一个正整数K,给出K Mod 一些质数的结果,求符合条件的最小的K。例如,K % 2 = 1, K % 3 = 2, K % 5 = 3。符合条件的最小的K = 23。
Input
第1行:1个数N表示后面输入的质数及模的数量。(2 <= N <= 10)
第2 - N + 1行,每行2个数P和M,中间用空格分隔,P是质数,M是K % P的结果。(2 <= P <= 100, 0 <= K < P)
Output
输出符合条件的最小的K。数据中所有K均小于10^9。
Input示例
3
2 1
3 2
5 3
Output示例
23
———————————————————————————
这道题是裸的剩余定理
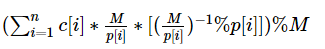

#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #define LL long long LL read(){ LL ans=0,f=1,c=getchar(); while(c<'0'||c>'9'){if(c=='-') f=-1; c=getchar();} while(c>='0'&&c<='9'){ans=ans*10+(c-'0'); c=getchar();} return ans*f; } int n; LL ans,c[15],p[15],mod; LL inv(LL a,LL b,LL c){ LL ans=1; while(b){ if(b&1) ans=ans*a%c; b>>=1; a=a*a%c; }return ans; } int main(){ n=read(); mod=1; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ p[i]=read(); c[i]=read(); mod*=p[i]; } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ LL ly=mod/p[i]*c[i]%mod; ans=(ans+(__int128)ly*inv(mod/p[i],p[i]-2,p[i]))%mod; }printf("%lld ",ans); return 0; }
