object collection_t1 { def flatMap1(): Unit = { val li = List(1,2,3) val res = li.flatMap(x => x match { case 3 => List('a','b') case _ => List(x*2) }) println(res) } def map1(): Unit = { val li = List(1,2,3) val res = li.map(x => x match { case 3 => List('a','b') case _ => x*2 }) println(res) }
val m = Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 343, 23).reduceLeft((x, y) => {
if (x < y) {
y
} else {
x
}
})
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { flatMap1() map1() } }
result: List(2, 4, a, b) List(2, 4, List(a, b))
flatMap就是在Map的基础上加了压平flatten的功能
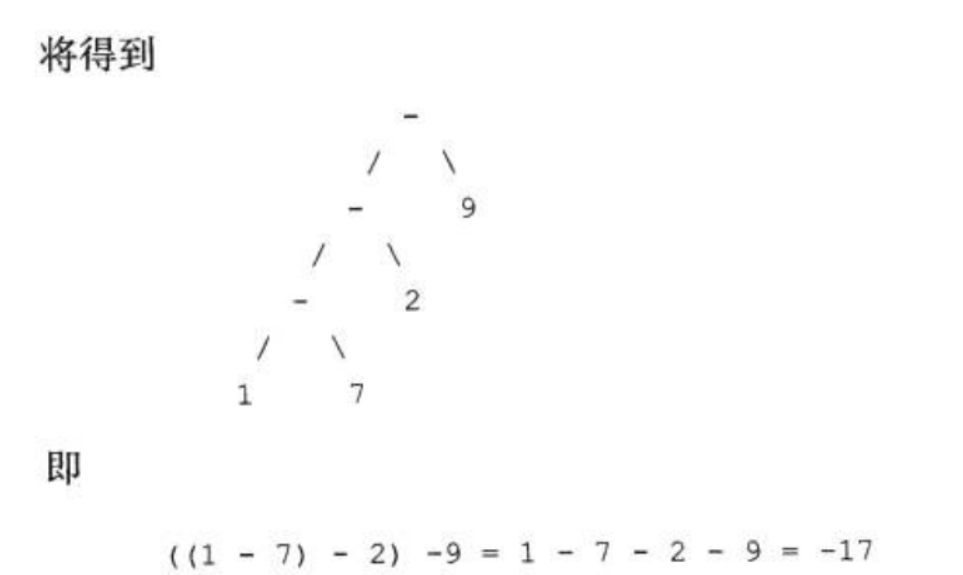
foldLeft 从左边起折叠,累加
https://alvinalexander.com/scala/scala-reduceleft-examples
1.reudceLeft和foldLeft最大的区别就是foldLeft有一个初始值,,也就是说foldLeft比reduceLeft更灵活
2.foldLeft 可以引入其他类型