要实现一个带动画效果的下拉列表,通常的做法是,将外部容器的高度设为一个固定值,设置其overflow为hidden, 同时为其应用CSS过渡属性,点击相应的按钮后改变外部容器的高度,如下面的实现。
<div id="p11-1-btn" onclick="toggleByHeight()">▼点我展开</div>
<ul id="p11-1" style="height: 0px;">
<li style="background: #FF6666">第一</li>
<li style="background: #FF9900">第二</li>
<li style="background: #CCFF00">第三</li>
<li style="background: #CC3399">第四</li>
</ul>
function toggleByHeight() {
const containerStyle = document.querySelector('#p11-1').style;
const buttonExpand = document.querySelector('#p11-3-btn');
if (containerStyle.height == '0px') {
containerStyle.height = '120px';
buttonExpand.innerText = '▲点我收起';
} else {
containerStyle.height = '0px';
buttonExpand.innerText = '▼点我展开 ';
}
}
#p11-1 {
overflow:hidden;
transition: height 1s;
margin: 0px;
}
#p11-1 li {
font-size: 16px;
color: #ffffff;
line-height: 30px;
text-align: center;
margin: 0px;
}
#p11-1-btn {
cursor: pointer;
background-color: #dcdcdc;
}
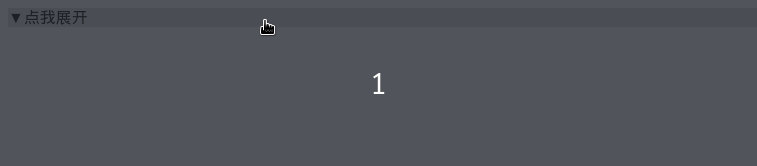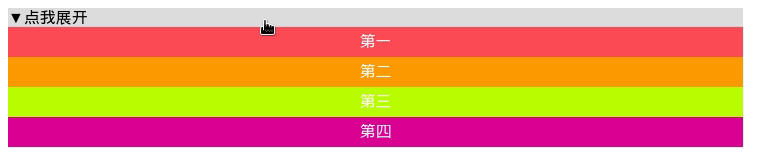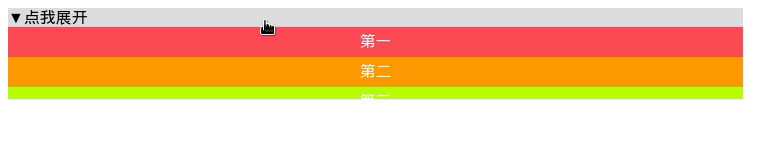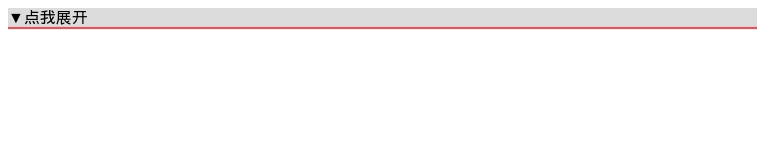
上面的方法只适用于内部元素高度已知的情况。我们知道每个 li 的行高为30px, 由于 li 没有边框、内边距、外边距,则每个li 的高度就是30px, 全部展开后总高度为150px.
但是现实中,我们并不总能知道内部元素的高度,而 display: none 与 display: auto 之间是无法应用过渡效果的(具体为啥我也不知道),因此这种方法就不适用了,那么内部元素的高度应该如何计算出来呢?有人会说可以为父元素设置最大高度 max-height, 这样只要 max-height 的值大于内部元素的总高度就行,但这样做要求我们提供的 max-height 值不能过小也不能过大,过小则内部元素不能全部显示出来,过大则动画会出现延时。
更好的方法是用JS去计算内部元素的高度,假设有如下的HTML结构,虽然外部容器的高度为0px, 但内部每个元素的高度仍旧为其原来的高度, 只是它被隐藏了起来而已,我们可以通过JS去计算内部元素的总高度。
<div id="p11-2" style="height: 0px; overflow: hidden;">
<div style="height: 40px; padding:10px">第一</div>
<div style="height: 80px;">第二</div>
<div style="height: 60px;">第三</div>
</div>
<script>
const parent = document.querySelector('#p11-2');
console.log(parent.style.height) // 0px
const childs = document.querySelectorAll('#p11-2 div');
let totalHeight = 0;
childs.forEach(child => {
totalHeight += parseInt(child.style.height);
});
console.log(totalHeight) // 180
</script>
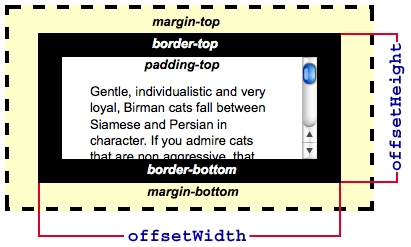
需要注意的是,你必须使用内联样式为元素指定高度,使用内部样式表或者外部样式表是无法正确通过JS获取高度值的。解决这个问题的办法是,获取该元素的
offsetHeight而不是height,offsetHeight包含该元素的内容高度、垂直内边距和边框,这样一来,不管内部元素有没有内边距、边框,我们总能正确的计算其高度。
下面利用这种方法重写一下上面的程序。
<div id="p11-3-btn" onclick="toggleByOffsetHeight()">▼点我展开</div>
<ul id="p11-3" style="height: 0px;">
<li style="background: #FF6666; padding: 10px 0px">第一</li>
<li style="background: #FF9900; border: solid 5px red">第二</li>
<li style="background: #CCFF00; padding: 15px 0px">第三</li>
<li style="background: #CC3399; border: double 3px blue">第四</li>
</ul>
function toggleByOffsetHeight() {
const containerStyle = document.querySelector('#p11-3').style;
const childs = document.querySelectorAll('#p11-3 li');
const buttonExpand = document.querySelector('#p11-3-btn');
let totalHeight = 0;
childs.forEach(child => {
totalHeight += parseInt(child.offsetHeight);
});
if (containerStyle.height == '0px') {
containerStyle.height = `${totalHeight}px`;
buttonExpand.innerText = '▲点我收起';
} else {
containerStyle.height = '0px';
buttonExpand.innerText = '▼点我展开 ';
}
}
#p11-3 {
overflow:hidden;
transition: height 1s;
margin: 0px;
}
#p11-3 li {
font-size: 16px;
color: #ffffff;
line-height: 30px;
text-align: center;
margin: 0px;
}
#p11-3-btn {
cursor: pointer;
background-color: #dcdcdc;
}
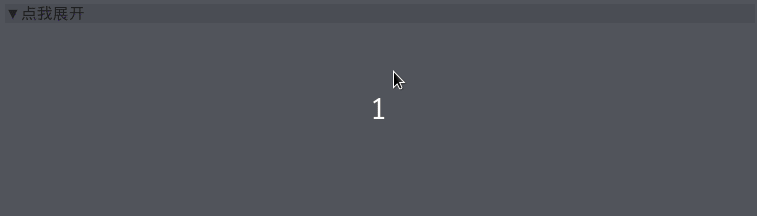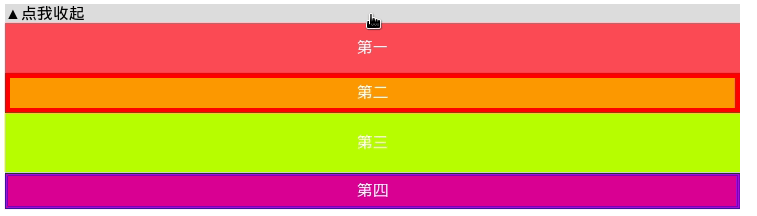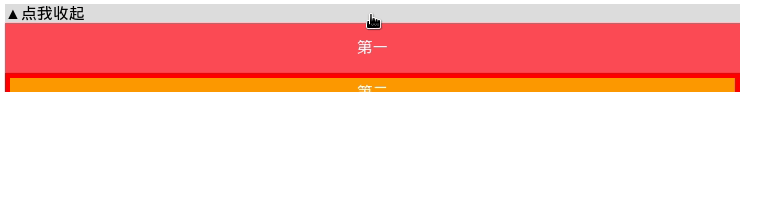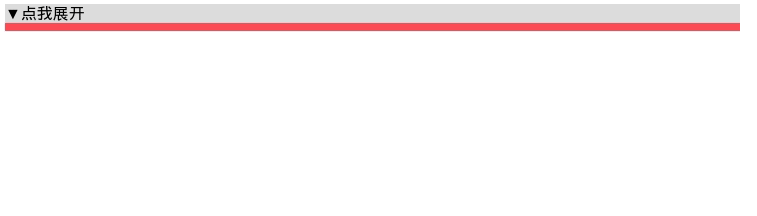
可以看到,无论内部元素占据的高度是什么,我们总能实现一个流畅的下拉列表过渡动画。
该篇博客内的代码已同步到Github
参考资料:
[1]. MDN文档 https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/HTMLElement/offsetHeight