能 属性名称 备注 value url的路径值 tags 如果设置这个值、value的值会被覆盖 description 对api资源的描述 basePath 基本路径可以不配置 position 如果配置多个Api 想改变显示的顺序位置 produces For example, "application/json, application/xml" consumes For example, "application/json, application/xml" protocols Possible values: http, https, ws, wss. authorizations 高级特性认证时配置 hidden 配置为true 将在文档中隐藏 response 返回的对象 responseContainer 这些对象是有效的 "List", "Set" or "Map".,其他无效 httpMethod "GET", "HEAD", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE", "OPTIONS" and "PATCH" code http的状态码 默认 200 extensions 扩展属性
@ApiParam:单个参数描述 示例: public UniVerResponse<HuaYangArea> huayang(@ApiParam(value = "create a entity HuaYangArea") @RequestBody HuaYangArea huaYangArea) 属性名称 备注 name 属性名称 value 属性值 defaultValue 默认属性值 allowableValues 可以不配置 required 是否属性必填 access 不过多描述 allowMultiple 默认为false hidden 隐藏该属性 example 举例子
@ApiResponse:用在@ApiResponses里面,HTTP响应其中1个描述 示例: @ApiOperation(value = "保存HUAYANG信息",notes = "传入HUAYANG实体,保存HUAYANG信息") @PostMapping() @ApiResponses({ @ApiResponse(code = 200,message = "success"), @ApiResponse(code = 10001,message = "参数错误"), @ApiResponse(code = 20001,message = "业务错误"), @ApiResponse(code = 50001,message = "系统异常")}) public UniVerResponse<HuaYangArea> huayang(@ApiParam(value = "create a entity HuaYangArea") @RequestBody HuaYangArea huaYangArea){ 属性名称 备注 code http的状态码 message 描述 response 默认响应类 Void reference 参考ApiOperation中配置 responseHeaders 参考 ResponseHeader 属性配置说明 responseContainer 参考ApiOperation中配置
==========================================================================
Get等价:
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
等价于:@GetMapping(value = "/{id}")
Post等价:【创建资源】
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
等价于:@PostMapping()
Delete等价:
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
等价于:@DeleteMapping(value = "/{id}")
Put等价:【更新已存在的资源,完全替换,所以接收到的是id和完整的对象,在处理上如果对象中有未给值的字段,则更新数据库中字段值替换为空】
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
等价于:@PutMapping(value = "/{id}")
Patch等价:【更新已经存在资源的部分字段,局部更新,仅提供id和要更新的字段,在处理上仅更新要更新的字段,其他字段不变】
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.PATCH)
等价于:@PatchMapping(value = "/{id}")
===========================================================================
【注意】:
因为返回的都是统一处理响应格式,所以每个API接口上都要加上@ResponseBody注解。
所以,可以选择在Controller上加上@RestController=@Controller+@ResponseBody
===========================================================================
下一篇地址:
