#、##、#@在#define中的用法
有如下C++代码:
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 #define A(exp) cout << "I am "#exp << endl; 5 #define B(exp) cout << sz##exp << endl; 6 #define C(exp) cout << #@exp << endl; 7 8 int main() 9 { 10 char *szStr = "test"; 11 A(Chinese); // cout << "I am ""Chinese" << endl; 12 B(Str); // cout << szStr << endl; 13 C(a); // cout << 'a' << endl; 14 C(ab); // cout << 'ab' << endl; 15 16 return 0; 17 }
运行结果如下:
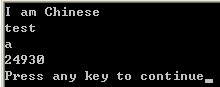
展开的时候,#exp被扩展成字符串,##exp被扩展成子串,#@exp被扩展成字符。
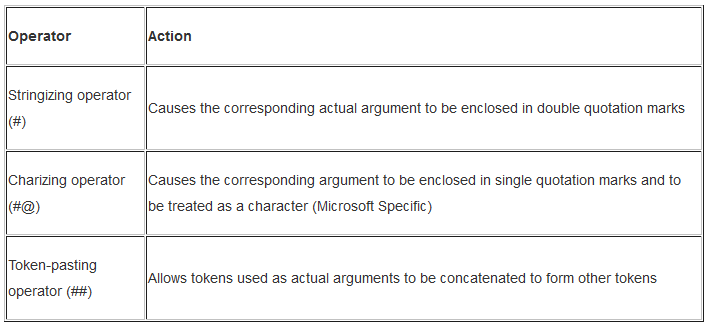
注意:#@只实用于windows系统,MSDN如下说明
可用作自定义ASSERT:
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 #ifdef ASSERT 5 #undef ASSERT 6 #endif 7 #define ASSERT(exp) 8 if (!(##exp)) 9 { 10 cout << "an error occured while execute ""#exp"" at " 11 << __FILE__ << "(" << __LINE__ << ")" << endl; 12 exit(-1); 13 } 14 15 int main() 16 { 17 int a = 0; 18 int b = 1; 19 20 ASSERT(a == b); 21 22 cout << "test" << endl; 23 24 return 0; 25 }
结果如下:

此段代码只能在VS下编译,GCC下不能编译通过。
参考
http://blog.csdn.net/beanjoy/article/details/7577944
http://www.cnblogs.com/wb-DarkHorse/p/3588787.html