迭代器模式是行为模式的一种,它把对容器中包含的内部对象的访问委让给外部类,使用iterator遍历访问。
角色和职责:
1.迭代器接口(Iterator):
2.Concrete Iterator(迭代器实现类) -:
3.容器接口(Aggregate):
4.容器实现类(Concrete Aggregate):
UML图:
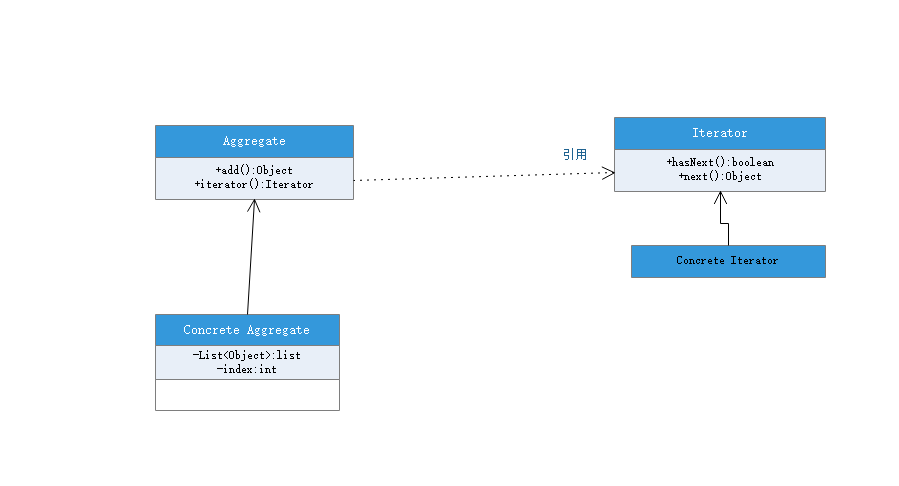
具体代码:
/** * 书对象 */ public class Book { private int id; private String name;//书名 public Book(int id,String name){ this.id = id; this.name = name; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void display(){ System.out.println(name); } }
/** * 具体迭代器模式 */ public class ConcreteIterator implements Iterator { @Override public boolean hasNext() { return false; } @Override public Object next() { return null; } }
/** * 模仿AbstractList写法,ArrayList就是一个迭代器模式 */ public class BookList{ private List<Book> list; private int index; public BookList(){ this.list = new ArrayList<Book>(); } /** * 添加书籍 */ public void addBook(Book book){ this.list.add(book); } public Iterator<Book> iterator() { return new ConcreteIterator(); } /** * 具体迭代器模式 */ private class ConcreteIterator implements Iterator { @Override public boolean hasNext() { if(index >= list.size()){ return false; } return true; } @Override public Object next() { return list.get(index++); } } }
import java.util.Iterator; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Book book1 = new Book(1,"空调说明书"); Book book2 = new Book(2,"电脑说明书"); BookList bookList = new BookList(); bookList.addBook(book1); bookList.addBook(book2); Iterator<Book> iterator = bookList.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ iterator.next().display(); } } }
结果:
空调说明书
电脑说明书
优缺点:
优:1.实现功能分离,简化容器接口。让容器只实现本身的基本功能,把迭代功能委让给外部类实现,符合类的设计原则
2.隐藏容器的实现细节
源码地址:https://github.com/qjm201000/design_pattern_iterator.git