一、删除链表的倒数第N个节点
题目:19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
分析:典型的利用双指针法解题。首先让指针first指向头节点,然后让其向后移动n步,接着让指针sec指向头结点,并和first一起向后移动。当first的next指针为NULL时,sec即指向了要删除节点的前一个节点,接着让first指向的next指针指向要删除节点的下一个节点即可。注意如果要删除的节点是首节点,那么first向后移动结束时会为NULL,这样加一个判断其是否为NULL的条件,若为NULL则返回头结点的next指针。
解法一:
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) 4 { 5 ListNode* first = head; 6 while(n--) 7 first = first->next; 8 if(!first) 9 return head->next; 10 ListNode* sec = head; 11 while(first->next) 12 { 13 sec = sec->next; 14 first = first->next; 15 } 16 sec->next = sec->next->next; 17 return head; 18 } 19 };
二、相交链表
题目:160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
解法一:
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) { 4 //这个思路就是 ListA + ListB = A + intersection + Bb + intersection 5 //ListB + ListA = Bb + intersection + A + intersection 6 //用大A表示ListA里面非共有 Bb表示listB里面非共有的,可以看到在第二个intersection的开头两个链表长度是一样的,必然相等 7 //所以我们可以遍历A再遍历B,另一个遍历B再遍历A,两个指针必定在第二个交集处相遇,没有交集就是空指针 8 ListNode *cursorA = headA; 9 ListNode *cursorB = headB; 10 if (!cursorA || !cursorB) 11 return NULL; 12 while (cursorA != cursorB) 13 { 14 if (!cursorA) 15 cursorA = headB; 16 else 17 cursorA = cursorA->next; 18 if (!cursorB) 19 cursorB = headA; 20 else 21 cursorB = cursorB->next; 22 } 23 return cursorA; 24 } 25 };
三、环形链表
解法一:
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) 4 { 5 ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head; 6 while (fast && fast->next) 7 { 8 slow = slow->next; 9 fast = fast->next->next; 10 if (slow == fast) return true; 11 } 12 return false; 13 } 14 };
四、环形链表 II
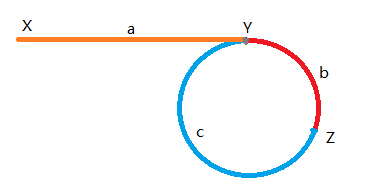
如下图所示,X,Y,Z分别为链表起始位置,环开始位置和两指针相遇位置,则根据快指针速度为慢指针速度的两倍,可以得出:
2*(a + b) = a + b + n * (b + c);即:a=(n - 1) * b + n * c = (n - 1)(b + c) +c;
注意到b+c恰好为环的长度,故可以推出,如将此时两指针分别放在起始位置和相遇位置,并以相同速度前进,当一个指针走完距离a时,另一个指针恰好走出 绕环n-1圈加上c的距离。故两指针会在环开始位置相遇。
解法一:
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) 4 { 5 if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) 6 return NULL; 7 ListNode * p = head; 8 ListNode * q = head; 9 while (q != NULL && q->next != NULL)//第一次pq相遇 10 { 11 p = p->next; 12 q = q->next->next; 13 if (p == q) break; 14 } 15 16 if (p == q) 17 { 18 p = head; 19 while (p != q)//从起点开始,在入口点相遇 20 { 21 p = p->next; 22 q = q->next; 23 } 24 return p; 25 } 26 return NULL; 27 } 28 };