集合的由来
数组长度是固定,如果要改变数组的长度需要创建新的数组将旧数组里面的元素拷贝过去,使用起来不方便。
java给开发者提供了一些集合类,能够存储任意长度的对象,长度可以随着元素的增加而增加,随着元素的减少而减少,使用起来方便一些。
集合继承体系图
java提供了一些集合类,这些集合类分别适用于不同的场景,下面是常用的一些集合基础体系图。
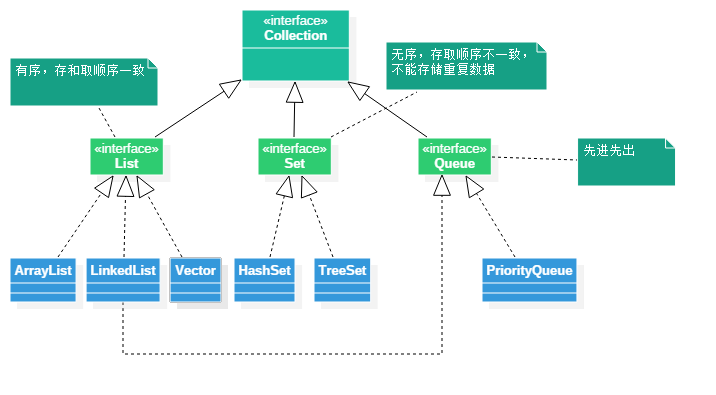
里面的Collection是接口,下面的List、Set、Queue也都是接口,并且继承了这个Collection。最下面的ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector、HashSet、TreeSet、PriorityQueue都是他们的实现类。
集合类的一些特点
List:里面存放的数据是有顺序的,可以存放重复的数据。
Set:里面存放的数据是没有顺序的,不能存放重复的数据。
Queue:是一个队列,里面的数据是先进先出,可以存放重复的数据。
数组和集合的区别
区别1:
数组既可以存储基本数据类型,又可以存储引用数据类型,基本数据类型存储的是值,引用数据类型存储的是地址值
集合只能存储引用数据类型(对象),如果存储基本数据类型时,会自动装箱变成相应的包装类
区别2:
数组长度是固定的,不能自动增长
集合的长度的是可变的,可以根据元素的增加而自动增长
Collection常用方法
boolean add(E e)
boolean remove(Object o)
void clear()
boolean contains(Object o)
boolean isEmpty()
int size()
使用集合存储String类型:
package com.monkey1024.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* Collection常用方法
*
*/
public class CollectionTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//多态
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add("a");
c.add("b");
c.add("c");
c.add("d");
//获取元素的个数
System.out.println(c.size());
System.out.println(c);
//删除指定元素
c.remove("b");
//将集合转换为数组遍历输出
Object[] o = c.toArray();
for(int i=0; i<o.length; i++){
System.out.println(o[i]);
}
//清空集合
c.clear();
//判断是否包含
System.out.println(c.contains("b"));
System.out.println(c.isEmpty());
}
}
使用集合存储自己创建的Person类型:
创建一个Person类
package com.monkey1024.bean;
/**
* Person类
*
*/
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(){
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//重写toString方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
//重写equals方法
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(this == obj){
return true;
}
if(obj instanceof Person){
Person p = (Person)obj;
if(this.name.equals(p.getName()) && this.age == p.getAge()){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
创建测试类:
package com.monkey1024.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import com.monkey1024.bean.Person;
/**
* Collection常用方法
*
*/
public class CollectionTest02 {
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" })//去除集合的警告
public static void main(String[] args) {
//多态
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add(new Person("张三",19));
c.add(new Person("李四",20));
c.add(new Person("王五",22));
c.add(new Person("赵六",23));
//获取元素的个数
System.out.println(c.size());
System.out.println(c);
//将集合转换为数组遍历输出
Object[] o = c.toArray();
for(int i=0; i<o.length; i++){
System.out.println(o[i]);
}
//判断是否包含
Person p = new Person("赵六",23);
//需要重写引用数据类型中的equals方法
System.out.println(c.contains(p));
//删除指定元素
c.remove(p);
//清空集合
c.clear();
System.out.println(c.isEmpty());
}
}
带有All的方法
package com.monkey1024.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* Collection常用方法
*
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" })//去除集合的警告
public class CollectionTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
retainAll();
containsAll();
removeAll();
addAll();
}
public static void retainAll() {
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
c1.add("a");
c1.add("b");
c1.add("c");
c1.add("d");
Collection c2 = new ArrayList();
c2.add("a");
c2.add("b");
c2.add("c");
c2.add("d");
c2.add("e");
c2.add("f");
//取交集,如果c1里面的元素全部包含在两者的交集里面,返回false,否则返回true
boolean b = c1.retainAll(c2);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c1);
}
public static void containsAll() {
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
c1.add("a");
c1.add("b");
c1.add("c");
c1.add("d");
Collection c2 = new ArrayList();
c2.add("a");
c2.add("b");
c2.add("z");
//判断调用的集合是否包含传入的集合
boolean b = c1.containsAll(c2);
System.out.println(b);
}
public static void removeAll() {
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
c1.add("a");
c1.add("b");
c1.add("c");
c1.add("d");
Collection c2 = new ArrayList();
c2.add("a");
c2.add("b");
c2.add("z");
//删除的是交集
boolean b = c1.removeAll(c2);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c1);
}
public static void addAll() {
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
c1.add("a");
c1.add("b");
c1.add("c");
c1.add("d");
Collection c2 = new ArrayList();
c2.add("a");
c2.add("b");
c2.add("c");
c2.add("d");
//将c2中的每一个元素添加到c1中
c1.addAll(c2);
System.out.println(c1);
}
}