1.二叉树的序列化
输入的一棵树:
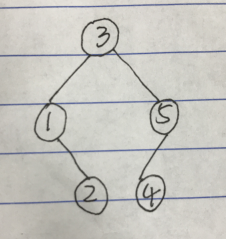
//二叉树的先序遍历-序列化 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <sstream> using namespace std; struct TreeNode { int val; TreeNode* left; TreeNode* right; TreeNode(int x) :val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} //构造函数 }; class Solution { public: string treeToStr(TreeNode* head) { if (head == NULL) { return "#_"; } string res = int2str(head->val) + "_"; res += treeToStr(head->left); res += treeToStr(head->right); return res; } //int to string string int2str(const int &int_temp) { stringstream stream; stream << int_temp; string string_temp = stream.str(); //此处也可以用 stream>>string_temp return string_temp; } }; int main() { //生成一棵二叉树 TreeNode* head = new TreeNode(3); head->left = new TreeNode(1); head->right = new TreeNode(5); head->left->right = new TreeNode(2); head->right->left = new TreeNode(4); Solution test; string s = test.treeToStr(head); for (auto c : s) { cout << c; } cout << endl; return 0;
2.二叉树的反序列化
2.1 上面采用的先序遍历序列化,方便再反序列化回来:
-
- 字符串的第一个结点就是根结点;
- 先序遍历的非递归写法,用栈容易实现;
class Solution { public: TreeNode* strToTree(string s) { //判空 int sz = s.size(); if (sz == 0) return NULL; //先序遍历,借助栈 stack<TreeNode*> stack; int idx = 0; TreeNode* head = new TreeNode((c2i(s[idx]))); idx = idx + 2;//跳过‘_’分隔符 TreeNode* cur = head; while ((cur || !stack.empty() )&& idx<sz) { //借助栈,先序遍历 if (cur) { stack.push(cur); cur->left = gNode(s[idx]); idx += 2;//跳过‘_’分隔符 cur = cur->left; } else { cur = stack.top(); cur->right = gNode(s[idx]); idx += 2; stack.pop(); cur = cur->right; } } return head; } //generate TreeNode TreeNode* gNode(char a) { if (a == '#') return NULL; else { return new TreeNode(c2i((a))); } } //char to int int c2i(const char &char_temp) { stringstream stream; stream << char_temp; int int_temp; stream >> int_temp; return int_temp; } };
2.2 测试的完整代码,通过字符串还原成树,再输出为字符串,判断是否正确
//二叉树的反序列化-先序遍历 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <sstream> #include <stack> using namespace std; struct TreeNode { int val; TreeNode* left; TreeNode* right; TreeNode(int x) :val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} //构造函数 }; class Solution1{ public: string serial_Of_Tree(TreeNode* head) { if (head == NULL) { return "#_"; } string res = int2str(head->val) + "_"; res += serial_Of_Tree(head->left); res += serial_Of_Tree(head->right); return res; } //int to string string int2str(const int &int_temp) { stringstream stream; stream << int_temp; string string_temp = stream.str(); //此处也可以用 stream>>string_temp return string_temp; } }; class Solution { public: TreeNode* strToTree(string s) { //判空 int sz = s.size(); if (sz == 0) return NULL; // stack<TreeNode*> stack; int idx = 0; TreeNode* head = new TreeNode((c2i(s[idx]))); idx = idx + 2; TreeNode* cur = head; while ((cur || !stack.empty() )&& idx<sz) { if (cur) { stack.push(cur); cur->left = gNode(s[idx]); idx += 2; cur = cur->left; } else { cur = stack.top(); cur->right = gNode(s[idx]); idx += 2; stack.pop(); cur = cur->right; } } return head; } //generate TreeNode TreeNode* gNode(char a) { if (a == '#') return NULL; else { return new TreeNode(c2i((a))); } } //char to int int c2i(const char &char_temp) { stringstream stream; stream << char_temp;//stream作为中转站,另外使用<<和>> int int_temp; stream >> int_temp; return int_temp; } }; int main() { string s = "3_1_#_2_#_#_5_4_#_#_#_"; Solution test1; TreeNode* t= test1.strToTree(s); Solution1 test; string s2 = test.serial_Of_Tree(test1.strToTree(s)); for (auto a : s2) { cout << a; } cout << endl; return 0; }

参考资料:
1.二叉树的序列化和反序列化 (层次遍历,用队列实现的反序列化,java)