1. 小尾循序
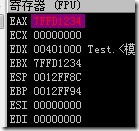
intel 处理器使用小尾循序的方案存取内存数据。所以我们这样定义一块数据的时候:
在内存中实际的表示是:
2. movzx和movsx
当我们试图从一个较小的操作数想一个较大的操作数移动数据的时候就会发生问题:
当然我们可以用如下方式解决:
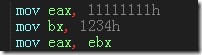
mov eax, 0
mov bx, 1234h
mov eax,ebx
但是当我们遇到有符号数字时候还是出错了。
所以intel设计了movzx和movsx指令来处理从较小的操作数向较大的操作数移动数据。
其中movzx给无符号的用, movsx给有符号的用。
3. 翻转字符串
1 ;翻转字符串
2 .data
3 source byte "this is the source string", 0
4 target byte sizeof source dup(0),0
5
6 .code
7 start:
8
9 mov esi, 0
10 mov ecx, sizeof source
11
12 L1:
13 movzx eax, source[esi]
14 push eax
15 inc esi
16 loop L1
17
18
19 mov esi, 0
20 mov ecx, sizeof source
21 L2:
22 pop eax
23 mov target[esi], al
24 inc esi
25 Loop L2
26
27
28 end start
4. 过程
;------------------------------------------------
;description: calculate and returns the sum of three 32-bit integers
;param: eax, ebx, ecx, the three intergets
;return: eax = sum, and the status flags are changed
;------------------------------------------------
sumof proc
add eax, ebx
add eax, ecx
ret
sumof endp
;3个整数相加
.data
.code
main:
mov eax, 1
mov ebx, 2
mov ecx, 3
call sumof
end main
5. 整数相加
1 ;整数求和
2 .data
3 intArray word 100h, 200h, 300h
4
5 .code
6 start:
7
8 mov edi, offset intArray
9 mov eax, 0
10 mov ecx, lengthof intArray
11
12 L1:
13 add eax, [edi]
14 add edi, type intArray
15 loop L1
16
17
18 end start