20172318 2017-2018-2 《程序设计与数据结构》第9周学习总结
教材学习内容总结
- 错误和异常都是对象,代表非正常情况或无效处理
- 处理异常三种方法:1.根本不处理异常 2.当异常发生时处理异常 3.在程序的某个位置集中处理异常
- 未捕获的异常:如果程序不处理异常,则将非正常地终止执行,并产生关于描述在何处发生什么异常的信息
- 异常抛出时所输出的信息,提供了方法调用堆栈踪迹
- try-catch语句:没有异常,执行完try语句后,将继续执行finally子句,有异常,则控制立刻转移到相应的catch子句处理异常
- 每一个catch子句处理一种try语句块发生的异常
- finally子句(可选):无论try语句块正常退出或由于抛出异常而退出,都将执行finally子句
- 异常的传递:如果想一个异常的发生处没有捕获和处理该异常,则该异常将传递给上级调用方法
- 自定义异常:可由Exception类或它的后代类派生一个新类来定义一个新的异常
- 可检测异常:必须由方法捕获,或者必须在可能抛出或传递异常方法的throws子句中列出来
- 不可检测异常:Java中唯一的不可检测异常是RuntimeExceptions类的对象或该类的后代类对象
- 递归:递归是一种方法能够调用自己的编程技术
- 无穷递归:任何一个递归定义中必须有称为基本情况的非递归定义部分,才能使递归最终结束
- 每一次对方法的递归调用,都会创建新的局部变量和参数
- 直接递归与间接递归:方法调用自己的递归为直接递归,一个方法调用其它方法,导致再次调用自己称为间接递归
- 递归的应用:1.迷宫旅行 2.汉诺塔问题
教材学习中的问题和解决过程
- 问题1:异常是对象?不是错误代码?
- 问题1解决方案:看完整章后发现,异常不仅是个对象,而且你还能自定义异常,捕获异常,
- 问题2:对于迷宫搜索的代码有些不理解
- 问题2解决方案:后来仔细研究了下发现先是使用一个方法判断是否走过该路,再一直判断上下左右是否可走,如果可走就坐标移动一位,一次次地走到终点
代码调试中的问题和解决过程
-
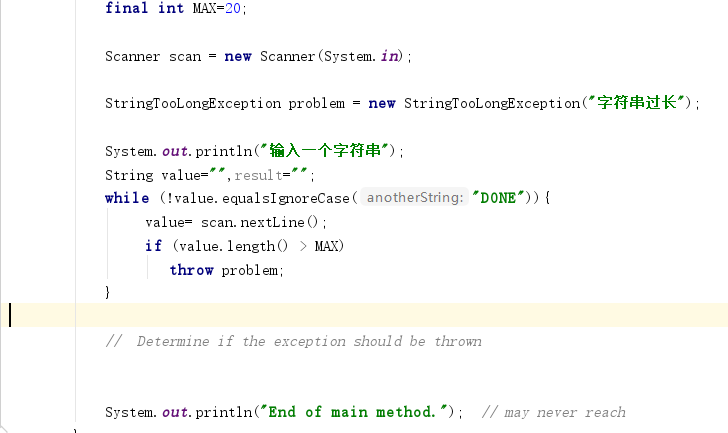
问题1:pp11.1不清楚异常要怎么编
-
问题1解决方案:使用了课本的例子,直接对其进行了修改
-
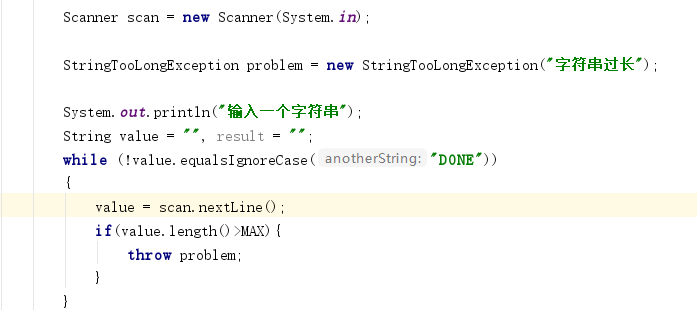
问题2:pp11.2使用catch语句时出现红色的报错
-
问题2解决方案:问了下其他同学发现必须先定义一个异常,并throw抛出,对这方面不太了解哈
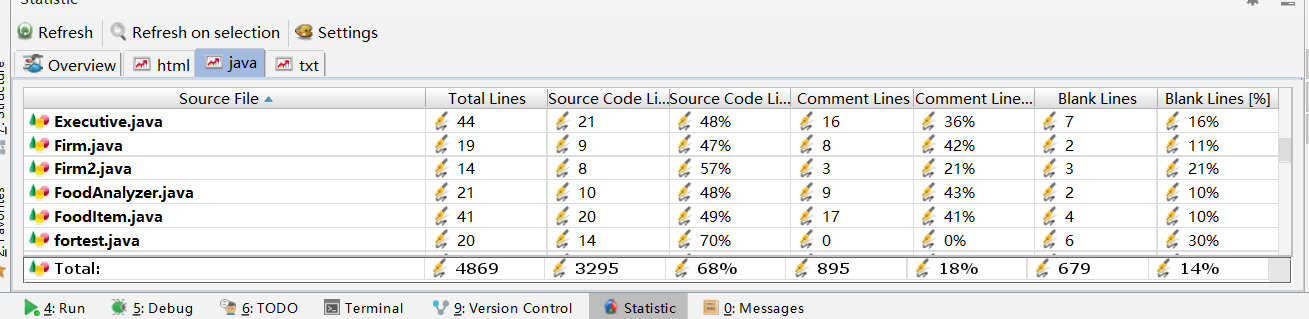
代码托管
上周考试错题总结
- 错题1及原因,理解情况
A Java program can handle an exception in several different ways. Which of the following is not a way that a Java program could handle an exception?
A . ignore the exception
B . handle the exception where it arose using try and catch statements
C . propagate the exception to another method where it can be handled
D . throw the exception to a pre-defined Exception class to be handled
E . all of the above are ways that a Java program could handle an exception
选D,异常不会抛出类 - 错题2及原因,理解情况
An exception can produce a "call stack trace" which lists
A . the active methods in the order that they were invoked
B . the active methods in the opposite order that they were invoked
C . the values of all instance data of the object where the exception was raised
D . the values of all instance data of the object where the exception was raised and all local variables and parameters of the method where the exception was raised
E . the name of the exception thrown
选B,方法名称从堆栈中删除以相反的顺序放置,最近调用的方法是在堆栈上最后一项,堆栈跟踪是以相反的顺序显示所有活动的方法 - 错题3及原因,理解情况
A finally clause will execute
A . only if the try statement that precedes it does not throw an exception
B . only if the try statement that precedes it throws an exception that is caught
C . only if the try statement that precedes it throws an exception that is not caught
D . only if the try statement that precedes it throws an exception, whether it is caught or not
E . in any circumstance
选E,无论try语句块正常退出或由于抛出异常而退出,都将执行finally子句 - 错题4及原因,理解情况
The idea that an object can exist separate from the executing program that creates it is called
A . transience
B . static
C . persistence
D . serialization
E . finality
选C,persistence的功能是将对象的实例数据保存到文件中。 - 错题5及原因,理解情况
In order to have some code throw an exception, you would use which of the following reserved words?
A . throw
B . throws
C . try
D . Throwable
E . goto
选A,throw用于在检测异常时抛出异常
点评模板:
- 博客中值得学习的或问题:
- 对教材内容解析的非常到位
-
代码中值得学习的或问题:
点评过的同学博客和代码
其他(感悟、思考等,可选)
课本简单实验难
学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 128/128 | 1/1 | 12/12 | |
| 第二周 | 212/340 | 1/2 | 18/30 | |
| 第三周 | 206/546 | 1/3 | 20/50 | |
| 第四周 | 483/1029 | 2/5 | 40/90 | |
| 第五周 | 633/1662 | 1/6 | 30/120 | |
| 第六周 | 560/2222 | 1/7 | 20/140 | |
| 第七周 | 511/2733 | 1/8 | 20/160 | |
| 第八周 | 817/3550 | 3/11 | 25/185 | |
| 第九周 | 1319/4869 | 2/11 | 20/205 |