一. 频率类源码
1. APIView的dispath方法中的self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs) 点进去 2. self.check_throttles(request) # 进行频率验证 # 频率组件核心源码分析 def check_throttles(self, request): throttle_durations = [] # 1. 遍历配置的频率认证类,初始化得到一个个频率认证类对象(会调用频率认证类的__init__()方法) # 2. 频率认证类对象调用allow_request方法,判断是否限次(没有限次可访问,限次不可访问) # 3. 频率认证类对象再限次后,调用wait方法, 获取还需等待多长的时间可以进行下一次访问 # 频率认证类都是继承 SimpleRateThrottles类 for throttle in self.get_throttles(): if not throttle.allow_request(request, self) # 只要频率限制了,allow_request 返回False了, 才会调用wait throttle_durations.append(throttle.wait()) if throttle_durations: durations=[ duration for duration in throttle_durations if duration is not None] duration = max(durations, default=None) self.throttled(request, duration)
自定义频率类:
1. 自定义一个继承SimpleRateThrottle类的频率类 2. 设置一个scope类属性, 属性值为任意见名知意的字符串 3. 在settings配置文件中,配置drf的DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES, 格式为{scope字符串:'次数/时间'} 4. 在自定义频率类中重写get_cache_key方法 # 限制的对象返回,与限制信息有关的字符串 # 不限制的对象返回None(只能放回None, 不能是False或者是''等)
短信接口1/min频率限制
频率: api/throttles.py
from rest_framework.throttling import SimpleRateThrottle class SMSRateThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle): scope = 'sms' # 只对提交手机号的get方法进行限制 def get_cache_key(self, request, view): mobile = request.query_params.get('mobile') # 没有手机号, 就不做频率限制 if not mobile: return None # 返回可以根据手机号动态变化,且不易重复的字符串,作为操作缓存的key return 'throttle_%(scope)s_%(ident)s' %{'scope': self.scope, 'ident': mobile}
配置: settings.py
drf 配置 REST_FRAMEWORK = { # 频率限制条件配置 'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': { 'sms': '1/min'}, }
视图; views.py
from . throttles import SMSRateThrottle class TestSMSAPIView(APIView): # 局部配置频率认证 throttle_classes = [SMSRateThrottle] def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return APIResponse(0, 'get 获取验证码') def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return APIResponse(0, 'post 获取验证码')
路由:api/url.py
url(r'^sms/$', views.TestSMSAPIView.as_view())
限制的接口
只会对/api/sms/?mobile=具体手机号 接口才会有频率限制 1. 对api/sms/ 或其他接口发送无限制 2. 对数据包提交mobile的api/sms接口无限制 3. 对不是mobile(如phone)字段提交的电话接口无限制
认证规则图
drf分类

认证规则演变图
数据库session认证: 低效

缓存认证:高效

jwt认证: 高效

缓存认证:不容易并发
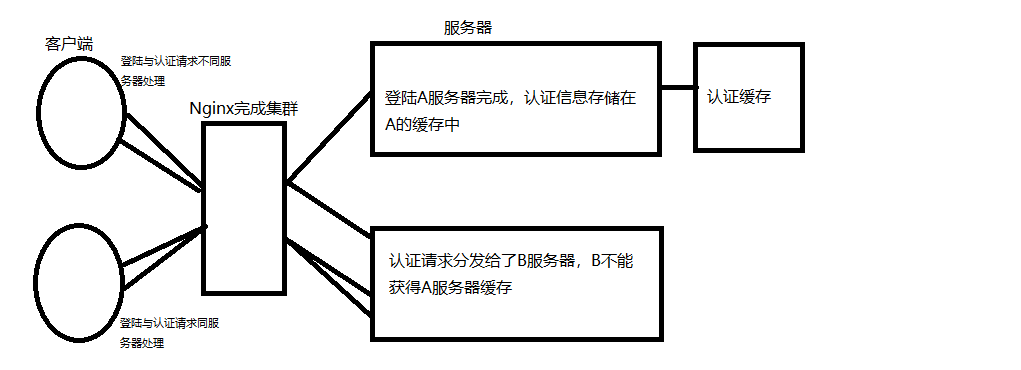
jwt认证: 容易并发

jwt认证
优点:
1) 服务器不要存储token,token交给每一个客户端自己存储,服务器压力小 2)服务器存储的是 签发和校验token 两段算法,签发认证的效率高 3)算法完成各集群服务器同步成本低,路由项目完成集群部署(适应高并发)
格式:
1) jwt token采用三段式:头部.载荷.签名 2)每一部分都是一个json字典加密形参的字符串 3)头部和载荷采用的是base64可逆加密(前台后台都可以解密) 4)签名采用hash256不可逆加密(后台校验采用碰撞校验) 5)各部分字典的内容: 头部:基础信息 - 公司信息、项目组信息、可逆加密采用的算法 载荷:有用但非私密的信息 - 用户可公开信息、过期时间 签名:头部+载荷+秘钥 不可逆加密后的结果 注:服务器jwt签名加密秘钥一定不能泄露 签发token:固定的头部信息加密.当前的登陆用户与过期时间加密.头部+载荷+秘钥生成不可逆加密 校验token:头部可校验也可以不校验,载荷校验出用户与过期时间,头部+载荷+秘钥完成碰撞检测校验token是否被篡改
drf_jwt插件
官网
https://github.com/jpadilla/django-rest-framework-jwt
安装
>: pip3 install djangorestframework-jwt
登录- 签发token: api/urls.py
# ObtainJSONWebToken视图类就是通过username和password得到user对象然后签发token from rest_framework_jwt.views import ObtainJSONWebToken, obtain_jwt_token urlpatterns = [ # url(r'^jogin/$', ObtainJSONWebToken.as_view()), url(r'^jogin/$', obtain_jwt_token), ]
认证-校验token: 全局或局部配置drf_jwt的认证类
from rest_framework.views import APIView from utils.response import APIResponse # 必须登录后才能访问 - 通过了认证权限组件 from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated from rest_framework_jwt.authentication import JSONWebTokenAuthentication class UserDetail(APIView): authentication_classes = [JSONWebTokenAuthentication] # jwt-token校验request.user permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated] # 结合权限组件筛选掉游客 def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return APIResponse(results={'username': request.user.username})
路由与接口测试
# 路由 url(r'^user/detail/$', views.UserDetail.as_view()), # 接口:/api/user/detail/ # 认证信息:必须在请求头的 Authorization 中携带 "jwt 后台签发的token" 格式的认证字符串