目录
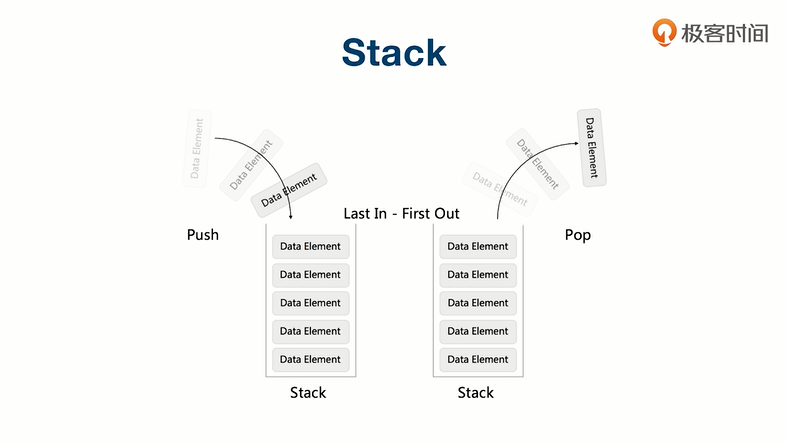
Stack
----有效的括号?
Queue
-----栈模拟队列
优先队列
数据流中第k大值
窗口滑动中的最大值
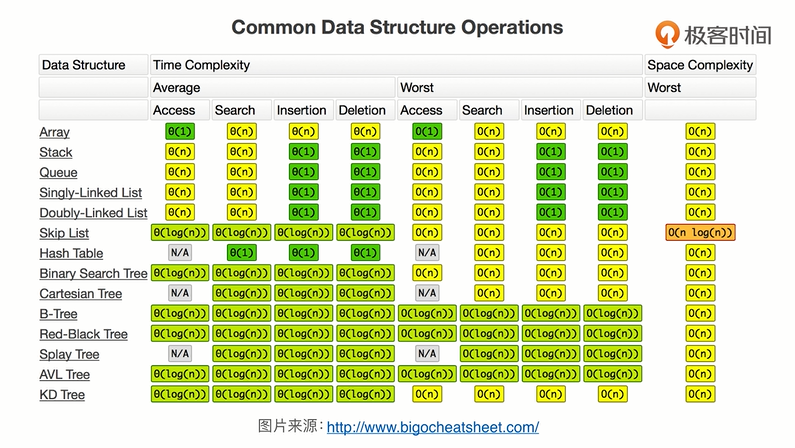
时间复杂度表
堆栈:先入后出
队列:先入先出

数据结构时间复杂度表。
http://www.bigocheatsheet.com/
题目:有效的括号
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-parentheses/submissions/
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
注意空字符串可被认为是有效字符串。
思路:
一、采用栈来存储其左括号,如果遇到右括号就出栈与之匹配。采用字典键值对存储右左括号。
如果遇到栈中有数据或者匹配不合理,那么就是无效。如果遍历完毕栈中为空则说明是有效
二、采用循环,将配对的括号消除掉,直到为空即可。
在LeetCode可以看大牛的分享代码。
代码:采用栈的思路
class Solution(object): def isValid(self, s): """ :type s: str :rtype: bool """ stack = [] #定义栈保存输入的左括号 paren_map = {')':'(','}':'{',']':'['} #字典保存左右括号对 for c in s: #遍历全部的括号 if c not in paren_map: #如果是左括号 print('------',c) stack.append(c) #将左括号存放在栈中 elif not stack or paren_map[c]!= stack.pop(): #如果右括号进入代码块 return False #栈空说明第一个字符就是右括号,此时栈为空则直接返回false #遇到右括号,从栈中进行返回左括号与右括号匹配 return not stack #在经历上步骤栈为空,则有效 if __name__ == '__main__': solution = Solution() s = '({[]})' result = solution.isValid(s) print(result)
栈模拟队列
题目:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/
思路:
入队:在第一个栈中进行模拟入队操作
出队:如果第二个队中没有元素则将第一个栈中的全部元素加入到第二个栈中,否则直接出队
判空:只有当两个栈同时为空,便判定队列为空
代码:
class MyQueue(object): def __init__(self): """ Initialize your data structure here. """ self.stack1 =[] #第一个栈进行队列的输入操作 self.stack2 = [] #第二个栈进行队列的出栈和查看操作 def push(self, x): """ Push element x to the back of queue. :type x: int :rtype: None """ self.stack1.append(x) #进行入队操作,将元素先在第一个栈中缓存 def pop(self): """ Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. :rtype: int """ if not self.stack2: #如果第二个栈是空的 while self.stack1: #循环遍历第一个栈 self.stack2.append(self.stack1.pop())#将第一个栈中的元素全部加入到第二个栈中 return self.stack2.pop() #出栈最后一个元素 def peek(self): """ Get the front element. :rtype: int """ if not self.stack2: #如果第二个栈是空的 while self.stack1: #将第一个占中的所有元素全部加载到第二个栈中 self.stack2.append(self.stack1.pop()) return self.stack2[-1] #返回最后一个元素的值 def empty(self): """ Returns whether the queue is empty. :rtype: bool """ if not self.stack1 and not self.stack2:#只有当两个栈同时(and)空时候,队列为空 return True else: return False #否则队列中还有值 # Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = MyQueue() # obj.push(x) # param_2 = obj.pop() # param_3 = obj.peek() # param_4 = obj.empty()
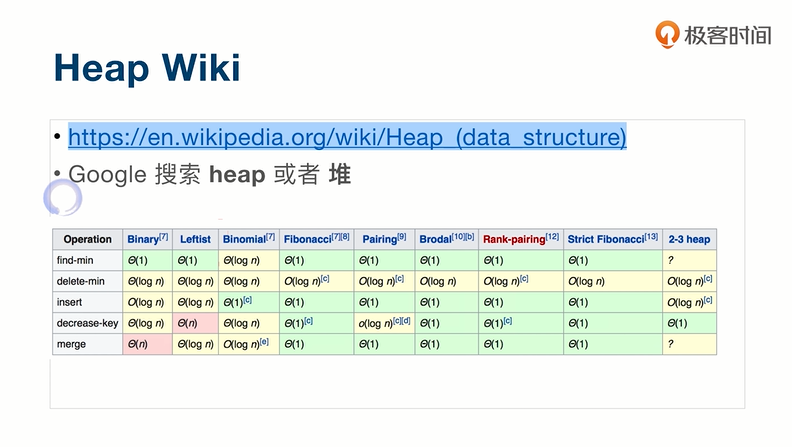
优先队列
优先队列的实现采用堆或者二叉搜索树。

Min Heap:父亲节点比子节点小。根节点永远最小。
时间复杂度
数据流中第K大元素
题目:
设计一个找到数据流中第K大元素的类(class)。注意是排序后的第K大元素,不是第K个不同的元素。
你的 KthLargest 类需要一个同时接收整数 k 和整数数组nums 的构造器,它包含数据流中的初始元素。每次调用 KthLargest.add,返回当前数据流中第K大的元素。
思路:
一、用k个存储器缓存前k个值,从k+1往后进行遍历,每次从前k个里面取出最小的和当前值比较。
如果当前值大于最小那么将其替换,否则程序继续。
问题就在如何从前k个值中取出最小的元素?
1、采用排序,较好的是快排,是N*klogk时间复杂度。python中有min和max函数,去min进行比较,最终返回max值便是第k大值。
2、优先队列思想,采用最小堆实现Min Heap,每次去维护最小堆即可。
代码:
class KthLargest(object): def __init__(self, k, nums): """ :type k: int :type nums: List[int] """ self.k = k self.heap = nums #构建堆 self.size = len(nums) heapq.heapify(self.heap) #heapq.heapify()方法原地转换为堆并进行排序 while self.size > k: #只有传入列表的个数大于要寻找的第k个数 heapq.heappop(self.heap) # self.size -= 1 def add(self, val): """ :type val: int :rtype: int """ if self.size < self.k: heaqp.heappush(self.heap,val) #构建堆元素 self.size += 1 elif val > self.heap[0]: #当堆顶元素小于当前值 heapq.heapreplace(self.heap,val) #将其替换 return self.heap[0] #返回堆顶元素 # Your KthLargest object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = KthLargest(k, nums) # param_1 = obj.add(val)
滑动窗口最大值
题目:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sliding-window-maximum/
给定一个数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口 k 内的数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。
返回滑动窗口最大值。
示例:
输入: nums =[1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], 和 k = 3 输出:[3,3,5,5,6,7] 解释:滑动窗口的位置 最大值 --------------- ----- [1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3 1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3 1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5 1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5 1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6 1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
思路:
一、采用最大堆,窗口中的值是最大堆,每次滑动便维护该最大堆
二、采用双向队列,每次滑动左边值为当前窗口的最大值;
如果滑动中当前的值大于队列中的值,便右出队列;
如果窗口滑动了,便将左边值出队;
都达标后将当前值加入到队列中
每次窗口滑动将左边值加入到最终结果中。
代码:
class Solution(object): def maxSlidingWindow(self, nums, k): """ :type nums: List[int] :type k: int :rtype: List[int] """ if not nums: return [] #边界判断 window, res = [], [] #window存放下标,res存放元素 for i, x in enumerate(nums): #枚举遍历 if i>=k and window[0]<=i-k: #往后遍历,超出队列的边界,则移出左边的数据(左出队) window.pop(0) while window and nums[window[-1]]<=x: #如果队列中的值小于当前的值,便出队,前提是队列中有元素 window.pop() window.append(i) #将前面的元素已经清理完毕,便将当前的值加入其中 if i>=k-1: #从第一个窗口开始起就将其加入 res.append(nums[window[0]]) #最终将下标转换为值 return res