1. 引入
- 给你一个数列 {1,2,3,4,5,6},要求创建一颗二叉排序树(BST)
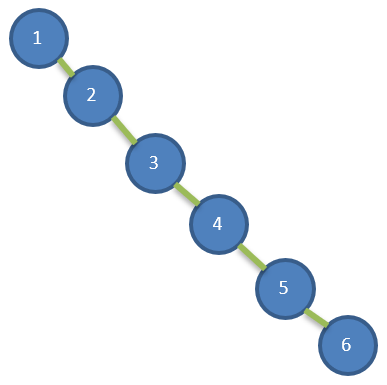
- 上述 BST 存在的问题分析
- 左子树全部为空,从形式上看,更像一个单链表
- 插入速度没有影响
- 查询速度明显降低,不能发挥 BST 的优势 // 因为每次还需要比较左子树,其查询速度比单链表还慢
- [解决方案] 平衡二叉树(AVL)
2. 平衡二叉树
- 平衡二叉树也叫平衡二叉搜索树(Self-balancing binary search tree), 可以保证查询效率较高。
- 特点
- 它是一棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1
- 左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树
- 注意,平衡二叉树中结点与其左右子结点仍旧满足 [二叉排序树] 的关系
- 平衡二叉树的常用实现方法
- 红黑树
- AVL
- 替罪羊树
- Treap
- 伸展树
- 举例说明
3. 思路分析
3.1 单旋转
-
左旋转

-
右旋转

3.2 双旋转
单旋转可能引发的问题

当符合旋转条件 右子树高度 - 左子树高度 > 1 时,要先做判断!若其中 {右子树的左子树} 高度 > {右子树的右子树} 高度,则要先对 [当前结点的右子结点] 进行“右旋转”,再对 [当前结点] 进行“左旋转”的操作。
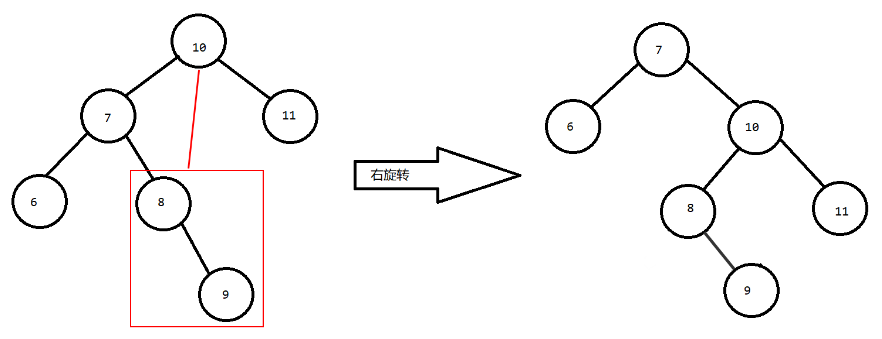
当符合旋转条件 左子树高度 - 右子树高度 > 1 时,要先做判断!若其中 {左子树的右子树} 高度 > {左子树的左子树} 高度,则还要先对 [当前结点的左子结点] 进行“左旋转”,再对 [当前结点] 进行“右旋转”的操作。
4. 代码实现
public class AVLTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int[] arr = {4, 3, 6, 5, 7, 8}; // 左旋转
// int[] arr = {10, 12, 8, 9, 7, 6}; // 右旋转
// int[] arr = {10, 11, 7, 6, 8, 9}; // 双旋转(先左再右)
int[] arr = {10, 4, 17, 12, 18, 11}; // 双旋转(先右再左)
AVLTree tree = new AVLTree();
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
tree.add(new Node(arr[i]));
tree.infixOrder();
System.out.printf("[AVL] 树的高度:%d, 左子树的高度:%d, 右子树的高度:%d
"
, tree.root.height(), tree.root.leftHeight(), tree.root.rightHeight());
System.out.println("root: " + tree.root);
}
}
class AVLTree {
public Node root;
public void add(Node node) {
if (root == null) root = node;
else root.add(node);
}
public void infixOrder() {
if (root != null) root.infixOrder();
else System.out.println("空树");
System.out.println();
}
}
class Node {
public int value; // 结点权值
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
// 返回以该结点为根结点的子树的高度
public int height() {
// + 1: Math.max统计的是子树高度, 根结点本身也算 1 层
return Math.max(left == null ? 0 : left.height(),
right == null ? 0 : right.height()) + 1;
}
// 返回左子树的高度
public int leftHeight() {
return left == null ? 0 : left.height();
}
// 返回右子树的高度
public int rightHeight() {
return right == null ? 0 : right.height();
}
public void leftRotate() {
// 1. 创建 [新的结点], 其 value 为 [当前结点] 的value
Node newNode = new Node(value);
// 2. [新的结点] 的左子结点 = [当前结点] 的左子结点
newNode.left = left;
// 3. [新的结点] 的右子结点 = [当前结点] 的右子结点的左子结点
newNode.right = right.left;
// 4. [当前结点] 的 value = 其右子结点的value
value = right.value;
// 5. [当前结点] 的右子结点 替换为 其右子结点的右子结点
right = right.right;
// 6. [当前结点] 的左子结点 替换为 [新的结点]
left = newNode;
}
public void rightRotate() {
// 1. 创建 [新的结点], 其 value 为 [当前结点] 的value
Node newNode = new Node(value);
// 2. [新的结点] 的右子结点 = [当前结点] 的右子结点
newNode.right = right;
// 3. [新的结点] 的左子结点 = [当前结点] 的左子结点的右子结点
newNode.left = left.right;
// 4. [当前结点] 的 value = 其的左子结点的value
value = left.value;
// 5. [当前结点] 的左子结点 替换为 其左子结点的左子结点
left = left.left;
// 6. [当前结点] 的右子结点 替换为 [新的结点]
right = newNode;
}
// (递归)添加结点
public void add(Node node) {
if (node == null) return;
// 判断 node 的 value 和当前子树根结点的 value 的大小关系
if (node.value < this.value) {
if(this.left != null) this.left.add(node);
else this.left = node;
} else {
if (this.right != null) this.right.add(node);
else this.right = node;
}
// 当添加一个结点后,递归返回过程中都得查看当前树结构是否还能满足 AVL 树结构
// a. 右子树 > 左子树 → 左旋转
if (rightHeight() - leftHeight() > 1) {
// 右子树的左子树 > 右子树的右子树
if (right.leftHeight() > right.rightHeight())
right.rightRotate(); // 得先来一次右旋转
leftRotate();
return;
}
// b. 左子树 > 右子树 → 右旋转
if (leftHeight() - rightHeight() > 1) {
// 左子树的右子树 > 左子树的左子树
if (left.rightHeight() > left.leftHeight())
left.leftRotate(); // 得先来一次左旋转
rightRotate();
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.left != null) this.left.infixOrder();
System.out.print(this + " ");
if (this.right != null) this.right.infixOrder();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[value=" + value + "]";
}
}
// 上述代码仅是在添加结点过程中实现平衡二叉树,删除结点后维系平衡二叉树的代码木有