softmax分类器
这篇文章介绍如何使用一个简单的多层感知机和softmax分类器对MNIST数据集进行分类。
1. 使用内建的函数加载MNIST数据
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True)2. 理解输入数据集
(1)独热码形式表示label
(2)训练集,验证集和测试集
- 55,000 data points
- mnist.train.images for inputs
- mnist.train.labels for outputs
----------------------------------------
- 5,000 data points
- mnist.validation.images for inputs
- mnist.validation.labels for outputs
-----------------------------------------
-10,000 data points
- mnist.test.images for inputs
- mnist.test.labels for outputs3. 创建一个交互式的会话
在Tensorflow中可以使用2找个基本的方式运行代码。
一种是把图都构建好了之后才创建会话执行张量和运行计算。
另外一种是交互式会话方式,创建代码时随意执行。
这里创建一个交互式的会话, 注意:当执行完后要关闭会话。
sess =tf.InteractiveSession()4. 创建占位符(placeholder)
在Tensorflow中,在给变量赋值之前要先创建占位符。这里我们为输入”Xs”和输出”Ys”创建占位符。
占位符x表示分配给输入的”空间”:
- 这里的每一个输入有28*28 = 784个像素;
- placeholder中变量“shape”用于定义张量的大小,格式为shape=[d1,d2];
- d1 = None 表示批的输入可以为任意大小;
- d2 = 784表示一个训练样本的像素个数。
占位符y表示最终的输出或者label:
- 10 个可能的输出类别
- placeholder中变量“shape”用于定义张量的大小,格式为shape=[d1,d2];
- d1 = None 表示批的输入可以为任意大小;
- d2 = 10 表示输出的个数。
占位符的类型(dtype)一般使用tf.float32或者tf.float64.
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape = [None, 784]
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape = [None, 10]5. 分配偏置和权重到空的张量
创建标量的时候需要给这个变量一个初值,当然这个初值还没有生效,只有执行初始化时才会生效。
初值全部设置为0。
初值的选取是十分重要的,但是这里只是示范,为了简单起见全部设置为零。
# Weight tensor
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10],tf.float32))
# Bias tensor
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10],tf.float32))6. 执行赋值操作
上面我们只是给分配权重和偏置,但是还没有初始化。
因为我们创建的是一个交互式的会话,所以在创建会话后任何地方执行run.sess()都可以。
执行tf.global_variables_initializer()初始化变量。
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())7. 添加权重和偏置到输入
如下如,我们将输入与权重相乘在加上偏置就得到输出。
注意:这里并没有使用激活函数。
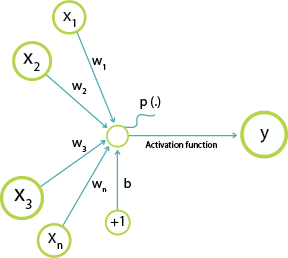
tf.matmul(x,w) + b8. softmax 回归
分类问题中常常使用softmax分类器解决分类问题。他能产生一个概率输出。在这个例子中,我们的模型不会提供一个100%确定的输出,而是一个概率分布,比如模型是正确的,对应某个输入,输出的结果概率就会比较大。
比如输入数字9,输出有很大概率是9.
0 -->.0.1%
1 -->...2%
2 -->...3%
3 -->...2%
4 -->..12%
5 -->..10%
6 -->..57%
7 -->..20%
8 -->..55%
9 -->..80% 9. 损失函数
用于最小化预测结果和真实结果的误差。
这里使用的是交叉熵。
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_*log(y),reduction_indices=[1]))10. 优化方法
Tensorflow集成许多优化方法,如SGD, Adam, RMSqr,Momentum等。
这里使用梯度下降:
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy)11. 训练批大小的设置
由于批梯度下降太过耗费计算资源,所以不常用。
所谓批梯度下降就是一次使用所有的数据作为输入,去训练模型。
因此,常用的是mini-batch梯度下降。
通过选择合适的nimi-batch,能够快速地训练网络。
for i in range(1000):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(50)
train_step.run(feed_dict={x:batch[0], y_:batch[1]})12. 测试
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1), tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
acc = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images, y_:mnist.test.labels})*100
print("The final accuracy for the simple ANN model is: {} % ".format(acc))13. 关闭会话
sess.close()完整代码及运行结果
import tensorflow as tf
# import MNIST dataset using tensoflow build-in function
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True)
# creating a interactive session
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
# creating placeholder for input and output
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape = [None, 784])
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 10])
# assign bias and weight to null tensors
w = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.zeros([784,10], dtype=tf.float32))
b = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.zeros([10],dtype=tf.float32))
#excute the assignment operation
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# softmax regression
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x,w) + b)
# cost function
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y), reduction_indices=[1]))
# optimizaiton
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy)
# mini- batch setting
for i in range(1000):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(50)
train_step.run(feed_dict={x:batch[0], y_:batch[1]})
# test
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1), tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
acc = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images, y_:mnist.test.labels})*100
print("The final accuracy for the simple ANN model is: {} % ".format(acc))
# close session
sess.close()结果:
The final accuracy for the simple ANN model is: 90.75000286102295 % 译自 Deep Learning with TensorFlow IBM Cognitive Class ML0120EN
ML0120EN-2.2-Review-CNN-MNIST-Dataset 1st part: classify MNIST using a simple model.