(color{#0066ff}{ 题目描述 })

(color{#0066ff}{输入格式})

(color{#0066ff}{输出格式})
对于每个询问操作,输出一行答案。
(color{#0066ff}{输入样例})
6 5
2 2 1 2 1 1
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
2 6
Q 3 5
C 2 1 1
Q 3 5
C 5 1 2
Q 3 5
(color{#0066ff}{输出样例})
3
1
2
(color{#0066ff}{数据范围与提示})
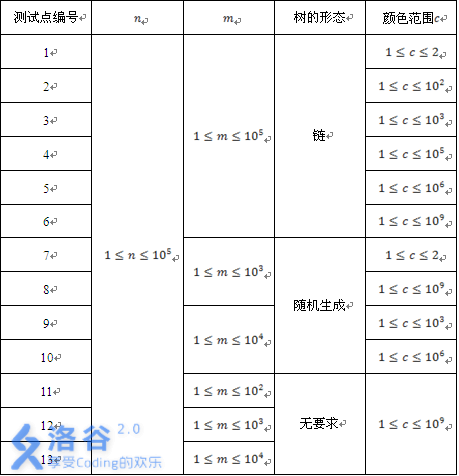
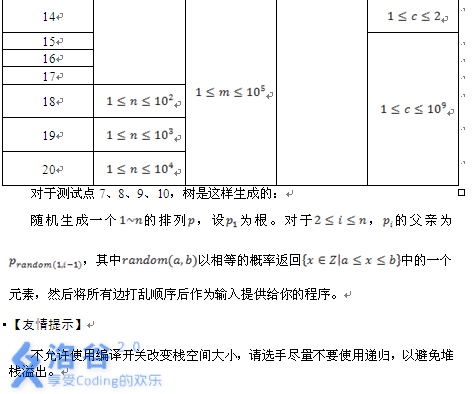
(color{#0066ff}{ 题解 })
树剖
线段树维护:区间两端点的颜色,区间颜色段数
区间合并的时候判断一下端点颜色即可
树剖的时候一起要判断端点处,那变量记录一下重链的上下,就是线段树区间query[l,r]的两端点颜色
如果相同要--
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
LL in() {
char ch; LL x = 0, f = 1;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar()))(ch == '-') && (f = -f);
for(x = ch ^ 48; isdigit(ch = getchar()); x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48));
return x * f;
}
const int maxn = 1e5 + 10;
struct node {
int to;
node *nxt;
node(int to = 0, node *nxt = NULL): to(to), nxt(nxt) {}
void *operator new(size_t) {
static node *S = NULL, *T = NULL;
return (S == T) && (T = (S = new node[1024]) + 1024), S++;
}
};
struct Tree {
protected:
int lc, rc;
struct node {
node *ch[2];
int l, r, num, tag;
int lc, rc;
node(int l = 0, int r = 0, int num = 1, int tag = -1, int lc = 0, int rc = 0)
:l(l), r(r), num(num), tag(tag), lc(lc), rc(rc) { ch[0] = ch[1] = NULL; }
void upd() {
num = ch[0]->num + ch[1]->num;
if(ch[0]->rc == ch[1]->lc) num--;
lc = ch[0]->lc;
rc = ch[1]->rc;
}
void trn(int c) {
num = 1;
lc = rc = tag = c;
}
void dwn() {
if(~tag) {
ch[0]->trn(tag);
ch[1]->trn(tag);
tag = -1;
}
}
};
node *root;
void build(node *&o, int l, int r, int *val, int *rev) {
o = new Tree::node(l, r, 1, -1, 0, 0);
if(l == r) return (void)(*o = Tree::node(l, r, 1, -1, val[rev[l]], val[rev[l]]));
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(o->ch[0], l, mid, val, rev);
build(o->ch[1], mid + 1, r, val, rev);
o->upd();
}
void lazy(node *o, int l, int r, int c) {
if(o->r < l || o->l > r) return;
if(l <= o->l && o->r <= r) {
o->tag = o->lc = o->rc = c;
o->num = 1;
return;
}
o->dwn();
lazy(o->ch[0], l, r, c), lazy(o->ch[1], l, r, c);
o->upd();
}
int query(node *o, int l, int r) {
if(o->r < l || o->l > r) return 0;
if(o->l == l) lc = o->lc;
if(o->r == r) rc = o->rc;
if(l <= o->l && o->r <= r) return o->num;
o->dwn();
int lans = query(o->ch[0], l, r);
int rans = query(o->ch[1], l, r);
o->upd();
if(lans && rans && o->ch[0]->rc == o->ch[1]->lc) return lans + rans - 1;
return lans + rans;
}
public:
int L() { return lc; }
int R() { return rc; }
void build(int l, int r, int *val, int *rev) { build(root, l, r, val, rev); }
void lazy(int l, int r, int c) { lazy(root, l, r, c); }
int query(int l, int r) { return query(root, l, r); }
}t;
node *head[maxn];
int top[maxn], dfn[maxn], redfn[maxn], son[maxn];
int siz[maxn], fa[maxn], val[maxn], cnt, dep[maxn];
int n, m;
void add(int from, int to) { head[from] = new node(to, head[from]); }
char getch() {
char ch;
while(!isalpha(ch = getchar()));
return ch;
}
void dfs1(int x, int f) {
fa[x] = f;
dep[x] = dep[f] + 1;
siz[x] = 1;
for(node *i = head[x]; i; i = i->nxt) {
if(i->to == f) continue;
dfs1(i->to, x);
siz[x] += siz[i->to];
if(!son[x] || siz[i->to] > siz[son[x]]) son[x] = i->to;
}
}
void dfs2(int x, int t) {
top[redfn[dfn[x] = ++cnt] = x] = t;
if(son[x]) dfs2(son[x], t);
for(node *i = head[x]; i; i = i->nxt)
if(!dfn[i->to])
dfs2(i->to, i->to);
}
void addpath(int x, int y, int c) {
int fx = top[x], fy = top[y];
while(fx != fy) {
if(dep[fx] >= dep[fy]) {
t.lazy(dfn[fx], dfn[x], c);
x = fa[fx];
}
else {
t.lazy(dfn[fy], dfn[y], c);
y = fa[fy];
}
fx = top[x];
fy = top[y];
}
if(dep[x] > dep[y]) t.lazy(dfn[y], dfn[x], c);
else t.lazy(dfn[x], dfn[y], c);
}
int querypath(int x, int y) {
int ans = 0, ansl = -1, ansr = -1;
int fx = top[x], fy = top[y];
while(fx != fy) {
if(dep[fx] >= dep[fy]) {
ans += t.query(dfn[fx], dfn[x]);
if(t.R() == ansl) ans--;
ansl = t.L();
x = fa[fx];
}
else {
ans += t.query(dfn[fy], dfn[y]);
if(t.R() == ansr) ans--;
ansr = t.L();
y = fa[fy];
}
fx = top[x];
fy = top[y];
}
if(dep[x] > dep[y]) {
ans += t.query(dfn[y], dfn[x]);
if(t.L() == ansr) ans--;
if(t.R() == ansl) ans--;
}
else {
ans += t.query(dfn[x], dfn[y]);
if(t.L() == ansl) ans--;
if(t.R() == ansr) ans--;
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
n = in(), m = in();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) val[i] = in();
int x, y, z;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) x = in(), y = in(), add(x, y), add(y, x);
dfs1(1, 0), dfs2(1, 1), t.build(1, n, val, redfn);
while(m --> 0) {
if(getch() == 'C') {
x = in(), y = in(), z = in();
addpath(x, y, z);
}
else {
x = in(), y = in();
printf("%d
", querypath(x, y));
}
}
return 0;
}