强引用
Java 默认的就是强引用
只要有强引用存在,对象就不会被回收
a = new Object();
软引用
如果内存足够就不进行回收,内存不够的时候会进行回收
比较适合做大对象的缓存
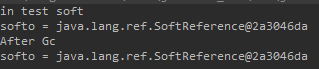
System.out.println("in test soft 1");
Object o = new Object();
SoftReference<Object> softo = new SoftReference<>(o);
o = null;
System.out.println("softo = " + softo);
System.gc();
System.out.println("After Gc");
System.out.println("softo = " + softo);
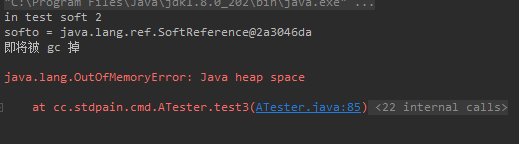
System.out.println("in test soft 2");
Object o = new Object(){
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
System.out.println("即将被 gc 掉");
}
};
SoftReference<Object> softo = new SoftReference<>(o);
o = null;
System.out.println("softo = " + softo);
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
int counter = 0;
while (true){
list.add(new int[10000]);
}
弱引用
如果垃圾回收发生,在线程扫描的时候,如果一个对象只有弱引用存在,那么就会被回收
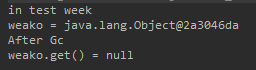
System.out.println("in test week");
Object o = new Object();
WeakReference<Object> weako = new WeakReference<>(o);
o = null;
System.out.println("weako = " + weako.get());
System.gc();
System.out.println("After Gc");
System.out.println("weako.get() = " + weako.get());
如果这个对象是偶尔的使用,并且希望在使用时随时就能获取到,但又不想影响此对象的垃圾收集,那么你应该用 Weak Reference 来记住此对象。
当你想引用一个对象,但是这个对象有自己的生命周期,你不想介入这个对象的生命周期,这时候你就是用弱引用。
这个引用不会在对象的垃圾回收判断中产生任何附加的影响。
虚引用
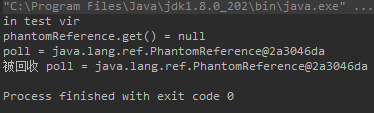
System.out.println("in test vir");
Object o = new Object() {
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
//放开这个注释引用队列死活都为空,原因暂时不清楚
//System.out.println("即将被 gc 掉");
}
};
ReferenceQueue referenceQueue = new ReferenceQueue();
PhantomReference phantomReference = new PhantomReference(o, referenceQueue);
//无法从这里获得一个有效的引用 一定是配合引用队列使用的
System.out.println("phantomReference.get() = " + phantomReference.get());
o = null;
System.gc();
System.runFinalization();
Thread.sleep(1000);
Reference<? extends Object> poll = referenceQueue.poll();
System.out.println("poll = " + poll);
if (poll != null) {
System.out.println("被回收 poll = " + poll);
}
至于为什么 重载finalize 方法不会入队 原因在这
https://www.zhihu.com/question/49760047?from=profile_question_card