一、OAuth2.0是OAuth协议的延续版本,但不向后兼容OAuth 1.0即完全废止了OAuth1.0。 OAuth 2.0关注客户端开发者的简易性。要么通过组织在资源拥有者和HTTP服务商之间的被批准的交互动作代表用户,要么允许第三方应用代表用户获得访问的权限。同时为Web应用,桌面应用和手机,和起居室设备提供专门的认证流程。
二、使用场景:
1、自己开发应用时,需要获取其他应用的资源。比如:使用QQ登录,然后获取QQ头像等信息
2、SSO认证服务器,在自己开发应用时使用统一的认证过程,不需要单独重写重写认证体系
三、概念
(1) Third-party application:第三方应用程序,本文中又称"客户端"(client)。
(2)HTTP service:HTTP服务提供商,本文中简称"服务提供商"。
(3)Resource Owner:资源所有者,本文中又称"用户"(user)。
(4)User Agent:用户代理,本文中就是指浏览器。
(5)Authorization server:认证服务器,即服务提供商专门用来处理认证的服务器。
(6)Resource server:资源服务器,即服务提供商存放用户生成的资源的服务器。它与认证服务器,可以是同一台服务器,也可以是不同的服务器。
OAuth在"客户端"与"服务提供商"之间,设置了一个授权层(authorization layer)。"客户端"不能直接登录"服务提供商",只能登录授权层,以此将用户与客户端区分开来。"客户端"登录授权层所用的令牌(token),与用户的密码不同。用户可以在登录的时候,指定授权层令牌的权限范围和有效期。
"客户端"登录授权层以后,"服务提供商"根据令牌的权限范围和有效期,向"客户端"开放用户储存的资料。
四、模式运行流程
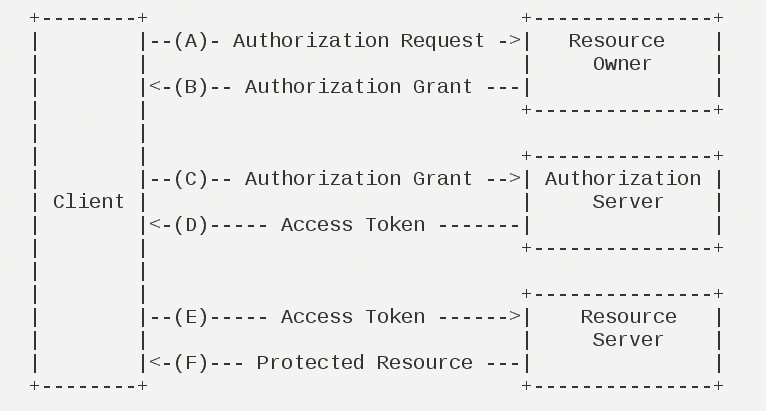
(A)用户打开客户端以后,客户端要求用户给予授权。
(B)用户同意给予客户端授权。
(C)客户端使用上一步获得的授权,向认证服务器申请令牌。
(D)认证服务器对客户端进行认证以后,确认无误,同意发放令牌。
(E)客户端使用令牌,向资源服务器申请获取资源。
(F)资源服务器确认令牌无误,同意向客户端开放资源。
五、授权模式
- 授权码模式(authorization code)
- 简化模式(implicit)
- 密码模式(resource owner password credentials)
- 客户端模式(client credentials)
1)授权码模式
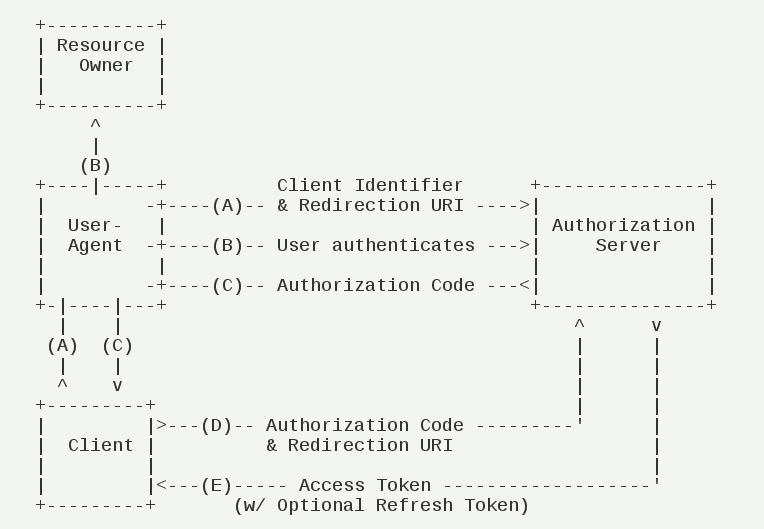
(A)用户访问客户端,后者将前者导向认证服务器。
(B)用户选择是否给予客户端授权。
(C)假设用户给予授权,认证服务器将用户导向客户端事先指定的"重定向URI"(redirection URI),同时附上一个授权码。
(D)客户端收到授权码,附上早先的"重定向URI",向认证服务器申请令牌。这一步是在客户端的后台的服务器上完成的,对用户不可见。
(E)认证服务器核对了授权码和重定向URI,确认无误后,向客户端发送访问令牌(access token)和更新令牌(refresh token)。
2)简化模式
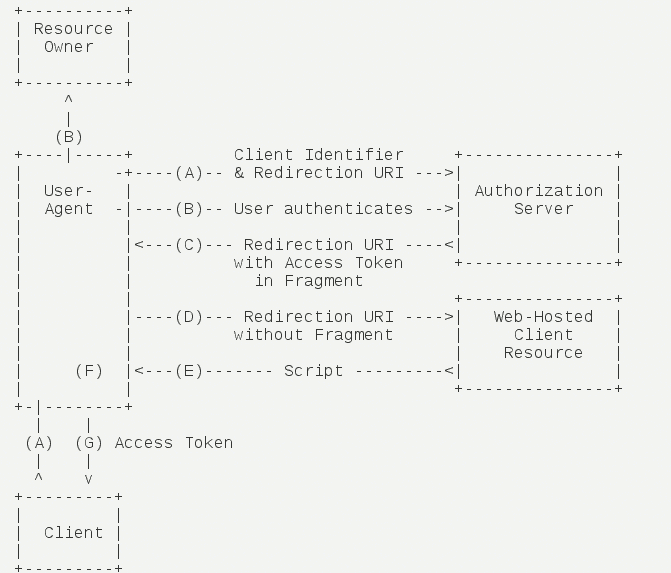
(A)客户端将用户导向认证服务器。
(B)用户决定是否给于客户端授权。
(C)假设用户给予授权,认证服务器将用户导向客户端指定的"重定向URI",并在URI的Hash部分包含了访问令牌。
(D)浏览器向资源服务器发出请求,其中不包括上一步收到的Hash值。
(E)资源服务器返回一个网页,其中包含的代码可以获取Hash值中的令牌。
(F)浏览器执行上一步获得的脚本,提取出令牌。
(G)浏览器将令牌发给客户端。
3)密码模式
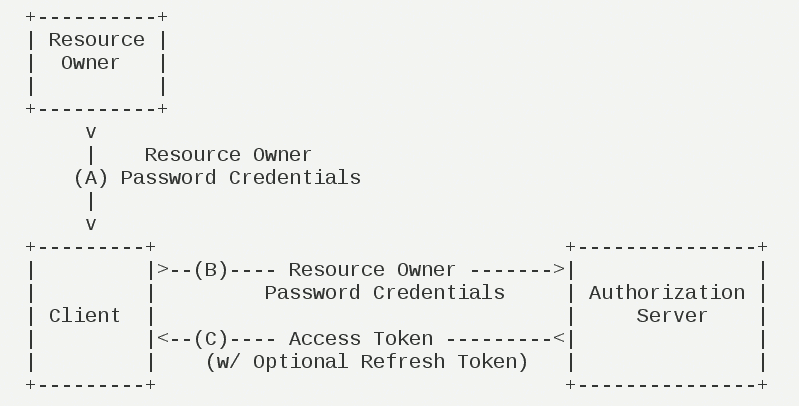
(A)用户向客户端提供用户名和密码。
(B)客户端将用户名和密码发给认证服务器,向后者请求令牌。
(C)认证服务器确认无误后,向客户端提供访问令牌。
4)客户端模式

(A)客户端向认证服务器进行身份认证,并要求一个访问令牌。
(B)认证服务器确认无误后,向客户端提供访问令牌。
六、授权码模式例子
这里说明一下这里主要只通过授权码模式来讲解oauth2的使用过程。
授权码模式(authorization code)是功能最完整、流程最严密的授权模式。它的特点就是通过客户端的后台服务器,与"服务提供商"的认证服务器进行互动。
简化模式(implicit grant type)不通过第三方应用程序的服务器,直接在浏览器中向认证服务器申请令牌,跳过了"授权码"这个步骤,因此得名。所有步骤在浏览器中完成,令牌对访问者是可见的,且客户端不需要认证。
密码模式(Resource Owner Password Credentials Grant)中,用户向客户端提供自己的用户名和密码。客户端使用这些信息,向"服务商提供商"索要授权。
客户端模式(Client Credentials Grant)指客户端以自己的名义,而不是以用户的名义,向"服务提供商"进行认证。严格地说,客户端模式并不属于OAuth框架所要解决的问题。在这种模式中,用户直接向客户端注册,客户端以自己的名义要求"服务提供商"提供服务,其实不存在授权问题。
相对来说授权码的方式使用上面,是非常严谨的。不存在,其他模式的相对弊病。
7、代码部分
1)需要的依赖
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.security.oauth.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-security-oauth2-autoconfigure</artifactId> <version>2.1.2.RELEASE</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
2)认证服务器
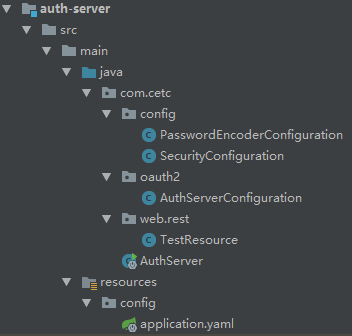
主要配置:SecurityConfiguration、AuthServerConfiguration
@Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Autowired private BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder; @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http .csrf().disable() .exceptionHandling() .and() .authorizeRequests() .anyRequest().authenticated() .and() .formLogin(); } @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder builder) throws Exception { //内存用户不多解释 builder.inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser("admin") .password(passwordEncoder.encode("admin")) .roles("ADMIN"); } @Override @Bean public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception { return super.authenticationManagerBean(); }
@Bean
@Override
protected UserDetailsService userDetailsService() {
return super.userDetailsService();
}
}
@Configuration @EnableAuthorizationServer public class AuthServerConfiguration extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter { @Autowired private BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder; @Autowired private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager; @Override public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception { //这里client使用存在模式,可以实际过程调整为jdbc的方式 //这里说明一下,redirectUris的连接可以是多个,这里通过access_token都可以访问的 //简单点,就是授权的过程 clients.inMemory() .withClient("client") .secret(passwordEncoder.encode("secret")) .authorizedGrantTypes("authorization_code", "refresh_token") .scopes("All") .autoApprove(true) .redirectUris("http://localhost:9001/login", "http://localhost:9002/login", "http://localhost:9003/authorize/login"); } @Override public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security) throws Exception { //权限控制 security.tokenKeyAccess("permitAll()") .checkTokenAccess("isAuthenticated()") .allowFormAuthenticationForClients(); } @Override public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) throws Exception { //认证体系使用security的方式 endpoints.authenticationManager(authenticationManager);//允许调用方式
endpoints.allowedTokenEndpointRequestMethods(HttpMethod.GET, HttpMethod.POST);
endpoints.userDetailsService(userDetailsService);
}
说明:这里我为了更好的区分,把认证服务器和资源服务器分开的,实际上可以使用认证服务器作为资源服务器
yaml配置
server:
port: 9000
servlet:
context-path: /auth #这里一定要加上contextPath,这个坑自己体会吧
3)资源服务器
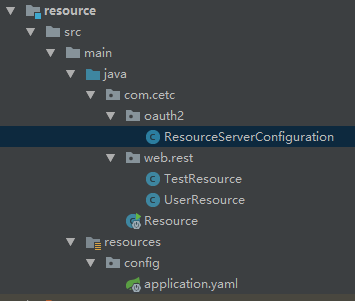
主要配置:ResourceServerConfiguration、application.yaml
/** * 资源服务器的配置也很简单 * 主要是EnableResourceServer,以及资源的控制 */ @Configuration @EnableResourceServer public class ResourceServerConfiguration extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter { @Override public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http .csrf().disable() .exceptionHandling() .and() .authorizeRequests() .anyRequest().authenticated(); } }
server: port: 9002 security: oauth2: client: client-id: client client-secret: secret access-token-uri: http://localhost:9000/auth/oauth/token user-authorization-uri: http://localhost:9000/auth/oauth/authorize resource: token-info-uri: http://localhost:9000/auth/oauth/check_token
说明:资源服务器主要用于资源拦截,需要获取授权码才能访问
4)sso客户端

主要配置:SecurityConfiguration、application.yaml
/** * 这里使用的是sso的方式,可以用于单点登录 * 构造方式也很简单,主要是sso的配置 */ @Configuration @EnableOAuth2Sso public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http .csrf().disable() .authorizeRequests() .anyRequest().authenticated(); } }
server: port: 9001 security: oauth2: client: client-id: client client-secret: secret access-token-uri: http://localhost:9000/auth/oauth/token user-authorization-uri: http://localhost:9000/auth/oauth/authorize resource: token-info-uri: http://localhost:9000/auth/oauth/check_token #user-info-uri: http://localhost:9002/user/me #这里两种获取用户的方式,都可以。但是只能存在一种
5)客户端:当然浏览器可以为一种客户端,自己开发的应用也可以为客户端
浏览器:
a、获取授权码
oauth/authorize?response_type=code&client_id=&redirect_uri=
本文中:
http://localhost:9000/auth/oauth/authorize?response_type=code&client_id=client&redirect_uri=http://localhost:9002/login
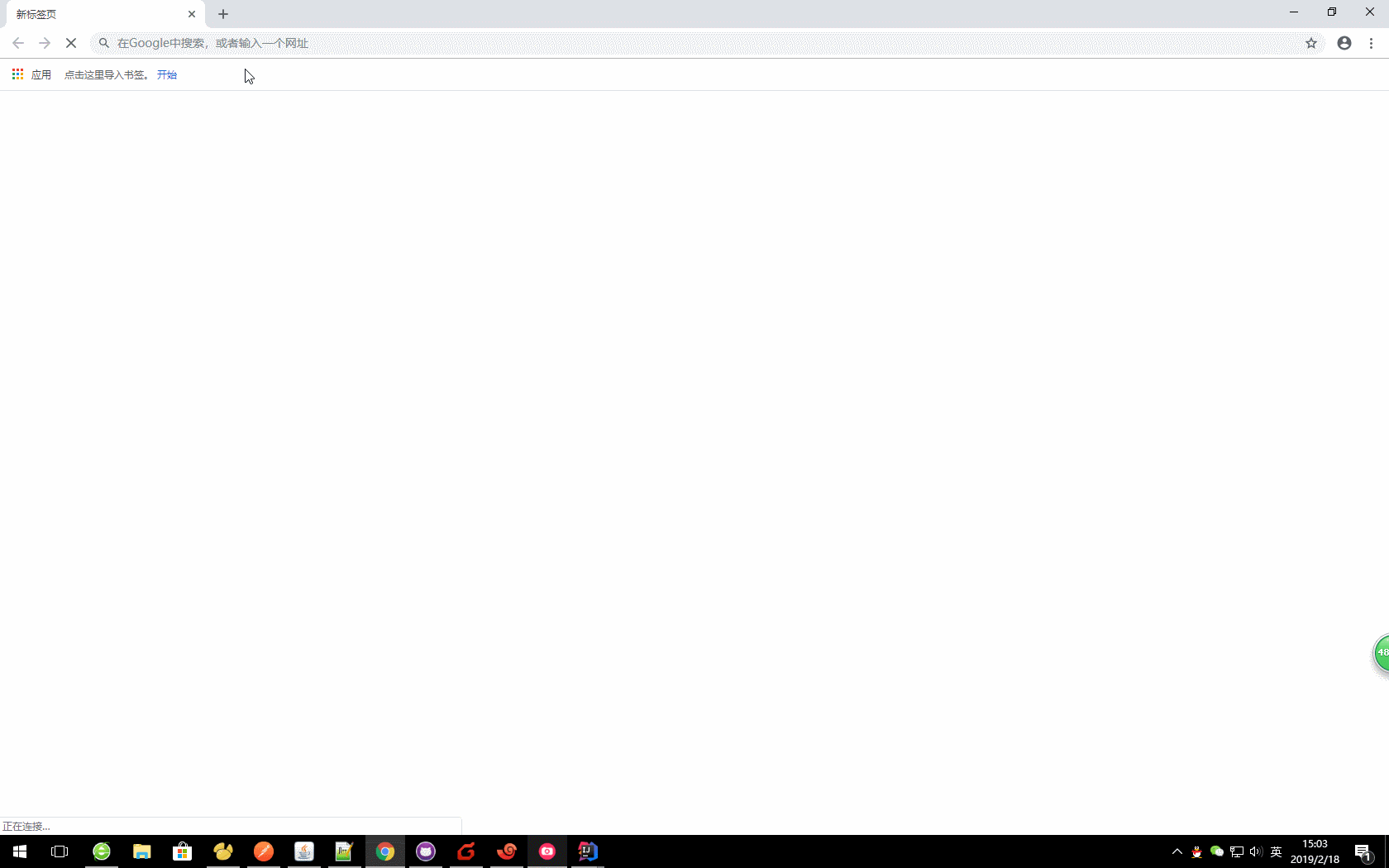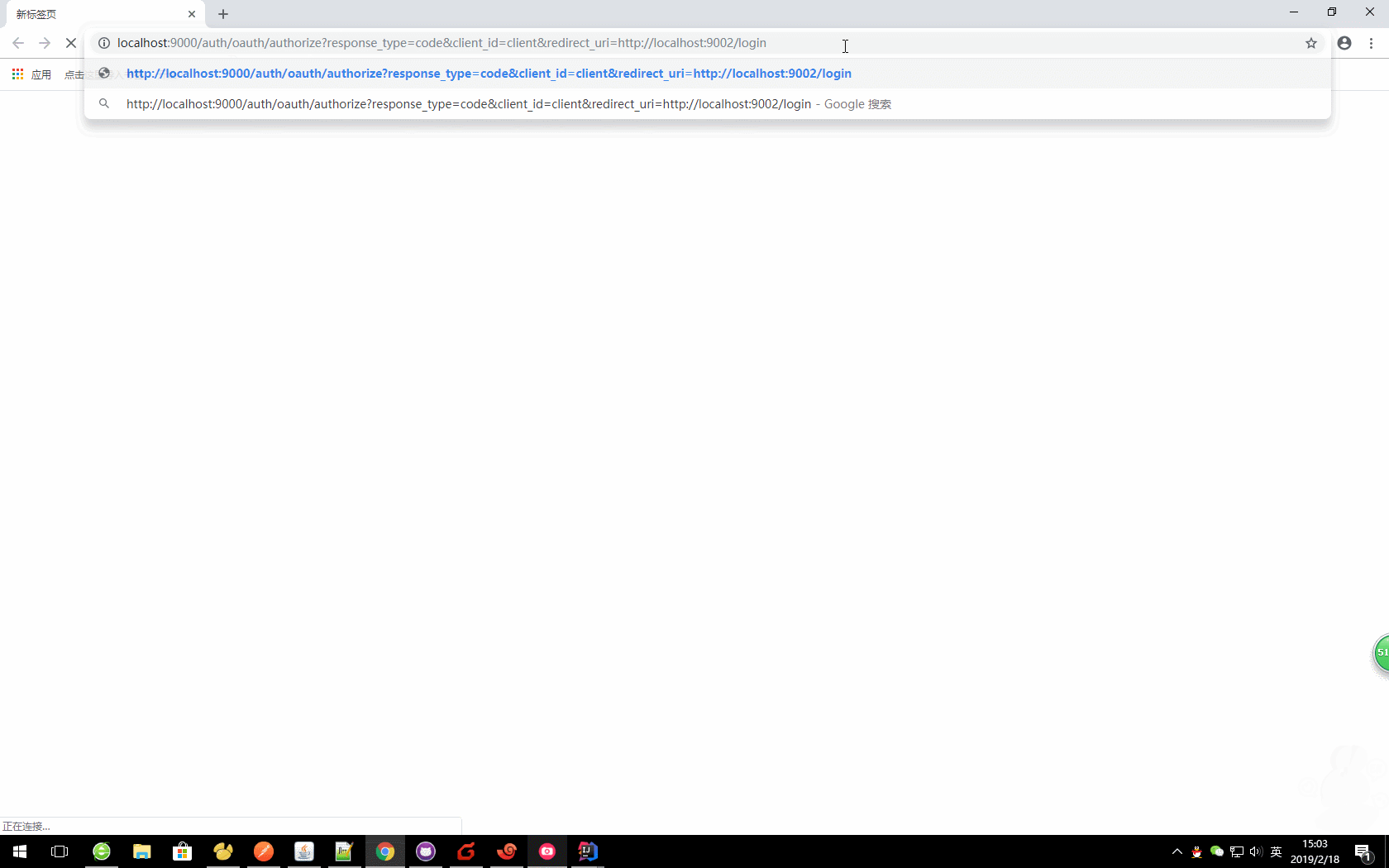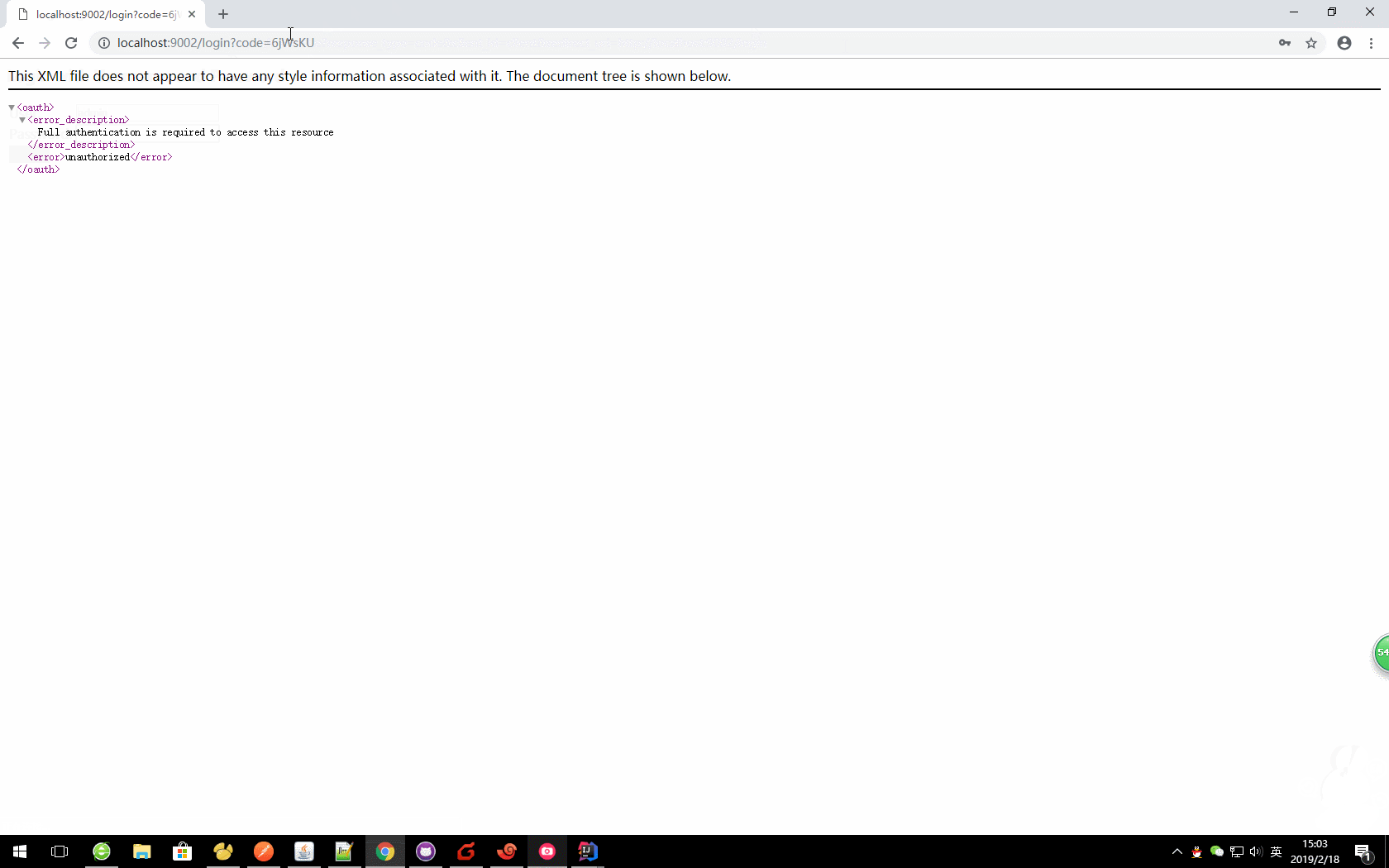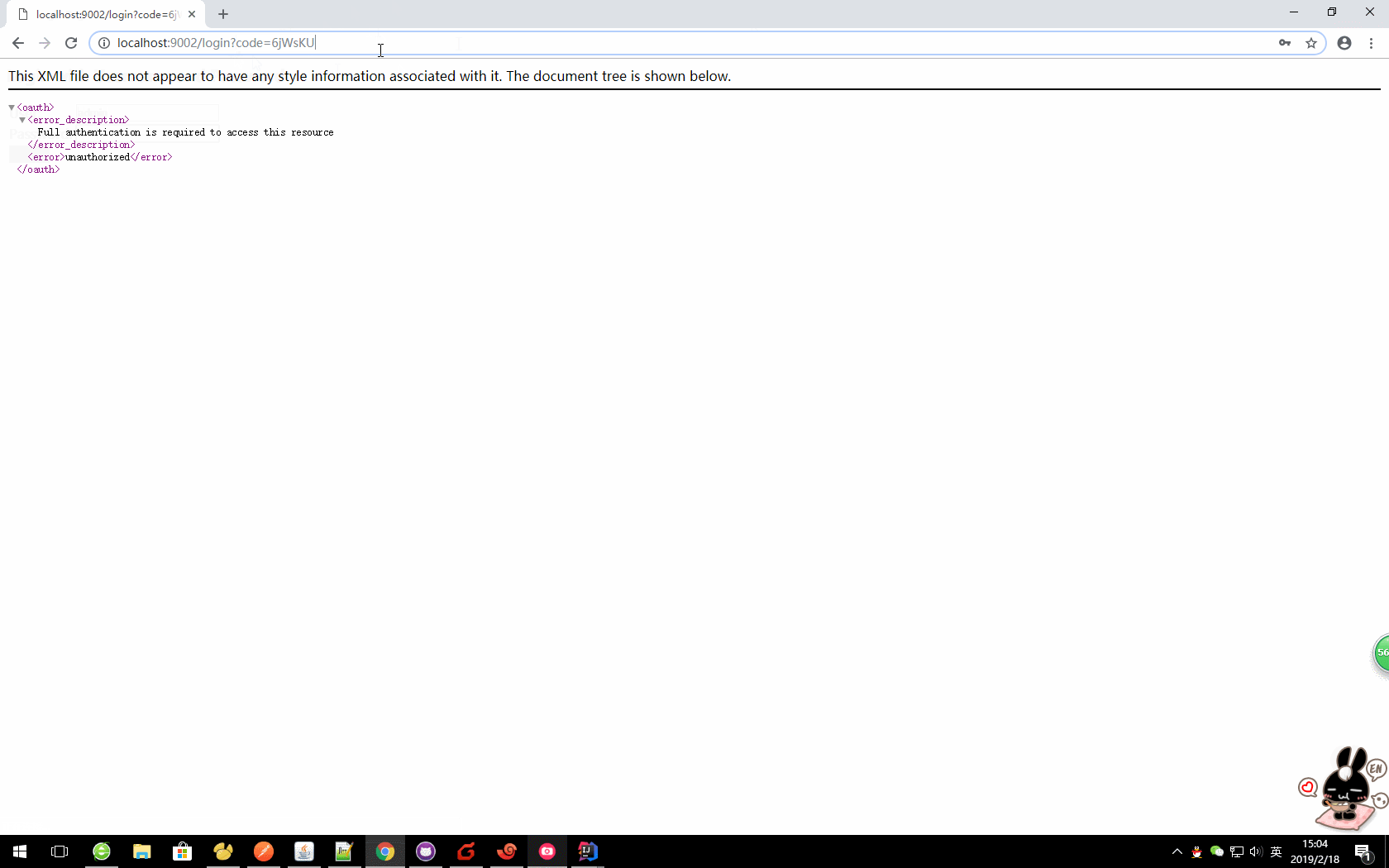
这里我们就获取到了code值
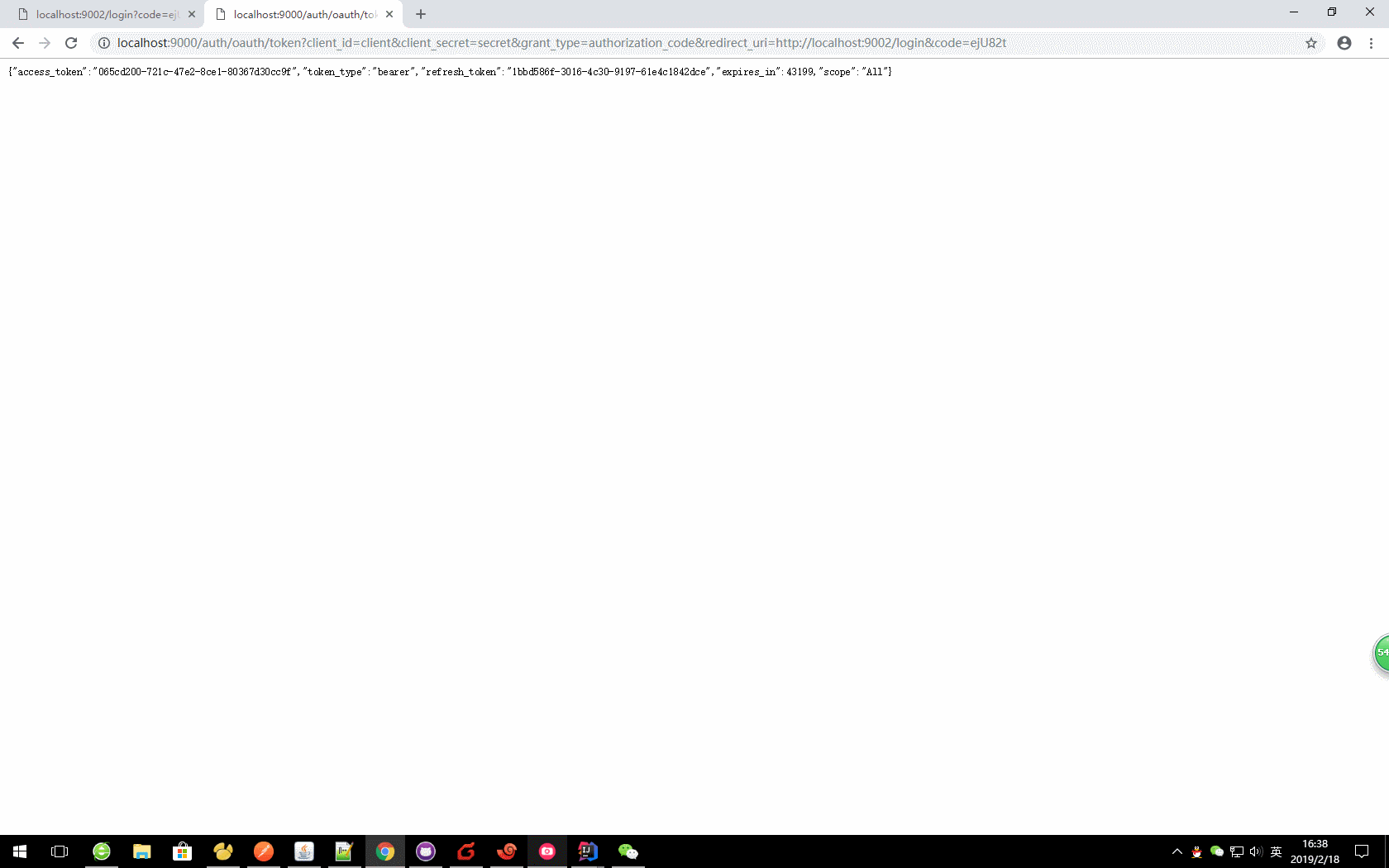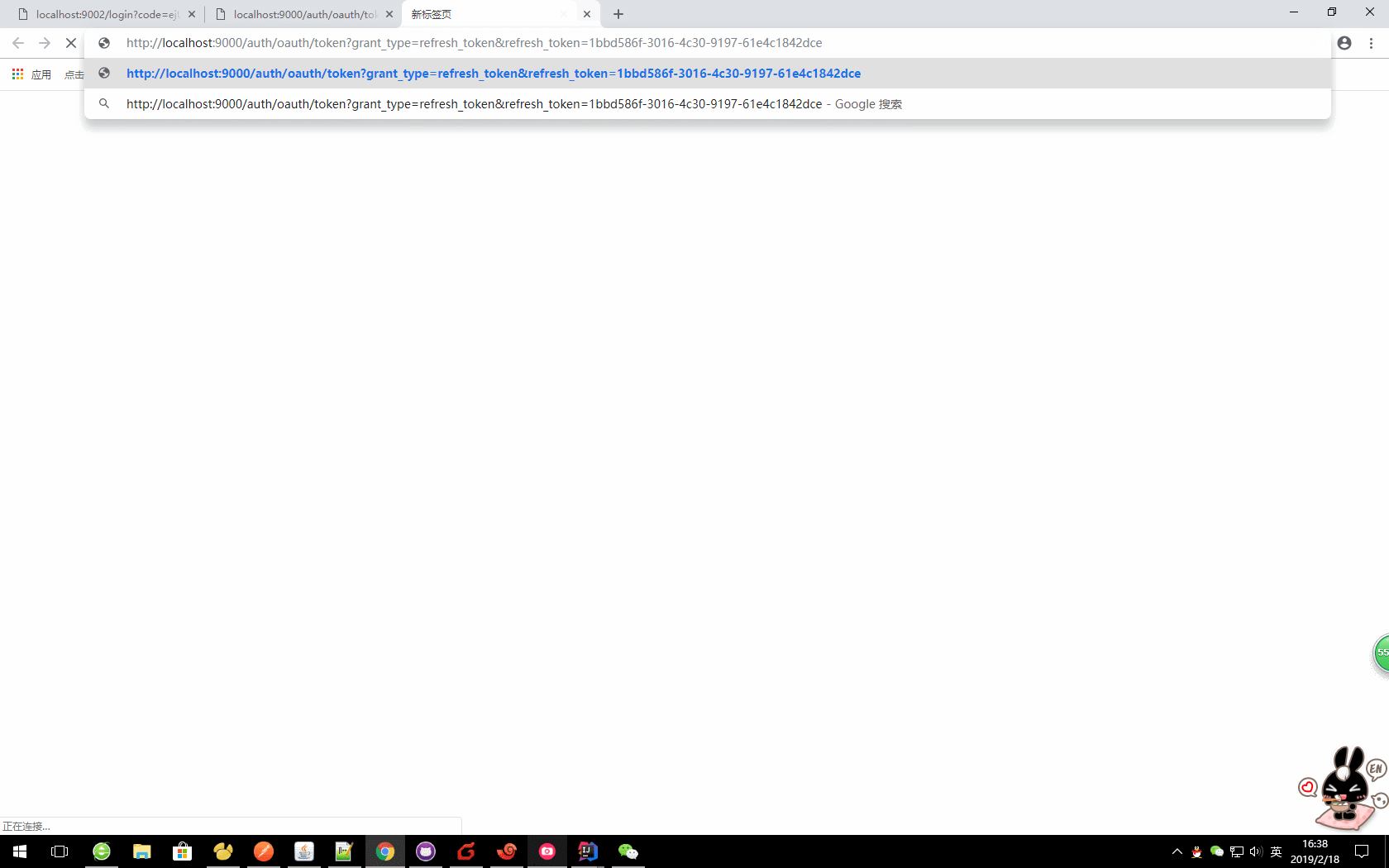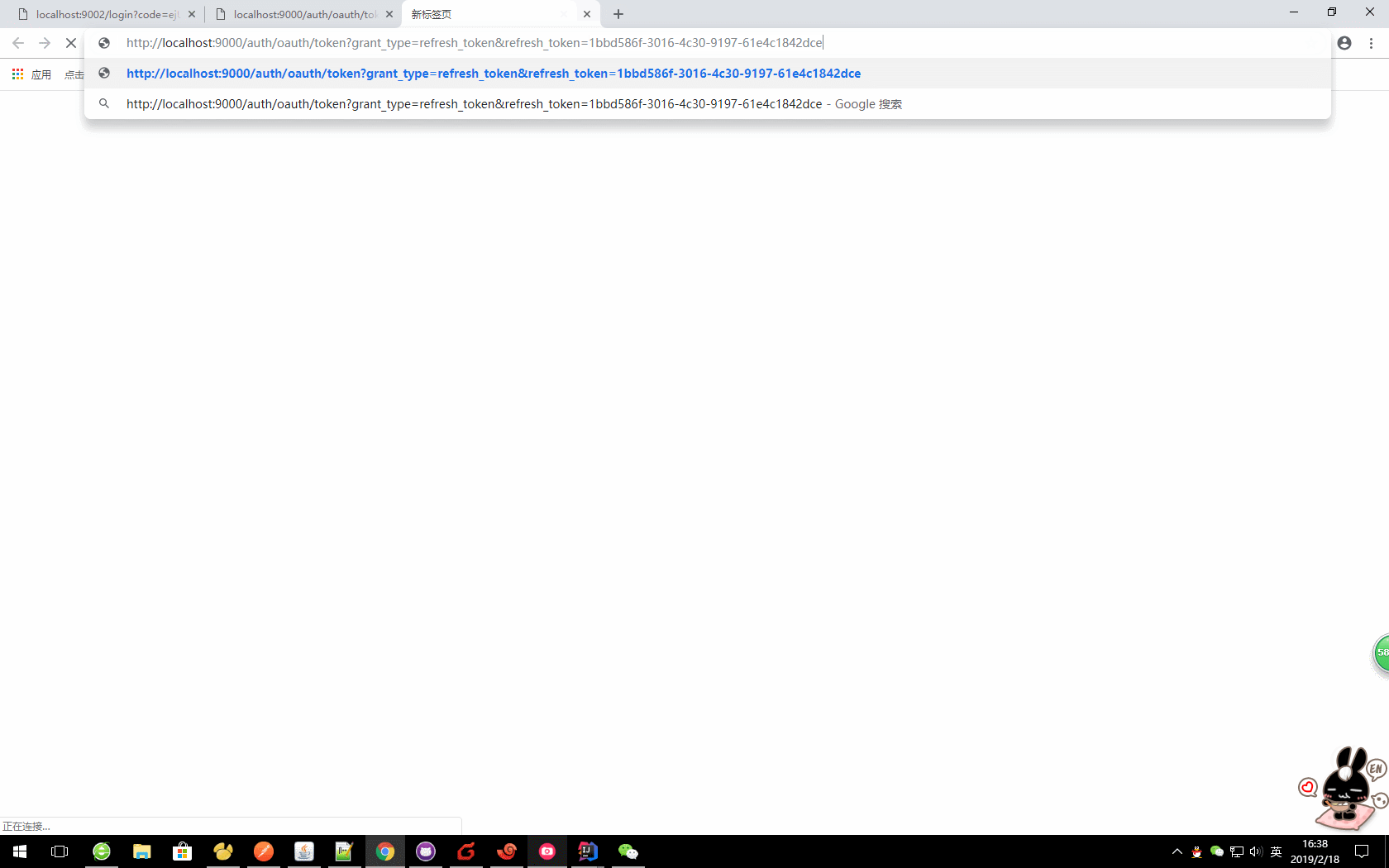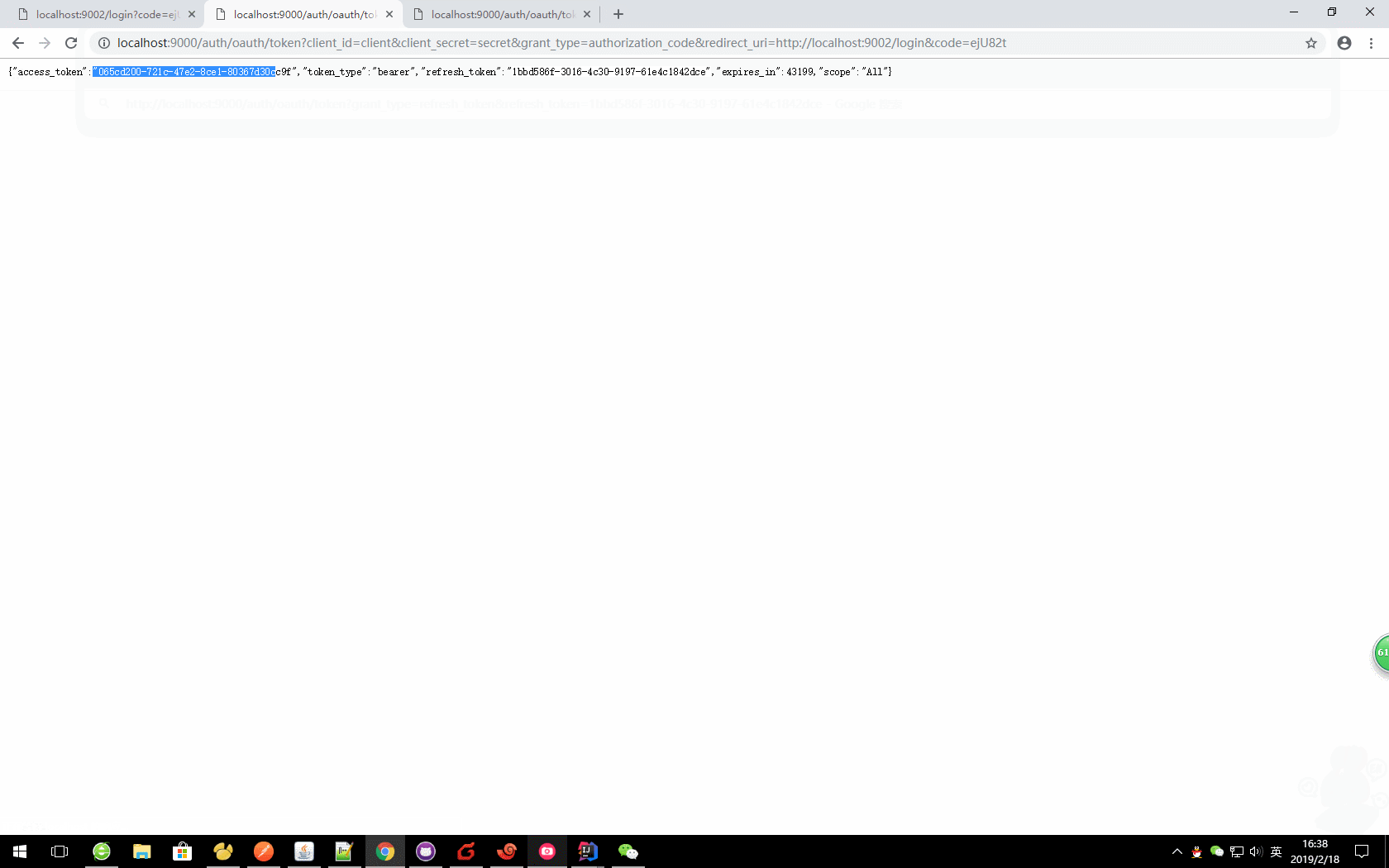
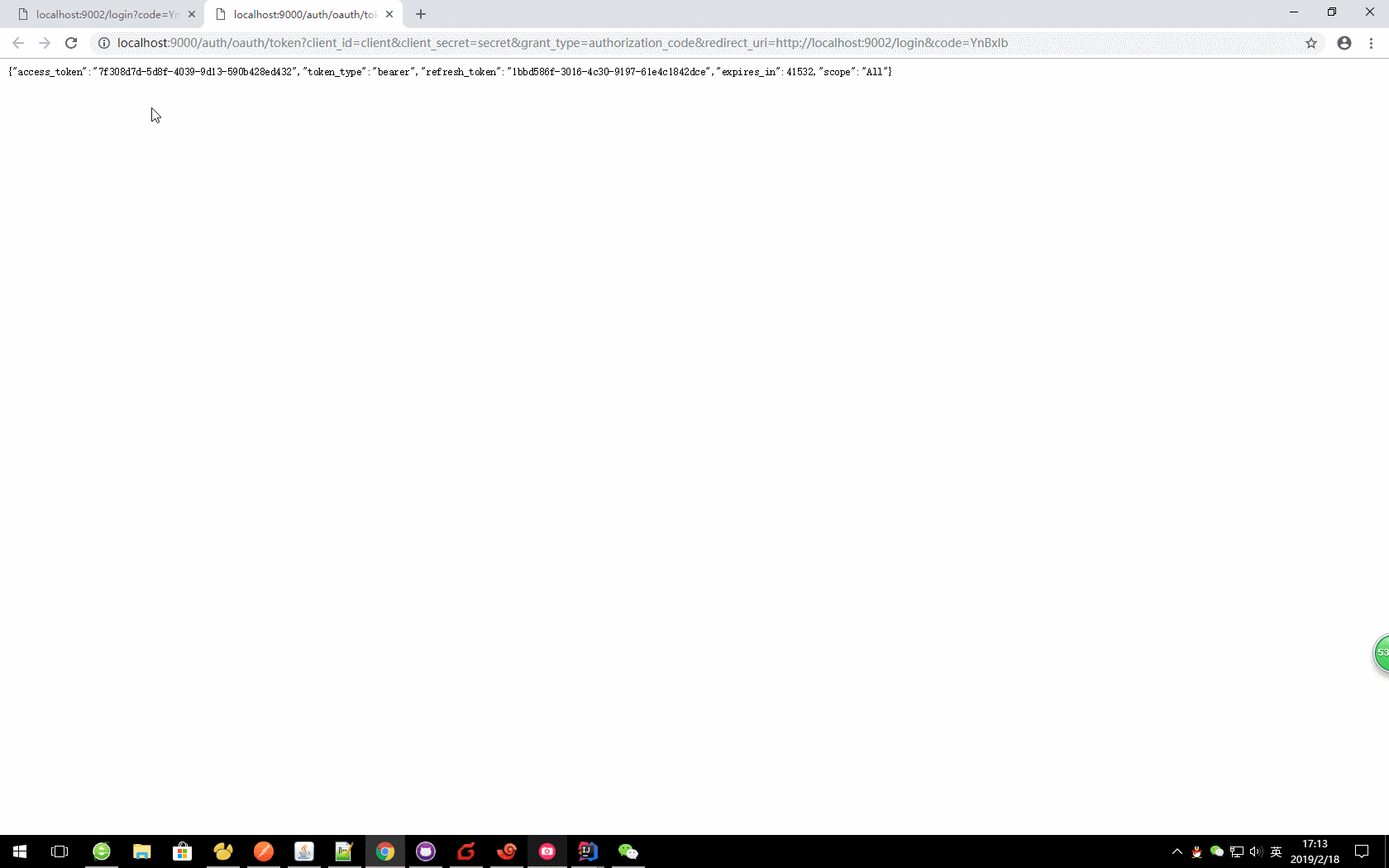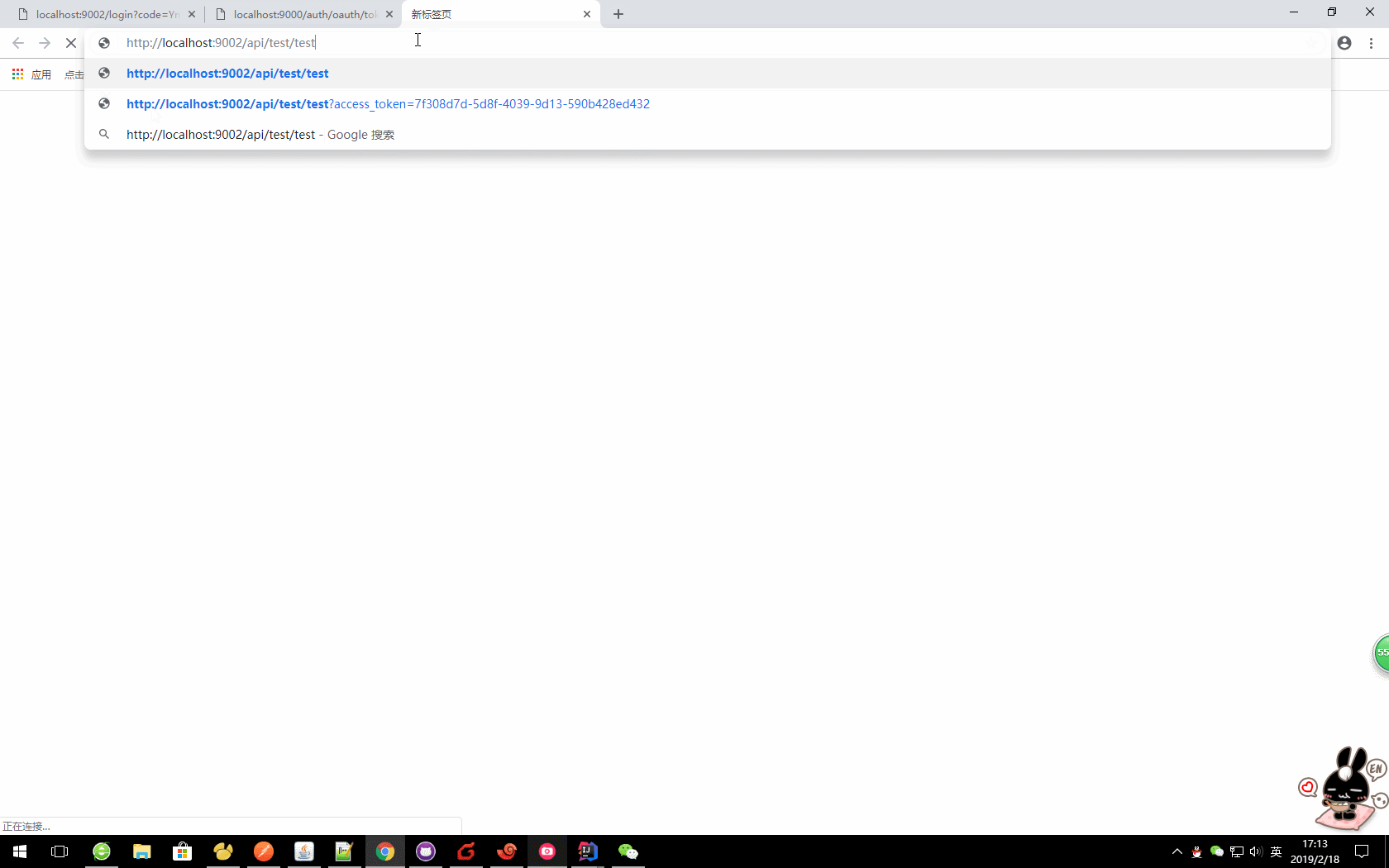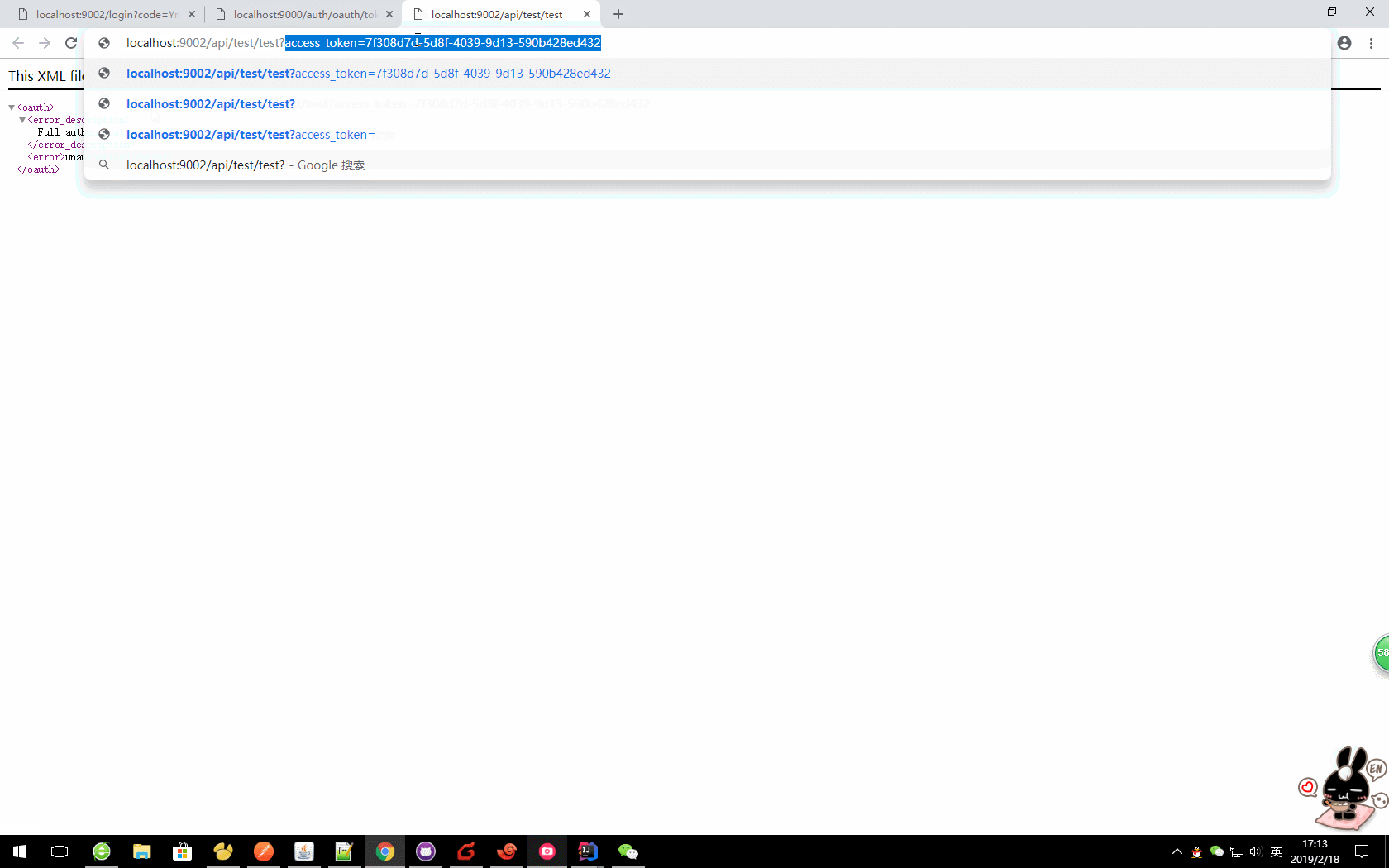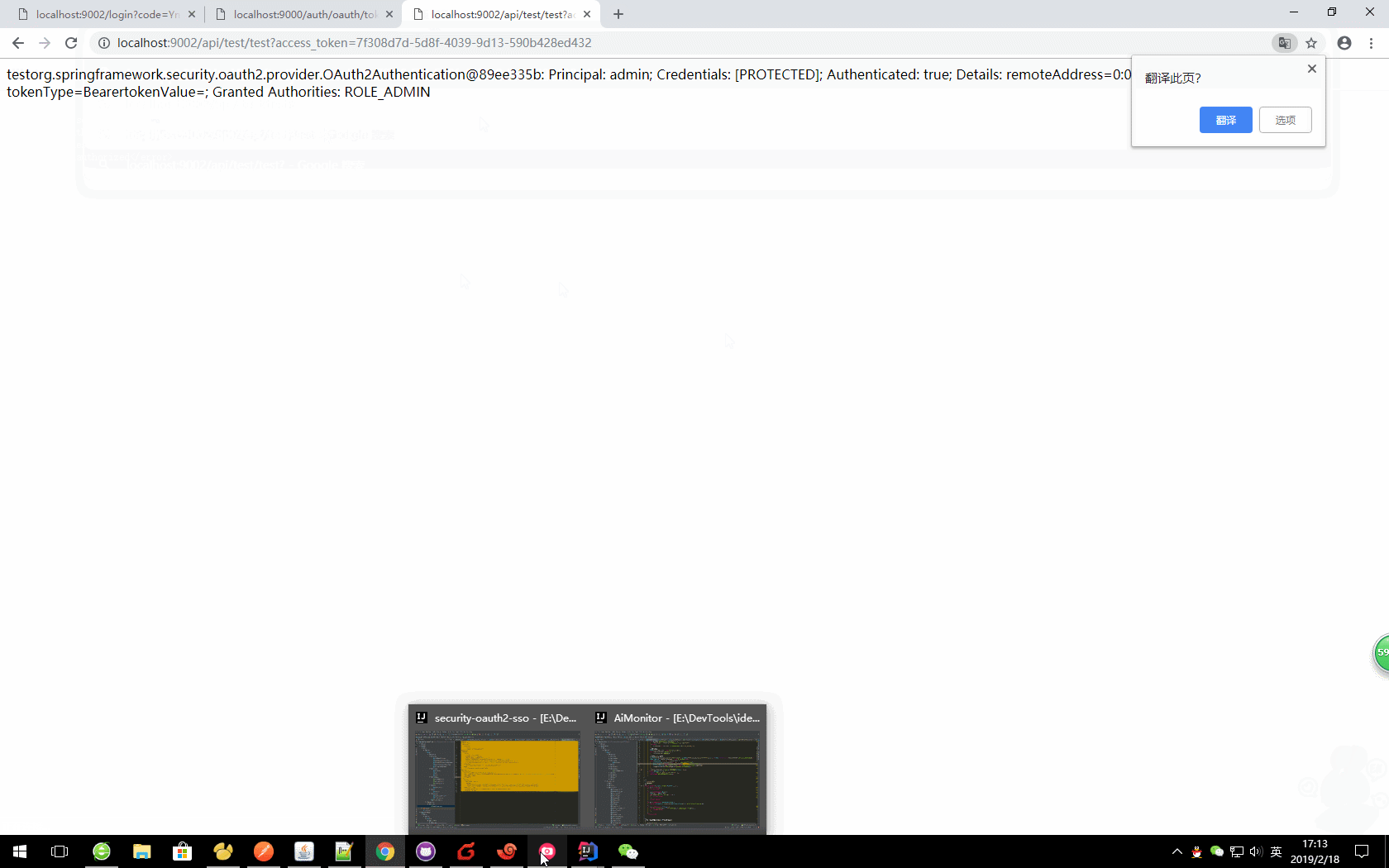
b、通过code获取令牌
oauth/token?client_id=&client_secret=&grant_type=authorization_code&redirect_uri=&code=
本文中:
http://localhost:9000/auth/oauth/token?client_id=client&client_secret=secret&grant_type=authorization_code&redirect_uri=http://localhost:9002/login&code=jrbBZS
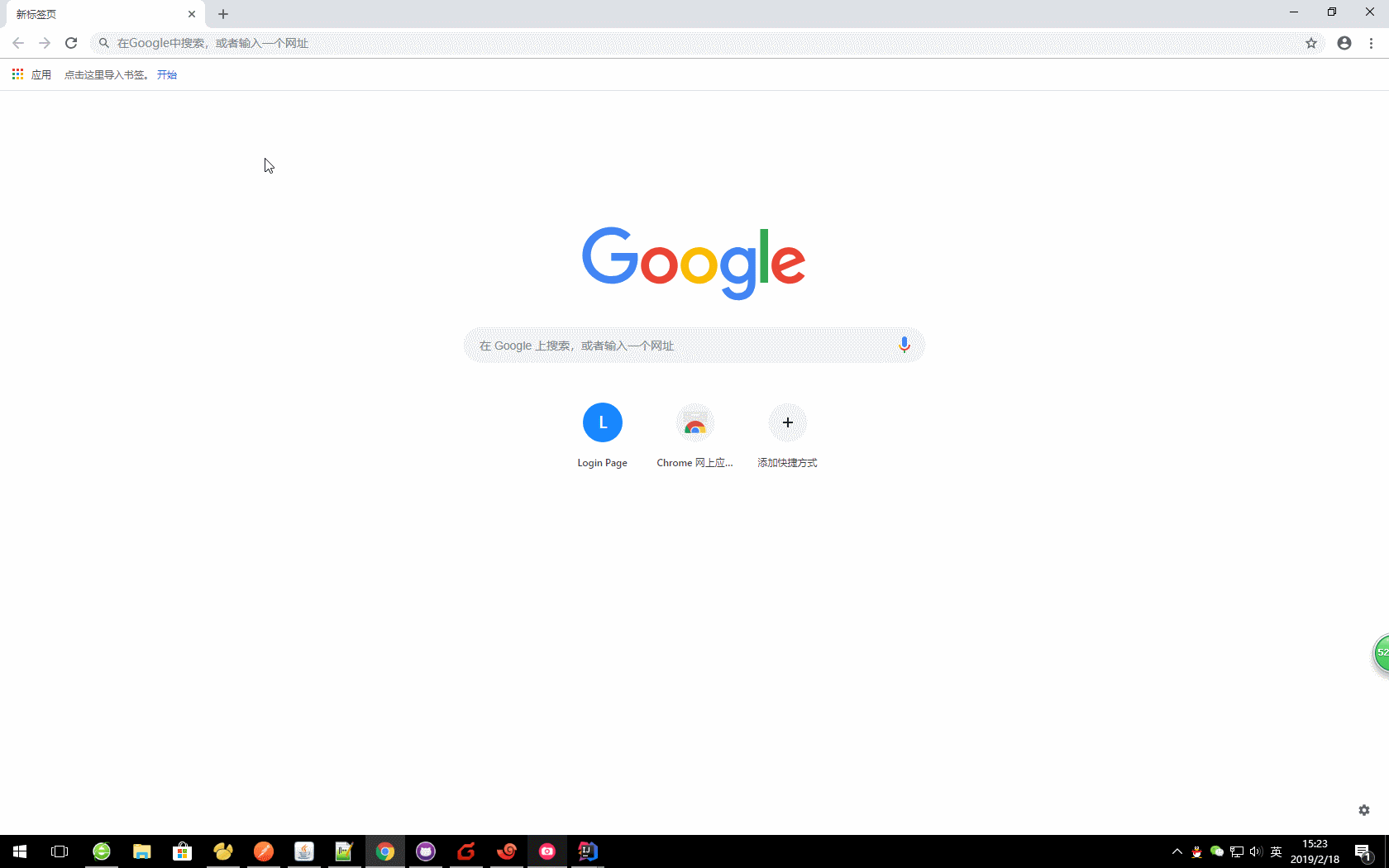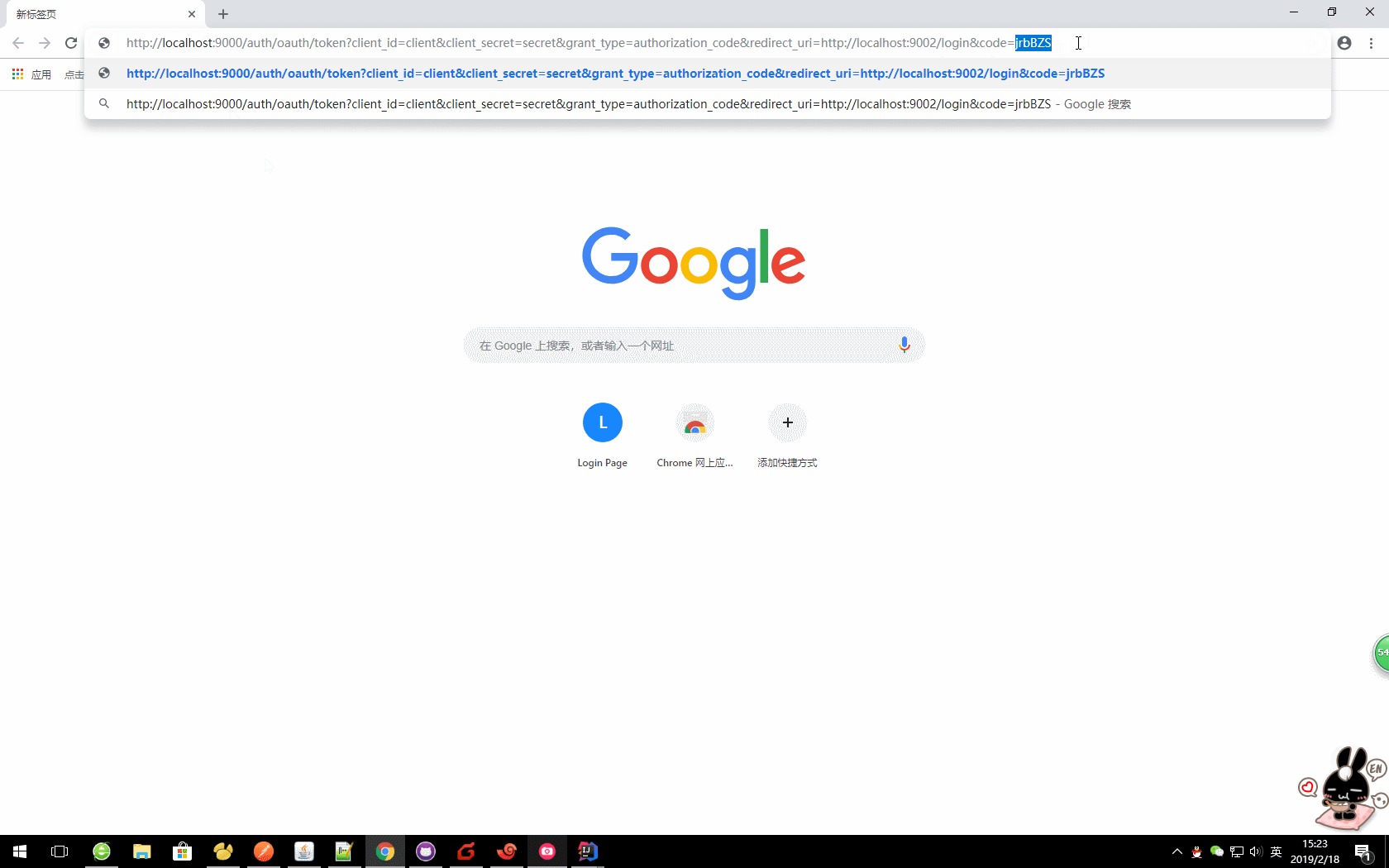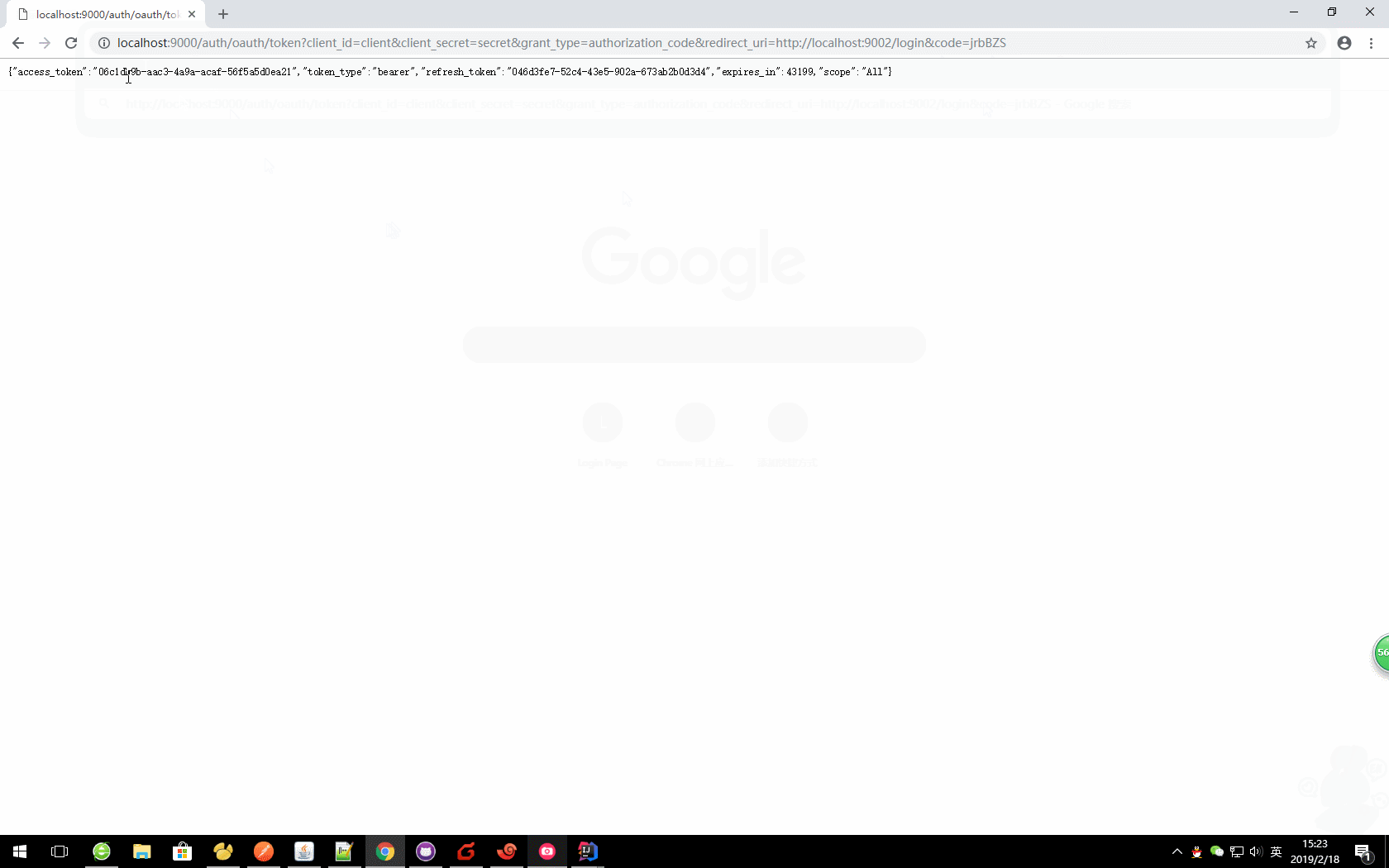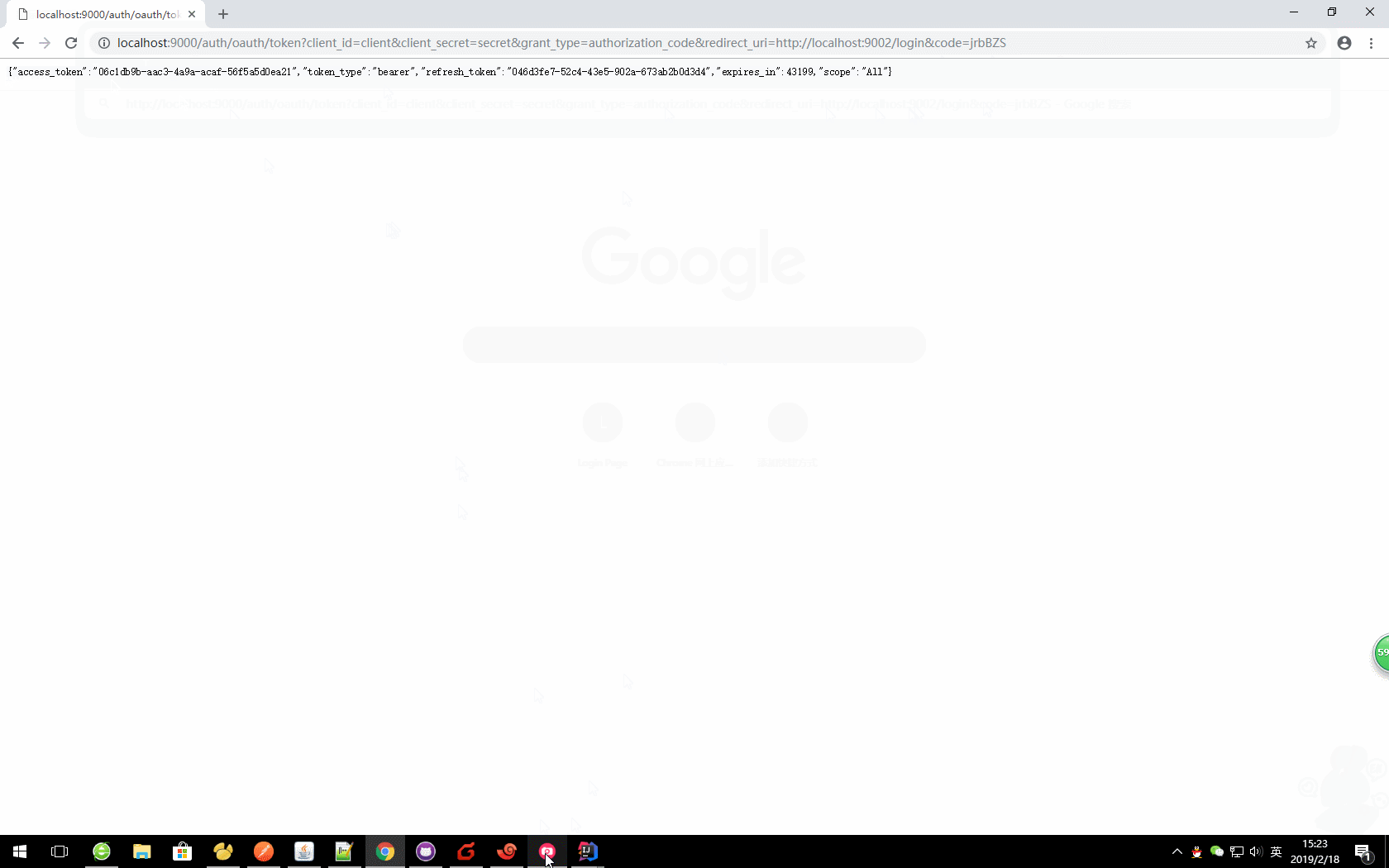
获取的对应值
{ "access_token": "06c1db9b-aac3-4a9a-acaf-56f5a5d0ea21", "token_type": "bearer", "refresh_token": "046d3fe7-52c4-43e5-902a-673ab2b0d3d4", "expires_in": 42981, "scope": "All" }
- access_token:表示访问令牌,必选项。
- token_type:表示令牌类型,该值大小写不敏感,必选项,可以是bearer类型或mac类型。
- expires_in:表示过期时间,单位为秒。如果省略该参数,必须其他方式设置过期时间。
- refresh_token:表示更新令牌,用来获取下一次的访问令牌,可选项。
- scope:表示权限范围,如果与客户端申请的范围一致,此项可省略。
c、更新令牌
oauth/token?grant_type=refresh_token&refresh_token=
本文:
http://localhost:9000/auth/oauth/token?grant_type=refresh_token&refresh_token=046d3fe7-52c4-43e5-902a-673ab2b0d3d4
注意:在使用refresh_token刷新令牌的时候,需要在认证服务器上面设置
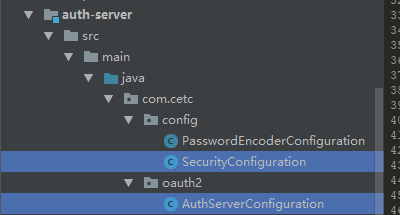
SecurityConfiguration加入UserDetailsService
@Bean @Override protected UserDetailsService userDetailsService() { return super.userDetailsService(); }
AuthServerConfiguration也加入UserDetailsService
@Autowired private UserDetailsService userDetailsService; @Override public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) throws Exception { //认证体系使用security的方式 endpoints.authenticationManager(authenticationManager); endpoints.allowedTokenEndpointRequestMethods(HttpMethod.GET, HttpMethod.POST); endpoints.userDetailsService(userDetailsService); }
否者报错:
Handling error: IllegalStateException, UserDetailsService is required.
d、访问资源
url?access_token=06c1db9b-aac3-4a9a-acaf-56f5a5d0ea21
应用:
a、默认方式获取code
http://localhost:9000/auth/oauth/authorize?response_type=code&client_id=client&redirect_uri=http://localhost:9003/authorize/login

第一步基本上都是通过浏览器进行登录的。
b、程序获取令牌
LinkedMultiValueMap<String, Object> valueMap = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>(); valueMap.add("client_id", authorizationCodeResourceDetails.getClientId()); valueMap.add("client_secret", authorizationCodeResourceDetails.getClientSecret()); valueMap.add("grant_type", authorizationCodeResourceDetails.getGrantType()); valueMap.add("redirect_uri", authorizationCodeResourceDetails.getPreEstablishedRedirectUri()); valueMap.add("code", code); Map<String, String> map = HttpUtils.doFrom(authorizationCodeResourceDetails.getAccessTokenUri(), valueMap, Map.class);
c、单点登录
//获取用户信息,说明这里主要目的就是通过资源服务器去获取用户信息 Map principal = HttpUtils.doGet(resourceServerProperties.getUserInfoUri() + "?access_token=" + map.get("access_token"), Map.class); //这里通过本地登录单点登录 String username = principal.get("name").toString(); //如果用户存在则不添加,这里如果生产应用中,可以更具规则修改 if (userRepository.findByUsername(username) == null) { Role role = roleRepository.findByRoleType(Role.RoleType.USER); User newUser = new User(); newUser.setUsername(username); newUser.setPassword(passwordEncoder.encode(username)); newUser.getRoles().add(role); userRepository.save(newUser); } //这里通过本地登录的方式来获取会话 HttpHeaders httpHeaders = new HttpHeaders(); httpHeaders.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED); LinkedMultiValueMap<String, Object> params = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>(); params.add("username", username); params.add("password", username); HttpEntity<LinkedMultiValueMap<String, ? extends Object>> httpEntity = new HttpEntity(params, httpHeaders); String url = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort() + "/login"; ResponseEntity<Object> exchange = restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.POST, httpEntity, Object.class); //将登录后的header原本的给浏览器,这就是当前浏览器的会话 HttpHeaders headers = exchange.getHeaders(); for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> entry : headers.entrySet()) { entry.getValue().stream().forEach(value -> response.addHeader(entry.getKey(), value)); } //这个状态是根据security的返回数据设定的 response.setStatus(exchange.getStatusCode().value());
d、登录的实现过程
@RestController @RequestMapping("/authorize") public class AuthorizedResource { @Autowired private AuthorizationCodeResourceDetails authorizationCodeResourceDetails; @Autowired private ResourceServerProperties resourceServerProperties; @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @Autowired private BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder; @Autowired private UserRepository userRepository; @Autowired private RoleRepository roleRepository; @RequestMapping("/login") public void login(String code, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(code)) { LinkedMultiValueMap<String, Object> valueMap = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>(); valueMap.add("client_id", authorizationCodeResourceDetails.getClientId()); valueMap.add("client_secret", authorizationCodeResourceDetails.getClientSecret()); valueMap.add("grant_type", authorizationCodeResourceDetails.getGrantType()); valueMap.add("redirect_uri", authorizationCodeResourceDetails.getPreEstablishedRedirectUri()); valueMap.add("code", code); Map<String, String> map = HttpUtils.doFrom(authorizationCodeResourceDetails.getAccessTokenUri(), valueMap, Map.class); System.out.println(map); //获取用户信息,说明这里主要目的就是通过资源服务器去获取用户信息 Map principal = HttpUtils.doGet(resourceServerProperties.getUserInfoUri() + "?access_token=" + map.get("access_token"), Map.class); //这里通过本地登录单点登录 String username = principal.get("name").toString(); //如果用户存在则不添加,这里如果生产应用中,可以更具规则修改 if (userRepository.findByUsername(username) == null) { Role role = roleRepository.findByRoleType(Role.RoleType.USER); User newUser = new User(); newUser.setUsername(username); newUser.setPassword(passwordEncoder.encode(username)); newUser.getRoles().add(role); userRepository.save(newUser); } //这里通过本地登录的方式来获取会话 HttpHeaders httpHeaders = new HttpHeaders(); httpHeaders.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED); LinkedMultiValueMap<String, Object> params = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>(); params.add("username", username); params.add("password", username); HttpEntity<LinkedMultiValueMap<String, ? extends Object>> httpEntity = new HttpEntity(params, httpHeaders); String url = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort() + "/login"; ResponseEntity<Object> exchange = restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.POST, httpEntity, Object.class); //将登录后的header原本的给浏览器,这就是当前浏览器的会话 HttpHeaders headers = exchange.getHeaders(); for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> entry : headers.entrySet()) { entry.getValue().stream().forEach(value -> response.addHeader(entry.getKey(), value)); } //这个状态是根据security的返回数据设定的 response.setStatus(exchange.getStatusCode().value()); } } }
说明:这里这是简单的应用,实际用户名等可以和密码都可以绑定现有账号,或者深度加密!
e、其他没有什么大的配置
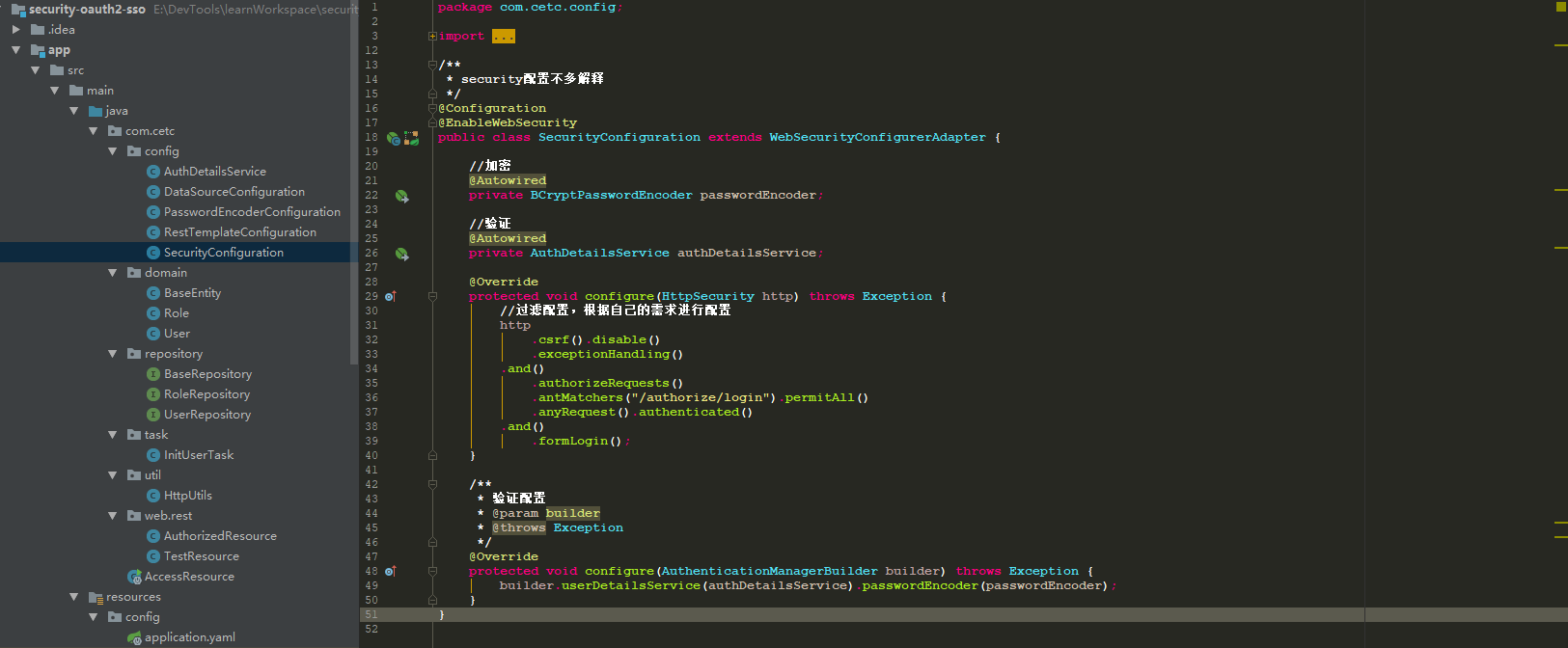
application.yaml
server: port: 9003 servlet: session: cookie: name: ACCESS_SESSION security: oauth2: client: client-id: client client-secret: secret grant-type: authorization_code access-token-uri: http://localhost:9000/auth/oauth/token user-authorization-uri: http://localhost:9000/auth/oauth/authorize pre-established-redirect-uri: http://localhost:9003/authorize/login resource: user-info-uri: http://localhost:9002/user/me sso: login-path: /authorize/login spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/model?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&allowMultiQueries=true username: root password: jpa: hibernate: ddl-auto: update naming: physical-strategy: org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.hibernate.SpringPhysicalNamingStrategy implicit-strategy: org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.hibernate.SpringImplicitNamingStrategy show-sql: true database-platform: org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect database: mysql
6)sso客户端

说明:个人还是很喜欢sso的模式的,简单方便高效
八、源码:https://github.com/lilin409546297/security-oauth2-sso
九、此博客借鉴阮一峰的理解OAuth 2.0