方法:一段用于完成特定功能的代码片段,类似于其他语言的函数。
方法用于定义该类或该类的失礼行为特征和功能实现。方法是类和对象行为特征的抽象。方法类似于面向过程中的函数。在面向对象中,整个程序的基本单位是类,方法是从属于类和对象的。方法包括方法名与参数。
方法的调用方式:
1.形式参数:在方法声明时用于接收外界传入的数据
2.实参:调用方法时实际传给方法的数据
3.返回值:方法在执行完毕后返回给调用它的环境的数据
4.返回值类型:事先约定的返回值的数据类型,如无返回值类型,必须显示指定为void
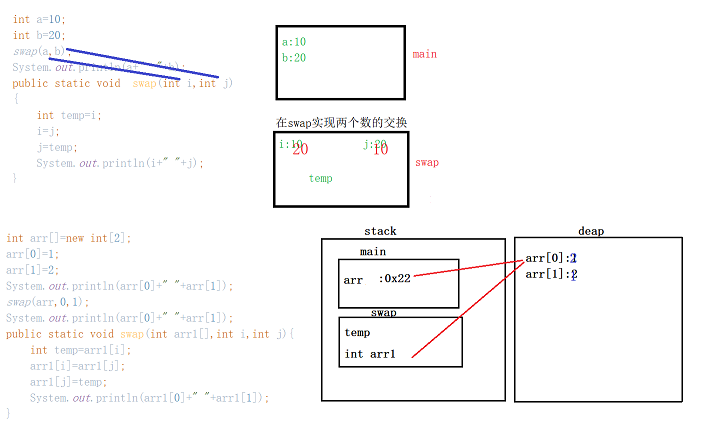
练习1•:两个数值的交换与对应的内存分析:
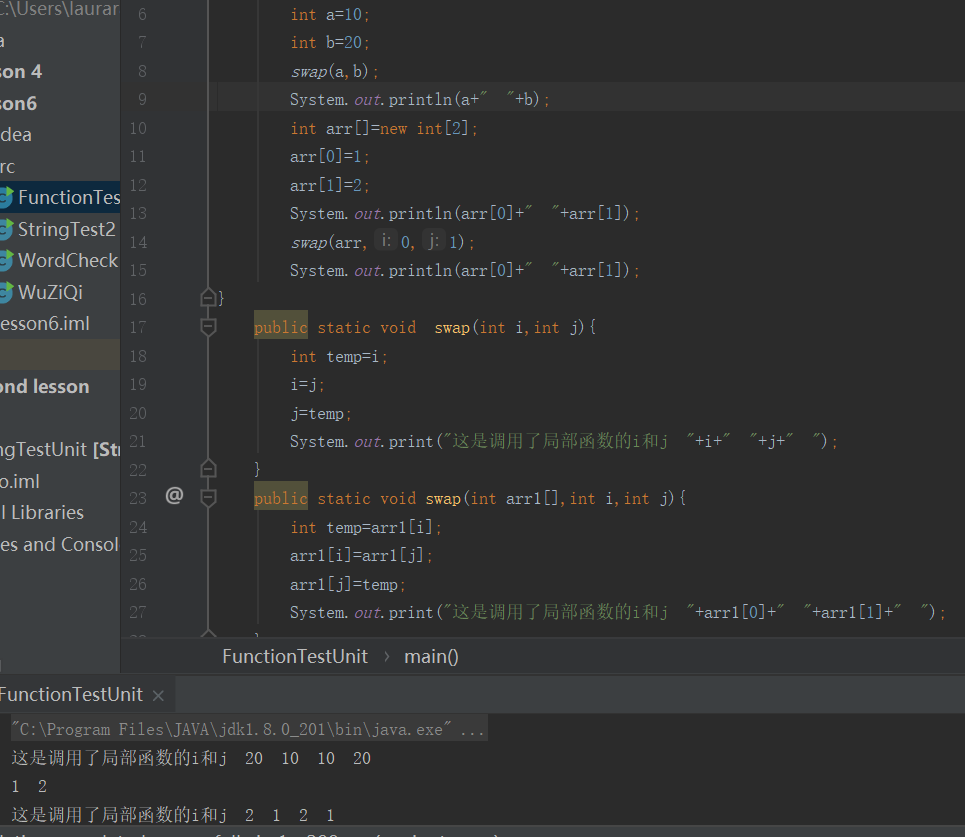
内存分析:
练习2•:字符串及字符的交换
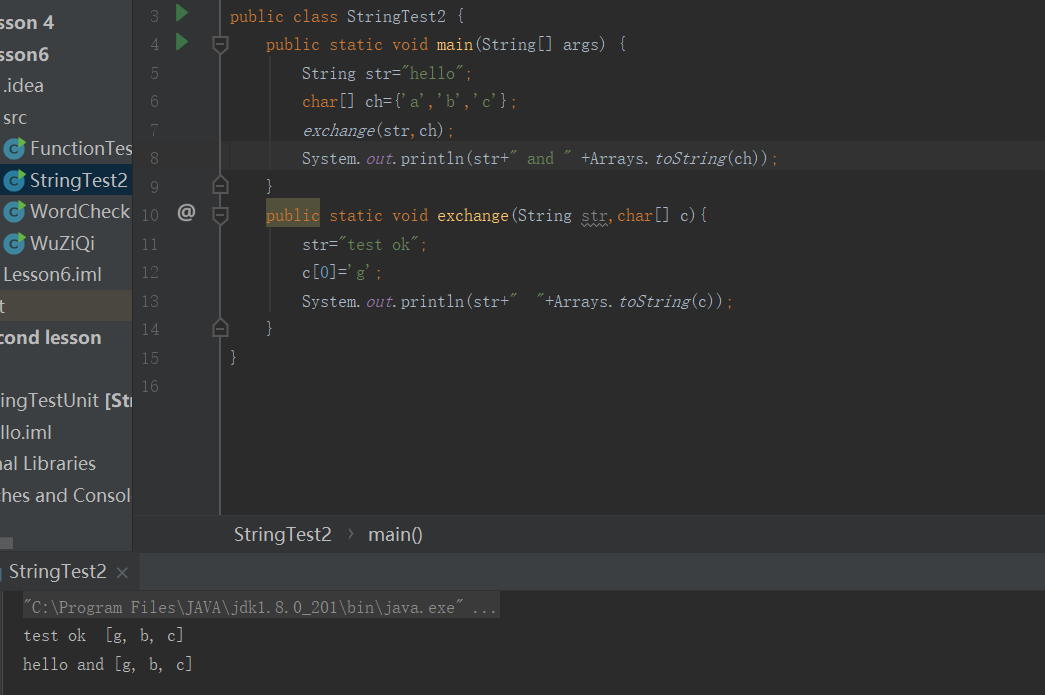
内存分析:
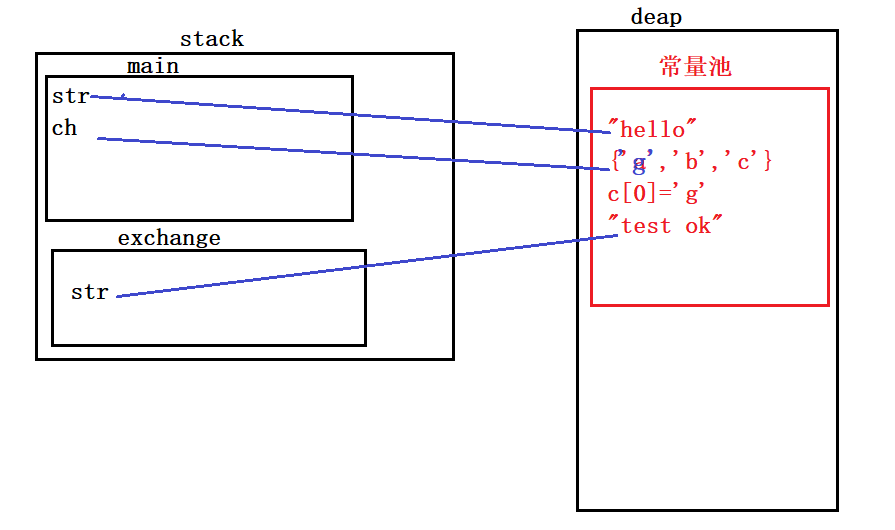
练习3•:数值的改变
i的值为多少?
public static void main(String[] args) { int i=0; fun(i); i=i++;//0 ++i为1
System.out.println("main函数里面的i: "+i);
}
public static void fun1(int i){
i++;
System.out.println("局部函数里面的i: "+i);
}i++:先把i赋给i,再相加,所以i的值不变,还是0,调用 fun(i) 函数,只是改变了局部函数的i值。
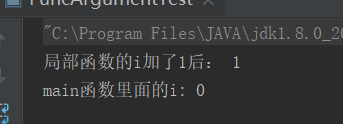
若为i=++1,main函数里的i输出结果为1.
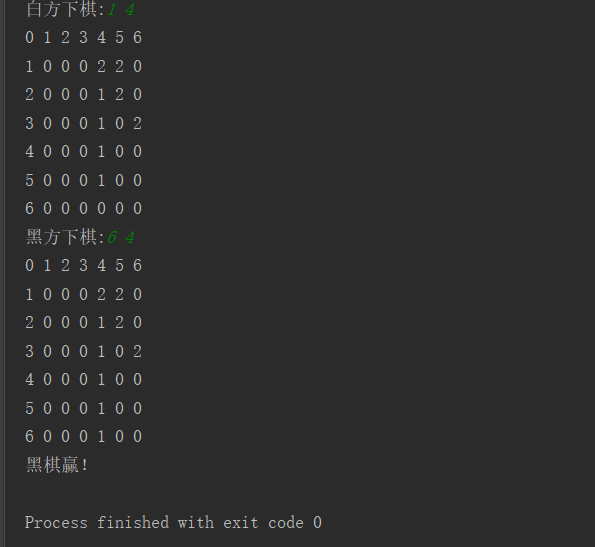
练习4:五子棋游戏(控制台版)
/**
* 二维数组的应用,实现一个简单的基于控制台应用程序的五子棋对战游戏
* 软件运行要求如下:
* 1.输入要生成的棋盘的行列数 m和n
* 2.显示五子棋盘,每一个位置默认都是0
* 3.提示黑方下棋:3 4 黑棋显示为1
* ===》 代码进行逻辑检查
* 横 竖 斜
* 4.提示白方下棋:2 5 白棋显示为2
*
* 如果哪一方胜出,则打印,程序退出
*/
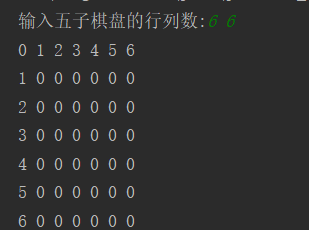
逻辑:1.输入(Scanner)要生成棋盘的行列数(m,n),以二维数组的方式显示棋盘chess[m+1][n+1],分别用一行一列显示行列数
2.将棋盘的数字默认为0(双重for循环),其中二维数组的第0行第0列分别显示列数和行数(chess[0][i]=i,chess[j][0]=j),效果如图
3.提示下棋,并输入相应坐标,定义一个flag,若为true则黑棋下,黑棋下了后,在坐标处显示1,否则白棋下了显示2,代码如下,效果如图:
if (flag) {
System.out.print("黑方下棋:");
m = in.nextInt();
n = in.nextInt();
chess[m][n] = 1;
} else {
System.out.print("白方下棋:");
m = in.nextInt();
n = in.nextInt();
chess[m][n] = 2;
}

此处,应该设置一个无限循环,直到有一方胜出,再退出程序
4.判断哪方胜的逻辑,分别从横,竖,斜三个方面
for (; ; ) { // 1.先提示下棋 if (flag) { System.out.print("黑方下棋:"); m = in.nextInt(); n = in.nextInt(); chess[m][n] = 1; } else { System.out.print("白方下棋:"); m = in.nextInt(); n = in.nextInt(); chess[m][n] = 2; } if (flag) { // 表示黑方(1)下的棋 // 黑方是否胜利的逻辑判断代码 if(judge(chess,m,n,1)){ System.out.println("黑棋赢!"); return; } // 该白方下棋了 flag = false; } else { // 表示白方(2)下的棋 // 白方是否胜利的逻辑判断代码 if (judge(chess, m, n, 2)) { System.out.println("白棋赢!"); return; } // 2.显示棋盘 i j i-1 j-1 i-2 for (int i = 0; i < chess.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < chess[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(chess[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } // 3.五子棋下棋以后的逻辑判断 胜出 继续提示白方下棋: } // 该黑方下棋了 flag = true; }
5.具体的judge函数的实现
/** * judge函数判断哪个琪赢 * @param chess 存储所有棋子的二维数组 * @param m 下棋的行 * @param n 下棋的列 * @param data 黑棋1或者白棋2 * @return 返回true,表示data胜利了,否则返回false则另一方胜利 */ private static boolean judge(int[][] chess, int m, int n, int data) { int count=1; int j=0; //先判断横向的左边 for(j=n-1;j>0;j--){ //判断横向的时候,i不变,j改变,从当前位置的左边一直向左边,直到第一列 if(chess[m][j]==data){ //如果第m行的纵坐标为1或者2,则对应的棋数加1 count++; //棋子数相加 } else{break; } } //横向的右边 for(j=n+1;j<chess[0].length;j++){ //棋子一直向右走 if(chess[m][j]==data){ count++; }else{break;} if(count == 5){ //如果横向判断完后count为5,则返回data对应的棋子,true的一方获胜 return true; } } count=1; int i=0; //竖向的上边 for(i=m-1;i>0;--i){ if(chess[i][n]==data){ count++; }else{break;} } //竖向的下边 for(i=m+1;i<chess.length;++i){ if(chess[i][n]==data){ count++; }else{break;} } if(count == 5){ return true; } count=1; //左斜上方 for(i=m-1,j=n+1;i>0&&j<chess[0].length;--i,++j){ if(chess[i][j]==data){ count++; }else{break;} } //左斜下方 for(i=m+1,j=n-1;i<chess.length&&j>0;++i,--j){ if(chess[i][j]==data){ count++; }else{break;} } //右斜上方 for(i=m-1,j=n-1;i>0&&j>0;--i,--j){ if(chess[i][j]==data){ count++; }else{break;} } if(count == 5){ return true; } count=1; //右斜下方 for(i=m+1,j=n+1;i<chess.length&&j<chess[0].length;--i,--j){ if(chess[i][j]==data){ count++; }else{break;} } if(count == 5){ return true; } // 上面检查了各个方向,都没有胜利,直接返回false,表示还又有赢棋 return false; }
具体整个代码的实现:
public class WuZiQi{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("输入五子棋盘的行列数:"); int row = in.nextInt(); //定义棋盘的行 int col = in.nextInt(); //定义棋盘的列 // 生成棋盘,包括数字梯子行,列;所以+1 int [][] chess = new int[row + 1][col + 1]; // 给第一行填数字 for (int i = 0; i < chess[0].length; i++) { chess[0][i] = i; } // 给第一列填数字 for (int i = 0; i < chess.length; i++) { chess[i][0] = i; } // 无限循环 int m, n; //下棋的时候的横、纵坐标 boolean flag = true; // true表示黑方下 false表示白方下 // 未下棋的时候的棋盘 for (int i = 0; i < chess.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < chess[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(chess[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } //无限循环,直到有一方胜出 for (; ; ) { // 1.先提示下棋 if (flag) { System.out.print("黑方下棋:"); m = in.nextInt(); n = in.nextInt(); chess[m][n] = 1; } else { System.out.print("白方下棋:"); m = in.nextInt(); n = in.nextInt(); chess[m][n] = 2; } // 2.显示棋盘 i j i-1 j-1 i-2 for (int i = 0; i < chess.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < chess[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(chess[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } // 3.五子棋下棋以后的逻辑判断 胜出 继续提示白方下棋: if (flag) { // 表示黑方(1)下的棋 // 黑方是否胜利的逻辑判断代码 if(judge(chess,m,n,1)){ System.out.println("黑棋赢!"); return; } // 该白方下棋了 flag = false; } else { // 表示白方(2)下的棋 // 白方是否胜利的逻辑判断代码 if(judge(chess,m,n,2)){ System.out.println("白棋赢!"); return; } // 该黑方下棋了 flag = true; } } } /** * judge函数判断哪个琪赢 * @param chess 存储所有棋子的二维数组 * @param m 下棋的行 * @param n 下棋的列 * @param data 黑棋1或者白棋2 * @return 返回true,表示data胜利了,否则返回false则另一方胜利 */ private static boolean judge(int[][] chess, int m, int n, int data) { int count=1; int j=0; //先判断横向的左边 for(j=n-1;j>0;j--){ if(chess[m][j]==data){ count++; } else{break; } } //横向的右边 for(j=n+1;j<chess[0].length;j++){ if(chess[m][j]==data){ count++; }else{break;} if(count == 5){ return true; } } count=1; int i=0; //竖向的上边 for(i=m-1;i>0;--i){ if(chess[i][n]==data){ count++; }else{break;} } //竖向的下边 for(i=m+1;i<chess.length;++i){ if(chess[i][n]==data){ count++; }else{break;} } if(count == 5){ return true; } count=1; //左斜上方 for(i=m-1,j=n+1;i>0&&j<chess[0].length;--i,++j){ if(chess[i][j]==data){ count++; }else{break;} } //左斜下方 for(i=m+1,j=n-1;i<chess.length&&j>0;++i,--j){ if(chess[i][j]==data){ count++; }else{break;} } //右斜上方 for(i=m-1,j=n-1;i>0&&j>0;--i,--j){ if(chess[i][j]==data){ count++; }else{break;} } if(count == 5){ return true; } count=1; //右斜下方 for(i=m+1,j=n+1;i<chess.length&&j<chess[0].length;--i,--j){ if(chess[i][j]==data){ count++; }else{break;} } if(count == 5){ return true; } // 上面检查了各个方向,都没有胜利,直接返回false,表示还又有赢棋 return false; } }
最后的成果控制台展示: