牛顿法
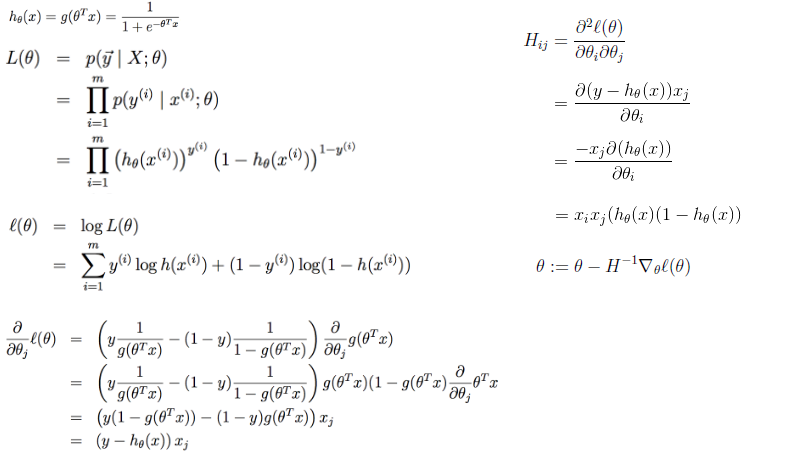
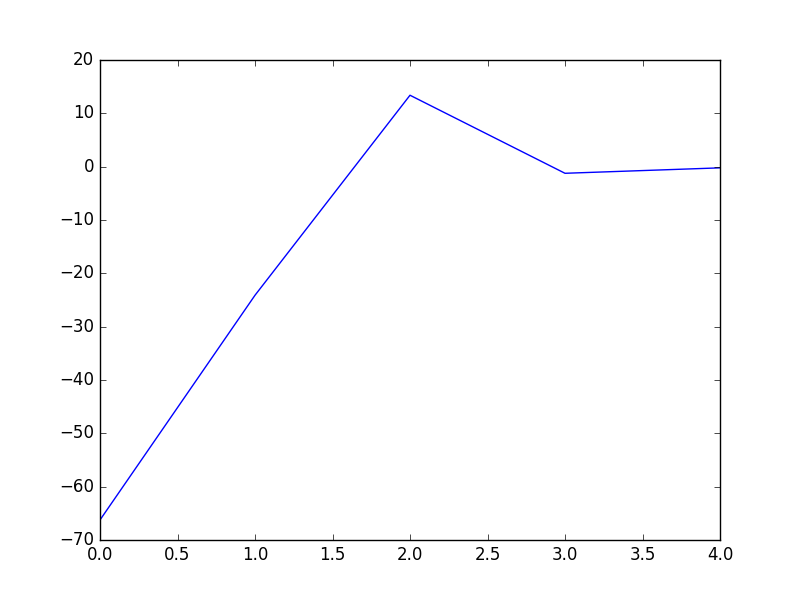
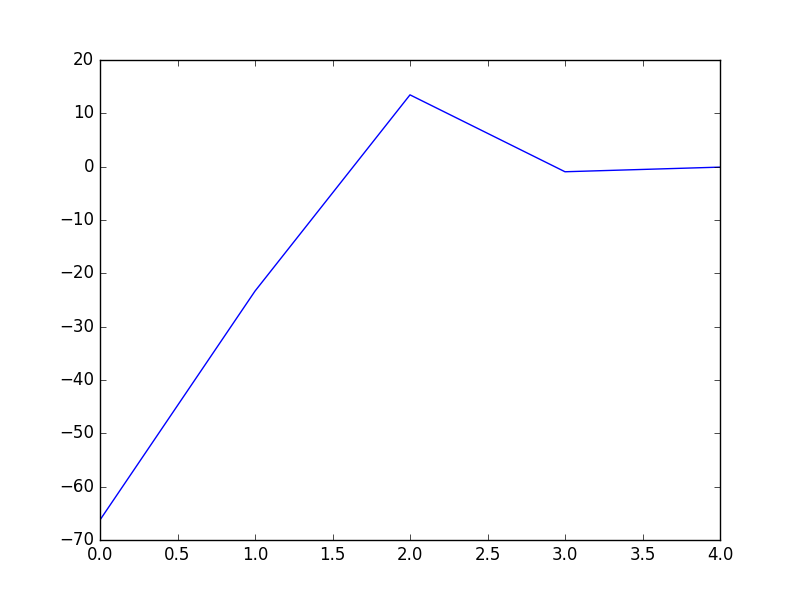
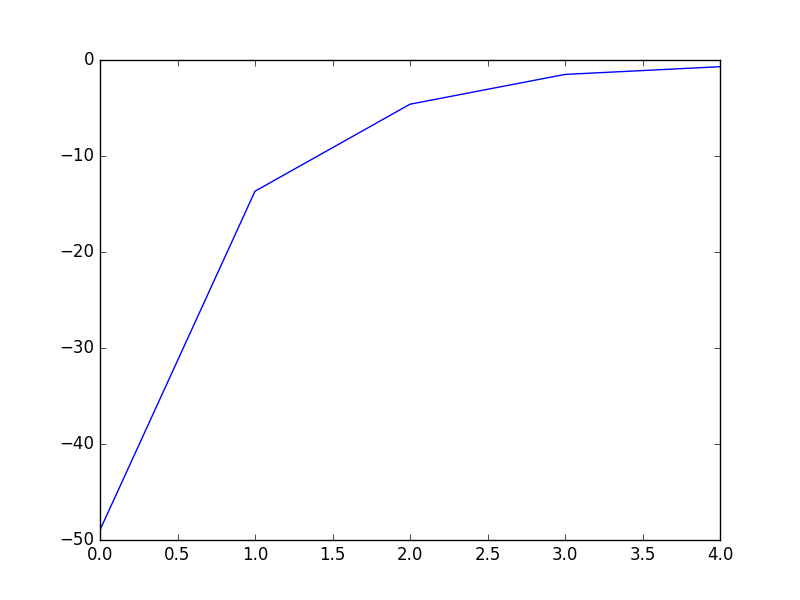
1 # coding:utf-8 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 import numpy as np 4 5 def dataN(length):#生成数据 6 x = np.ones(shape = (length,3)) 7 y = np.zeros(length) 8 for i in np.arange(0,length/100,0.02): 9 x[100*i][0]=1 10 x[100*i][1]=i 11 x[100*i][2]=i + 1 + np.random.uniform(0,1.2) 12 y[100*i]=1 13 x[100*i+1][0]=1 14 x[100*i+1][1]=i+0.01 15 x[100*i+1][2]=i+0.01 + np.random.uniform(0,1.2) 16 y[100*i+1]=0 17 return x,y 18 19 def sigmoid(x): #simoid 函数 20 return 1.0/(1+np.exp(-x)) 21 22 def DFP(x,y, iter):#DFP拟牛顿法 23 n = len(x[0]) 24 theta=np.ones((n,1)) 25 y=np.mat(y).T 26 Gk=np.eye(n,n) 27 grad_last = np.dot(x.T,sigmoid(np.dot(x,theta))-y) 28 cost=[] 29 for it in range(iter): 30 pk = -1 * Gk.dot(grad_last) 31 rate=alphA(x,y,theta,pk) 32 theta = theta + rate * pk 33 grad= np.dot(x.T,sigmoid(np.dot(x,theta))-y) 34 delta_k = rate * pk 35 y_k = (grad - grad_last) 36 Pk = delta_k.dot(delta_k.T) / (delta_k.T.dot(y_k)) 37 Qk= Gk.dot(y_k).dot(y_k.T).dot(Gk) / (y_k.T.dot(Gk).dot(y_k)) * (-1) 38 Gk += Pk + Qk 39 grad_last = grad 40 cost.append(np.sum(grad_last)) 41 return theta,cost 42 43 def BFGS(x,y, iter):#BFGS拟牛顿法 44 n = len(x[0]) 45 theta=np.ones((n,1)) 46 y=np.mat(y).T 47 Bk=np.eye(n,n) 48 grad_last = np.dot(x.T,sigmoid(np.dot(x,theta))-y) 49 cost=[] 50 for it in range(iter): 51 pk = -1 * np.linalg.solve(Bk, grad_last) 52 rate=alphA(x,y,theta,pk) 53 theta = theta + rate * pk 54 grad= np.dot(x.T,sigmoid(np.dot(x,theta))-y) 55 delta_k = rate * pk 56 y_k = (grad - grad_last) 57 Pk = y_k.dot(y_k.T) / (y_k.T.dot(delta_k)) 58 Qk= Bk.dot(delta_k).dot(delta_k.T).dot(Bk) / (delta_k.T.dot(Bk).dot(delta_k)) * (-1) 59 Bk += Pk + Qk 60 grad_last = grad 61 cost.append(np.sum(grad_last)) 62 return theta,cost 63 64 def alphA(x,y,theta,pk): #选取前20次迭代cost最小的alpha 65 c=float("inf") 66 t=theta 67 for k in range(1,200): 68 a=1.0/k**2 69 theta = t + a * pk 70 f= np.sum(np.dot(x.T,sigmoid(np.dot(x,theta))-y)) 71 if abs(f)>c: 72 break 73 c=abs(f) 74 alpha=a 75 return alpha 76 77 def newtonMethod(x,y, iter):#牛顿法 78 m = len(x) 79 n = len(x[0]) 80 theta = np.zeros(n) 81 cost=[] 82 for it in range(iter): 83 gradientSum = np.zeros(n) 84 hessianMatSum = np.zeros(shape = (n,n)) 85 for i in range(m): 86 hypothesis = sigmoid(np.dot(x[i], theta)) 87 loss =hypothesis-y[i] 88 gradient = loss*x[i] 89 gradientSum = gradientSum+gradient 90 hessian=[b*x[i]*(1-hypothesis)*hypothesis for b in x[i]] 91 hessianMatSum = np.add(hessianMatSum,hessian) 92 hessianMatInv = np.mat(hessianMatSum).I 93 for k in range(n): 94 theta[k] -= np.dot(hessianMatInv[k], gradientSum) 95 cost.append(np.sum(gradientSum)) 96 return theta,cost 97 98 def tesT(theta, x, y):#准确率 99 length=len(x) 100 count=0 101 for i in xrange(length): 102 predict = sigmoid(x[i, :] * np.reshape(theta,(3,1)))[0] > 0.5 103 if predict == bool(y[i]): 104 count+= 1 105 accuracy = float(count)/length 106 return accuracy 107 108 def showP(x,y,theta,cost,iter):#作图 109 plt.figure(1) 110 plt.plot(range(iter),cost) 111 plt.figure(2) 112 color=['or','ob'] 113 for i in xrange(length): 114 plt.plot(x[i, 1], x[i, 2],color[int(y[i])]) 115 plt.plot([0,length/100],[-theta[0],-theta[0]-theta[1]*length/100]/theta[2]) 116 plt.show() 117 length=200 118 iter=5 119 x,y=dataN(length) 120 121 theta,cost=BFGS(x,y,iter) 122 print theta #[[-18.93768161][-16.52178427][ 16.95779981]] 123 print tesT(theta, np.mat(x), y) #0.935 124 showP(x,y,theta.getA(),cost,iter) 125 126 theta,cost=DFP(x,y,iter) 127 print theta #[[-18.51841028][-16.17880599][ 16.59649161]] 128 print tesT(theta, np.mat(x), y) #0.935 129 showP(x,y,theta.getA(),cost,iter) 130 131 theta,cost=newtonMethod(x,y,iter) 132 print theta #[-14.49650536 -12.78692552 13.05843361] 133 print tesT(theta, np.mat(x), y) #0.935 134 showP(x,y,theta,cost,iter)