C与C++
C语言实现思路
定义:乘客结构体(from, to, status), 电梯运行函数, 决策函数
全局变量:电梯状态,世界状态,乘客数组
在主函数中,首先读入输入,并初始化电梯和世界状态,填充乘客数组,然后进入电梯运行函数
电梯运行函数:循环:检查已递送乘客数量,遍历乘客数组并更新乘客状态(已触发,未触发),调用决策函数并根据结果运行电梯(上、下、停靠),更新状态,若为停靠则更新乘客状态(出入厢)
其实也可以通过给函数加一个参数模拟面向对象吧
C++实现类图
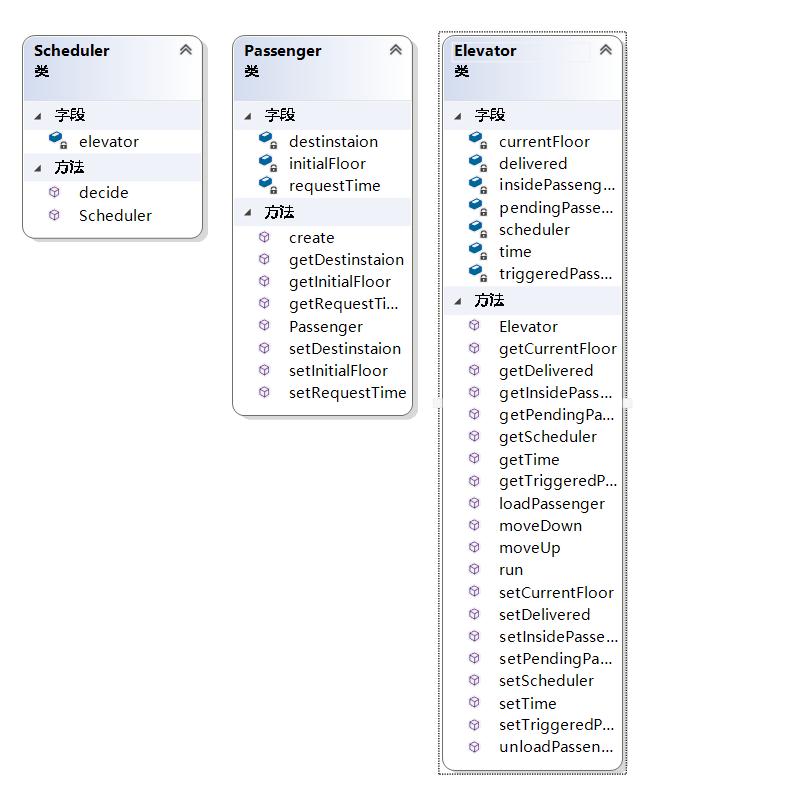
区别
面向过程需要分析解决问题所需要的子步骤,并把一些子步骤组合起来成为函数,然后按照解决问题的过程互相调用来解决问题
而面向对象可以把现实中的一类实体抽象成类,并用对象表示一个实体,对象的成员表示实体的状态,对象的方法表示实体能执行的操作。这样抽象使程序结构更清晰,扩展性也更好,且降低了名称污染。面向对象的封装性使程序模块内聚性更好,继承和多态使热插拔更加便捷
电梯类
Elevator.h
#ifndef SIMPLE_ELEVATOR_ELEVATOR_H
#define SIMPLE_ELEVATOR_ELEVATOR_H
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
class Elevator {
private:
int currentFloor;
queue<int> destinstionQueue;
int time;
public:
int getTime() const;
public:
Elevator();
virtual ~Elevator();
int getCurrentFloor() const;
const queue<int> &getDestinstionQueue() const;
void goToFloor(const int destinstion);
int getDirection() const;
void run();
};
#endif //SIMPLE_ELEVATOR_ELEVATOR_H
Elevator.cpp
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdlib>
#include "Elevator.h"
Elevator::Elevator() : time(0) {}
Elevator::~Elevator() {
}
int Elevator::getCurrentFloor() const {
return currentFloor;
}
const queue<int> &Elevator::getDestinstionQueue() const {
return destinstionQueue;
}
void Elevator::goToFloor(const int destinstion) {
this->destinstionQueue.push(destinstion);
}
int Elevator::getTime() const {
return time;
}
int Elevator::getDirection() const {
if (destinstionQueue.front() > currentFloor) {
return 1;
}
if (destinstionQueue.front() < currentFloor) {
return -1;
}
if (destinstionQueue.front() == currentFloor) {
return 0;
}
}
void Elevator::run() {
time += abs(destinstionQueue.front() - currentFloor);
currentFloor = destinstionQueue.front();
destinstionQueue.pop();
}