If you use a dictionary in a for statement, it traverses the keys of the dictionary. For example, print_hist prints each key and the corresponding value:

Print dictionary in alphabetical order:

Reverse lookup
Given a dictionary d and a key k, it is easy to find the corresponding value v = d[k]. This operation is called lookup. But what if you have v and you want to find k? You have two problems: first, there might be more than one key that maps to the value v. Depending on the application, you might be able to pick one, or you might have to make a list that contains all of them. Second, there is no simple syntax to do a reverse lookup; you have to search.
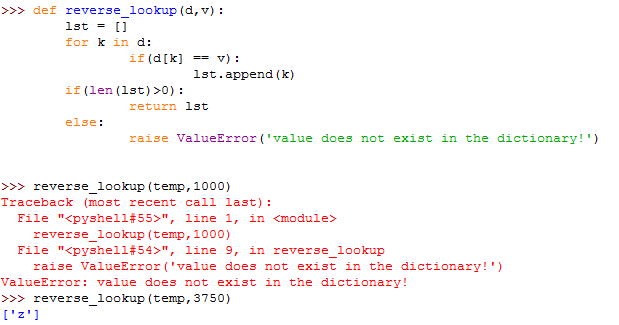
A reverse lookup is much slower than a forward lookup; if you have to do it often, or if the dictionary gets big, the performance of your program will suffer.
from Thinking in Python