一、目标任务:

检验实验环境

[root@jenkins ~]# su - deploy [deploy@jenkins ~]$ source /home/deploy/.py3-a2.5-env/bin/activate (.py3-a2.5-env) [deploy@jenkins ~]$ source /home/deploy/.py3-a2.5-env/ansible/hacking/env-setup -q (.py3-a2.5-env) [deploy@jenkins ~]$ ansible-playbook --version ansible-playbook 2.5.15 (stable-2.5 c8dfe5b6d3) last updated 2021/02/05 18:19:52 (GMT +800) config file = None configured module search path = ['/home/deploy/.ansible/plugins/modules', '/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules'] ansible python module location = /home/deploy/.py3-a2.5-env/ansible/lib/ansible executable location = /home/deploy/.py3-a2.5-env/ansible/bin/ansible-playbook python version = 3.6.5 (default, Feb 5 2021, 13:52:27) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-36)] (.py3-a2.5-env) [deploy@jenkins ~]$ ssh root@test.example.com Last login: Tue Feb 23 17:02:08 2021 from 10.10.10.10 [root@testbox ~]# #免密登录成功
wordpress 目录结构和文件内容
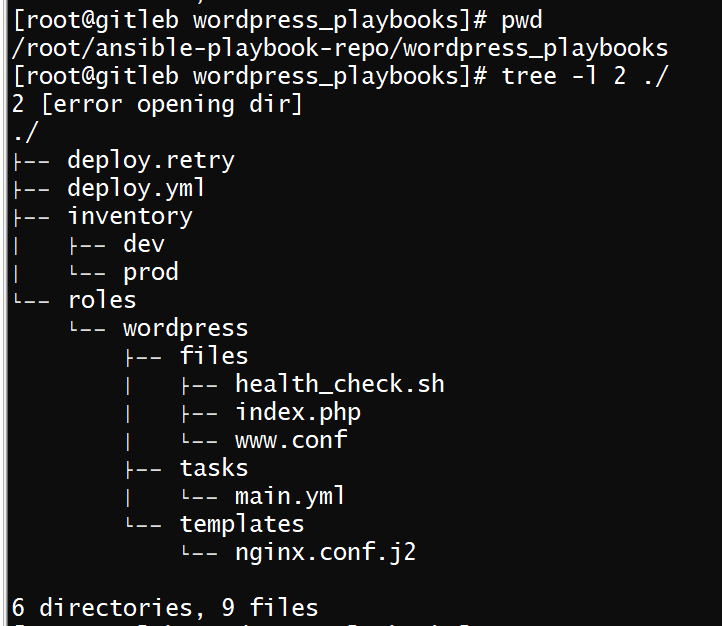
文件内容

[root@gitleb wordpress_playbooks]# cat deploy.retry test.example.com [root@gitleb wordpress_playbooks]# cat deploy.yml - hosts: "wordpress" gather_facts: true remote_user: root roles: - wordpress [root@gitleb wordpress_playbooks]# cat inventory/dev [wordpress] test.example.com [wordpress:vars] server_name=test.example.com port=8080 user=deploy worker_processes=2 max_open_file=3000 root=/data/www gitlab_user='root' gitlab_pass='xxxxxxxx' [root@gitleb wordpress_playbooks]# cat inventory/prod [wordpress] test.example.com [wordpress:vars] server_name=test.example.com port=80 user=deploy worker_processes=4 max_open_file=65505 root=/data/www gitlab_user='root' gitlab_pass='xxxxxxxx' [root@gitleb wordpress_playbooks]# cat roles/wordpress/files/health_check.sh #!/bin/sh URL=$1 PORT=$2 gitlab_user='root' curl -Is http://$URL:$PORT/info.php > /dev/null && echo "The remote side is healthy" || echo "The remote side is failed, please check" [root@gitleb wordpress_playbooks]# cat roles/wordpress/files/index.php <?php phpinfo(); ?> [root@gitleb wordpress_playbooks]# cat roles/wordpress/files/www.conf ; Start a new pool named 'www'. [www] ; Unix user/group of processes ; Note: The user is mandatory. If the group is not set, the default user's group ; will be used. ; RPM: apache Choosed to be able to access some dir as httpd user = deploy ; RPM: Keep a group allowed to write in log dir. group = deploy ; The address on which to accept FastCGI requests. ; Valid syntaxes are: ; 'ip.add.re.ss:port' - to listen on a TCP socket to a specific IPv4 address on ; a specific port; ; '[ip:6:addr:ess]:port' - to listen on a TCP socket to a specific IPv6 address on ; a specific port; ; 'port' - to listen on a TCP socket to all addresses ; (IPv6 and IPv4-mapped) on a specific port; ; '/path/to/unix/socket' - to listen on a unix socket. ; Note: This value is mandatory. ;listen = 127.0.0.1:9000 listen = /var/run/php-fpm/php-fpm.sock ; Set listen(2) backlog. ; Default Value: 511 (-1 on FreeBSD and OpenBSD) ;listen.backlog = 511 ; Set permissions for unix socket, if one is used. In Linux, read/write ; permissions must be set in order to allow connections from a web server. Many ; BSD-derived systems allow connections regardless of permissions. ; Default Values: user and group are set as the running user ; mode is set to 0660 listen.owner = deploy listen.group = deploy ;listen.mode = 0660 ; When POSIX Access Control Lists are supported you can set them using ; these options, value is a comma separated list of user/group names. ; When set, listen.owner and listen.group are ignored ;listen.acl_users = ;listen.acl_groups = ; List of addresses (IPv4/IPv6) of FastCGI clients which are allowed to connect. ; Equivalent to the FCGI_WEB_SERVER_ADDRS environment variable in the original ; PHP FCGI (5.2.2+). Makes sense only with a tcp listening socket. Each address ; must be separated by a comma. If this value is left blank, connections will be ; accepted from any ip address. ; Default Value: any listen.allowed_clients = 127.0.0.1 ; Specify the nice(2) priority to apply to the pool processes (only if set) ; The value can vary from -19 (highest priority) to 20 (lower priority) ; Note: - It will only work if the FPM master process is launched as root ; - The pool processes will inherit the master process priority ; unless it specified otherwise ; Default Value: no set ; process.priority = -19 ; Choose how the process manager will control the number of child processes. ; Possible Values: ; static - a fixed number (pm.max_children) of child processes; ; dynamic - the number of child processes are set dynamically based on the ; following directives. With this process management, there will be ; always at least 1 children. ; pm.max_children - the maximum number of children that can ; be alive at the same time. ; pm.start_servers - the number of children created on startup. ; pm.min_spare_servers - the minimum number of children in 'idle' ; state (waiting to process). If the number ; of 'idle' processes is less than this ; number then some children will be created. ; pm.max_spare_servers - the maximum number of children in 'idle' ; state (waiting to process). If the number ; of 'idle' processes is greater than this ; number then some children will be killed. ; ondemand - no children are created at startup. Children will be forked when ; new requests will connect. The following parameter are used: ; pm.max_children - the maximum number of children that ; can be alive at the same time. ; pm.process_idle_timeout - The number of seconds after which ; an idle process will be killed. ; Note: This value is mandatory. pm = dynamic ; The number of child processes to be created when pm is set to 'static' and the ; maximum number of child processes when pm is set to 'dynamic' or 'ondemand'. ; This value sets the limit on the number of simultaneous requests that will be ; served. Equivalent to the ApacheMaxClients directive with mpm_prefork. ; Equivalent to the PHP_FCGI_CHILDREN environment variable in the original PHP ; CGI. ; Note: Used when pm is set to 'static', 'dynamic' or 'ondemand' ; Note: This value is mandatory. pm.max_children = 50 ; The number of child processes created on startup. ; Note: Used only when pm is set to 'dynamic' ; Default Value: min_spare_servers + (max_spare_servers - min_spare_servers) / 2 pm.start_servers = 5 ; The desired minimum number of idle server processes. ; Note: Used only when pm is set to 'dynamic' ; Note: Mandatory when pm is set to 'dynamic' pm.min_spare_servers = 5 ; The desired maximum number of idle server processes. ; Note: Used only when pm is set to 'dynamic' ; Note: Mandatory when pm is set to 'dynamic' pm.max_spare_servers = 35 ; The number of seconds after which an idle process will be killed. ; Note: Used only when pm is set to 'ondemand' ; Default Value: 10s ;pm.process_idle_timeout = 10s; ; The number of requests each child process should execute before respawning. ; This can be useful to work around memory leaks in 3rd party libraries. For ; endless request processing specify '0'. Equivalent to PHP_FCGI_MAX_REQUESTS. ; Default Value: 0 ;pm.max_requests = 500 ; The URI to view the FPM status page. If this value is not set, no URI will be ; recognized as a status page. It shows the following informations: ; pool - the name of the pool; ; process manager - static, dynamic or ondemand; ; start time - the date and time FPM has started; ; start since - number of seconds since FPM has started; ; accepted conn - the number of request accepted by the pool; ; listen queue - the number of request in the queue of pending ; connections (see backlog in listen(2)); ; max listen queue - the maximum number of requests in the queue ; of pending connections since FPM has started; ; listen queue len - the size of the socket queue of pending connections; ; idle processes - the number of idle processes; ; active processes - the number of active processes; ; total processes - the number of idle + active processes; ; max active processes - the maximum number of active processes since FPM ; has started; ; max children reached - number of times, the process limit has been reached, ; when pm tries to start more children (works only for ; pm 'dynamic' and 'ondemand'); ; Value are updated in real time. ; Example output: ; pool: www ; process manager: static ; start time: 01/Jul/2011:17:53:49 +0200 ; start since: 62636 ; accepted conn: 190460 ; listen queue: 0 ; max listen queue: 1 ; listen queue len: 42 ; idle processes: 4 ; active processes: 11 ; total processes: 15 ; max active processes: 12 ; max children reached: 0 ; ; By default the status page output is formatted as text/plain. Passing either ; 'html', 'xml' or 'json' in the query string will return the corresponding ; output syntax. Example: ; http://www.foo.bar/status ; http://www.foo.bar/status?json ; http://www.foo.bar/status?html ; http://www.foo.bar/status?xml ; ; By default the status page only outputs short status. Passing 'full' in the ; query string will also return status for each pool process. ; Example: ; http://www.foo.bar/status?full ; http://www.foo.bar/status?json&full ; http://www.foo.bar/status?html&full ; http://www.foo.bar/status?xml&full ; The Full status returns for each process: ; pid - the PID of the process; ; state - the state of the process (Idle, Running, ...); ; start time - the date and time the process has started; ; start since - the number of seconds since the process has started; ; requests - the number of requests the process has served; ; request duration - the duration in µs of the requests; ; request method - the request method (GET, POST, ...); ; request URI - the request URI with the query string; ; content length - the content length of the request (only with POST); ; user - the user (PHP_AUTH_USER) (or '-' if not set); ; script - the main script called (or '-' if not set); ; last request cpu - the %cpu the last request consumed ; it's always 0 if the process is not in Idle state ; because CPU calculation is done when the request ; processing has terminated; ; last request memory - the max amount of memory the last request consumed ; it's always 0 if the process is not in Idle state ; because memory calculation is done when the request ; processing has terminated; ; If the process is in Idle state, then informations are related to the ; last request the process has served. Otherwise informations are related to ; the current request being served. ; Example output: ; ************************ ; pid: 31330 ; state: Running ; start time: 01/Jul/2011:17:53:49 +0200 ; start since: 63087 ; requests: 12808 ; request duration: 1250261 ; request method: GET ; request URI: /test_mem.php?N=10000 ; content length: 0 ; user: - ; script: /home/fat/web/docs/php/test_mem.php ; last request cpu: 0.00 ; last request memory: 0 ; ; Note: There is a real-time FPM status monitoring sample web page available ; It's available in: @EXPANDED_DATADIR@/fpm/status.html ; ; Note: The value must start with a leading slash (/). The value can be ; anything, but it may not be a good idea to use the .php extension or it ; may conflict with a real PHP file. ; Default Value: not set ;pm.status_path = /status ; The ping URI to call the monitoring page of FPM. If this value is not set, no ; URI will be recognized as a ping page. This could be used to test from outside ; that FPM is alive and responding, or to ; - create a graph of FPM availability (rrd or such); ; - remove a server from a group if it is not responding (load balancing); ; - trigger alerts for the operating team (24/7). ; Note: The value must start with a leading slash (/). The value can be ; anything, but it may not be a good idea to use the .php extension or it ; may conflict with a real PHP file. ; Default Value: not set ;ping.path = /ping ; This directive may be used to customize the response of a ping request. The ; response is formatted as text/plain with a 200 response code. ; Default Value: pong ;ping.response = pong ; The access log file ; Default: not set ;access.log = log/$pool.access.log ; The access log format. ; The following syntax is allowed ; %%: the '%' character ; %C: %CPU used by the request ; it can accept the following format: ; - %{user}C for user CPU only ; - %{system}C for system CPU only ; - %{total}C for user + system CPU (default) ; %d: time taken to serve the request ; it can accept the following format: ; - %{seconds}d (default) ; - %{miliseconds}d ; - %{mili}d ; - %{microseconds}d ; - %{micro}d ; %e: an environment variable (same as $_ENV or $_SERVER) ; it must be associated with embraces to specify the name of the env ; variable. Some exemples: ; - server specifics like: %{REQUEST_METHOD}e or %{SERVER_PROTOCOL}e ; - HTTP headers like: %{HTTP_HOST}e or %{HTTP_USER_AGENT}e ; %f: script filename ; %l: content-length of the request (for POST request only) ; %m: request method ; %M: peak of memory allocated by PHP ; it can accept the following format: ; - %{bytes}M (default) ; - %{kilobytes}M ; - %{kilo}M ; - %{megabytes}M ; - %{mega}M ; %n: pool name ; %o: output header ; it must be associated with embraces to specify the name of the header: ; - %{Content-Type}o ; - %{X-Powered-By}o ; - %{Transfert-Encoding}o ; - .... ; %p: PID of the child that serviced the request ; %P: PID of the parent of the child that serviced the request ; %q: the query string ; %Q: the '?' character if query string exists ; %r: the request URI (without the query string, see %q and %Q) ; %R: remote IP address ; %s: status (response code) ; %t: server time the request was received ; it can accept a strftime(3) format: ; %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S %z (default) ; The strftime(3) format must be encapsuled in a %{<strftime_format>}t tag ; e.g. for a ISO8601 formatted timestring, use: %{%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S%z}t ; %T: time the log has been written (the request has finished) ; it can accept a strftime(3) format: ; %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S %z (default) ; The strftime(3) format must be encapsuled in a %{<strftime_format>}t tag ; e.g. for a ISO8601 formatted timestring, use: %{%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S%z}t ; %u: remote user ; ; Default: "%R - %u %t "%m %r" %s" ;access.format = "%R - %u %t "%m %r%Q%q" %s %f %{mili}d %{kilo}M %C%%" ; The log file for slow requests ; Default Value: not set ; Note: slowlog is mandatory if request_slowlog_timeout is set slowlog = /var/log/php-fpm/www-slow.log ; The timeout for serving a single request after which a PHP backtrace will be ; dumped to the 'slowlog' file. A value of '0s' means 'off'. ; Available units: s(econds)(default), m(inutes), h(ours), or d(ays) ; Default Value: 0 ;request_slowlog_timeout = 0 ; The timeout for serving a single request after which the worker process will ; be killed. This option should be used when the 'max_execution_time' ini option ; does not stop script execution for some reason. A value of '0' means 'off'. ; Available units: s(econds)(default), m(inutes), h(ours), or d(ays) ; Default Value: 0 ;request_terminate_timeout = 0 ; Set open file descriptor rlimit. ; Default Value: system defined value ;rlimit_files = 1024 ; Set max core size rlimit. ; Possible Values: 'unlimited' or an integer greater or equal to 0 ; Default Value: system defined value ;rlimit_core = 0 ; Chroot to this directory at the start. This value must be defined as an ; absolute path. When this value is not set, chroot is not used. ; Note: chrooting is a great security feature and should be used whenever ; possible. However, all PHP paths will be relative to the chroot ; (error_log, sessions.save_path, ...). ; Default Value: not set ;chroot = ; Chdir to this directory at the start. ; Note: relative path can be used. ; Default Value: current directory or / when chroot ;chdir = /var/www ; Redirect worker stdout and stderr into main error log. If not set, stdout and ; stderr will be redirected to /dev/null according to FastCGI specs. ; Note: on highloaded environement, this can cause some delay in the page ; process time (several ms). ; Default Value: no ;catch_workers_output = yes ; Clear environment in FPM workers ; Prevents arbitrary environment variables from reaching FPM worker processes ; by clearing the environment in workers before env vars specified in this ; pool configuration are added. ; Setting to "no" will make all environment variables available to PHP code ; via getenv(), $_ENV and $_SERVER. ; Default Value: yes ;clear_env = no ; Limits the extensions of the main script FPM will allow to parse. This can ; prevent configuration mistakes on the web server side. You should only limit ; FPM to .php extensions to prevent malicious users to use other extensions to ; exectute php code. ; Note: set an empty value to allow all extensions. ; Default Value: .php ;security.limit_extensions = .php .php3 .php4 .php5 .php7 ; Pass environment variables like LD_LIBRARY_PATH. All $VARIABLEs are taken from ; the current environment. ; Default Value: clean env ;env[HOSTNAME] = $HOSTNAME ;env[PATH] = /usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin ;env[TMP] = /tmp ;env[TMPDIR] = /tmp ;env[TEMP] = /tmp ; Additional php.ini defines, specific to this pool of workers. These settings ; overwrite the values previously defined in the php.ini. The directives are the ; same as the PHP SAPI: ; php_value/php_flag - you can set classic ini defines which can ; be overwritten from PHP call 'ini_set'. ; php_admin_value/php_admin_flag - these directives won't be overwritten by ; PHP call 'ini_set' ; For php_*flag, valid values are on, off, 1, 0, true, false, yes or no. ; Defining 'extension' will load the corresponding shared extension from ; extension_dir. Defining 'disable_functions' or 'disable_classes' will not ; overwrite previously defined php.ini values, but will append the new value ; instead. ; Default Value: nothing is defined by default except the values in php.ini and ; specified at startup with the -d argument ;php_admin_value[sendmail_path] = /usr/sbin/sendmail -t -i -f www@my.domain.com ;php_flag[display_errors] = off php_admin_value[error_log] = /var/log/php-fpm/www-error.log php_admin_flag[log_errors] = on ;php_admin_value[memory_limit] = 128M ; Set session path to a directory owned by process user php_value[session.save_handler] = files php_value[session.save_path] = /var/lib/php/session php_value[soap.wsdl_cache_dir] = /var/lib/php/wsdlcache [root@gitleb wordpress_playbooks]# cat roles/wordpress/templates/nginx.conf.j2 # For more information on configuration, see: user {{ user }}; worker_processes {{ worker_processes }}; error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; pid /var/run/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections {{ max_open_file }}; } http { include /etc/nginx/mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #gzip on; # Load config files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory # The default server is in conf.d/default.conf #include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; server { listen {{ port }} default_server; server_name {{ server_name }}; root {{ root }}; #charset koi8-r; location / { index index.html index.htm index.php; } location ~ .php$ { try_files $uri =404; fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php-fpm/php-fpm.sock; fastcgi_index index.php; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; include fastcgi_params; } } } [root@gitleb wordpress_playbooks]# cat roles/wordpress/tasks/main.yml - name: Update yum dependency shell: 'yum update -y warn=False' - name: Disable system firewall service: name=firewalld state=stopped - name: Disable SELINX selinux: state=disabled - name: Setup epel yum source for nginx and mariadb(mysql) yum: pkg=epel-release state=latest - name: Setup webtatic yum source for php-fpm yum: name=https://mirror.webtatic.com/yum/el7/webtatic-release.rpm - name: Ensure nginx is at the latest version yum: pkg=nginx state=latest - name: Write the nginx config file template: src=roles/wordpress/templates/nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf - name: Create nginx root folder file: 'path={{ root }} state=directory owner={{ user }} group={{ user }} mode=0755' - name: Copy info.php to remote copy: 'remote_src=no src=roles/wordpress/files/info.php dest=/data/www/info.php mode=0755' - name: Restart nginx service service: name=nginx state=restarted - name: Setup php-fpm command: 'yum install -y php70w php70w-fpm php70w-common php70w-mysql php70w-gd php70w-xml php70w-mbstring php70w-mcrypt warn=False' - name: Restart php-fpm service service: name=php-fpm state=restarted - name: Copy php-fpm config file to remote copy: 'remote_src=no src=roles/wordpress/files/www.conf dest=/etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf mode=0755 owner={{ user }} group={{ user }} force=yes' - name: Restart php-fpm service service: name=php-fpm state=restarted - name: Run the health check locally shell: "sh roles/wordpress/files/health_check.sh {{ server_name }} {{ port }}" delegate_to: localhost register: health_status - debug: msg="{{ health_status.stdout }}" - name: Setup mariadb(mysql) command: "yum install -y mariadb mariadb-server warn=False" - name: Backup current www folder shell: 'mv {{ root }} {{ backup_to }}' - name: Close git ssl verification shell: 'git config --global http.sslVerify false' - name: Clone WordPress repo to remote git: "repo=https://{{ gitlab_user | urlencode }}:{{ gitlab_pass | urlencode }}@gitlab.example.com/root/Wordpress-project.git dest=/data/www version={{ branch }}" when: project == 'wordpress' - name: Change www folder permission file: "path=/data/www mode=0755 owner={{ user }} group={{ user }}"
git 操作
[root@gitleb wordpress_playbooks]# git pull [root@gitleb wordpress_playbooks]# git add . [root@gitleb wordpress_playbooks]# git commit -m"First commit" [root@gitleb wordpress_playbooks]# git push origin master Username for 'https://gitlab.example.com': root Password for 'https://root@gitlab.example.com': Counting objects: 21, done. Delta compression using up to 2 threads. Compressing objects: 100% (15/15), done. Writing objects: 100% (19/19), 8.85 KiB | 0 bytes/s, done. Total 19 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0) To https://gitlab.example.com/root/ansible-playbook-repo.git 022c2c3..e225d45 master -> master

jenkins 界面操作
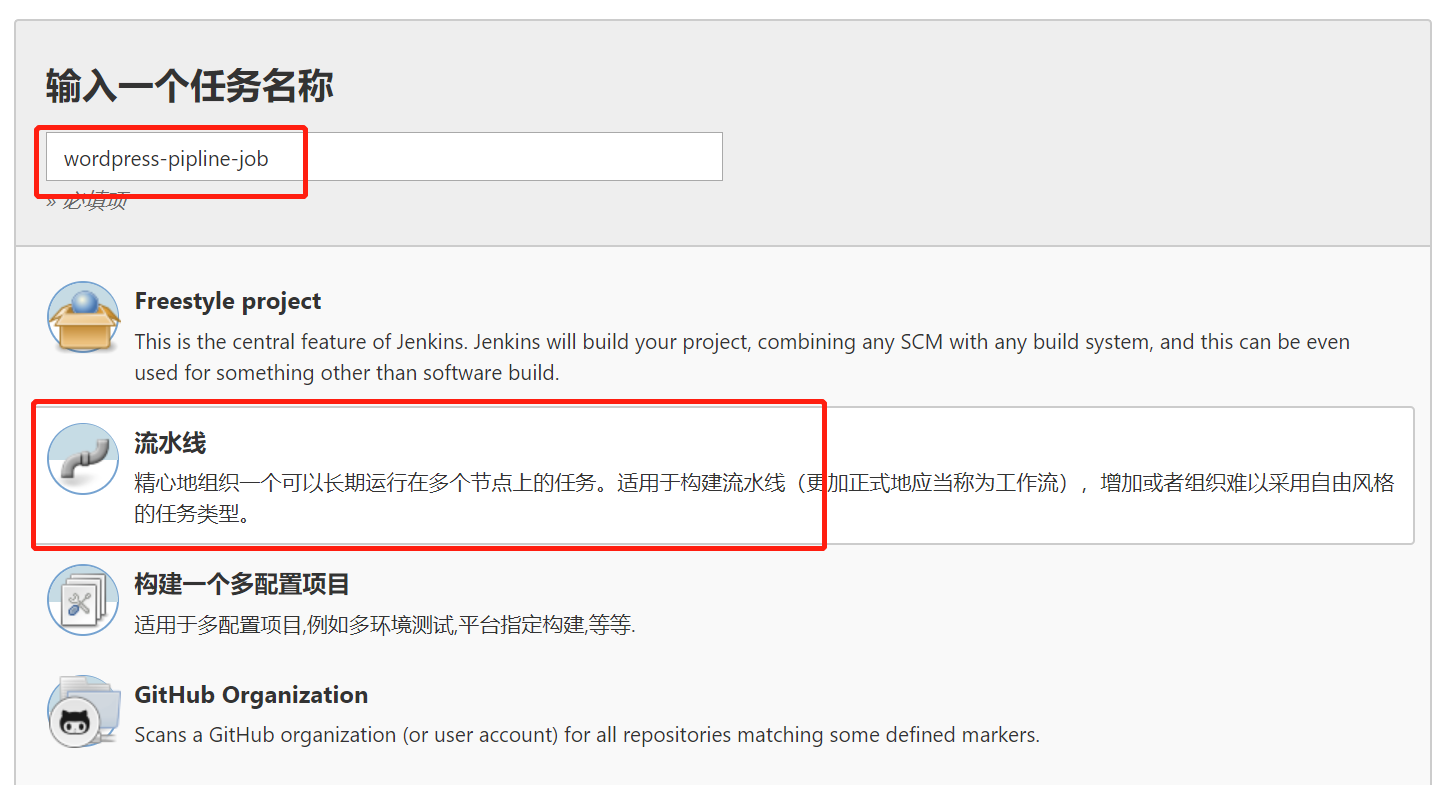
注意凭据的更换!!

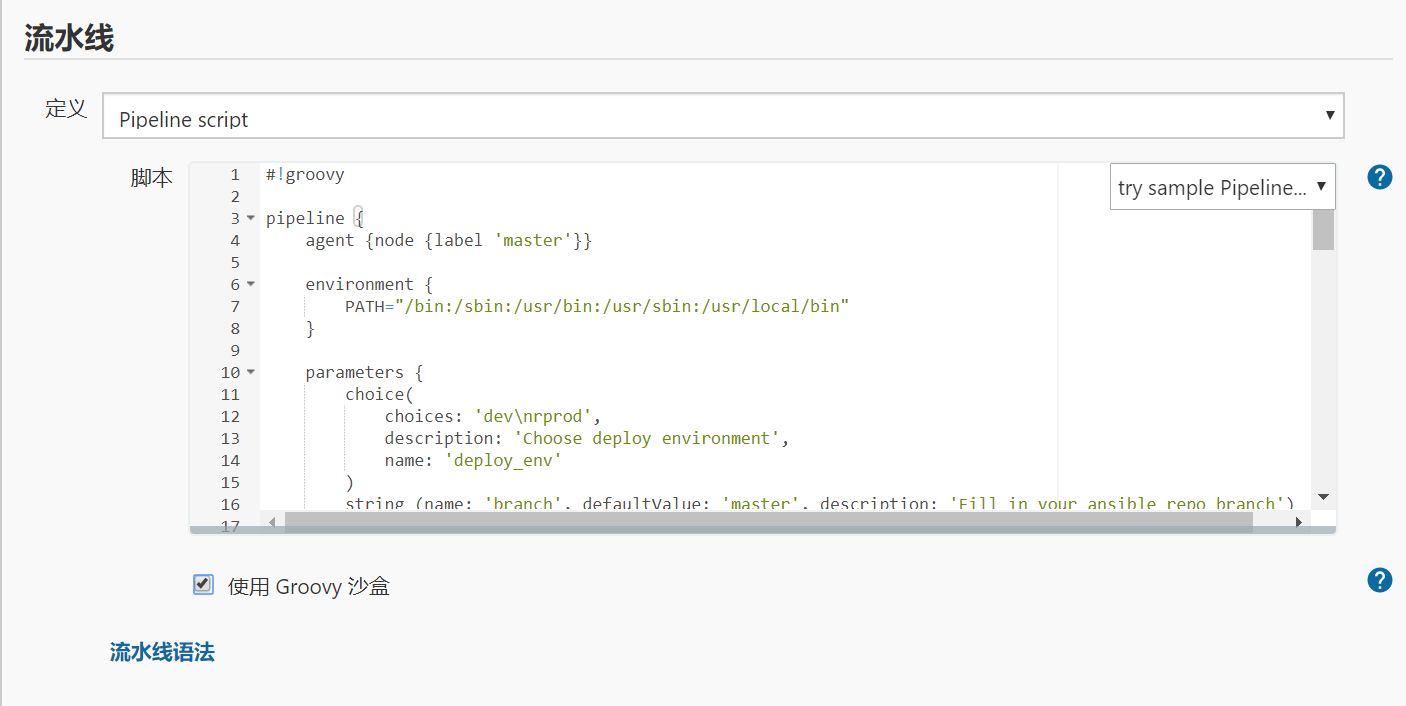
pipline脚本

#!groovy pipeline { agent {node {label 'master'}} environment { PATH="/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/local/bin" } parameters { choice( choices: 'dev rprod', description: 'Choose deploy environment', name: 'deploy_env' ) string (name: 'branch', defaultValue: 'master', description: 'Fill in your ansible repo branch') } stages { stage ("Pull deploy code") { steps{ sh 'git config --global http.sslVerify false' dir ("${env.WORKSPACE}"){ git branch: 'master', credentialsId: '9aa11671-aab9-47c7-a5e1-a4be146bd587', url: 'https://gitlab.example.com/root/ansible-playbook-repo.git' } } } stage ("Check env") { steps { sh """ set +x user=`whoami` if [ $user == deploy ] then echo "[INFO] Current deployment user is $user" source /home/deploy/.py3-a2.5-env/bin/activate source /home/deploy/.py3-a2.5-env/ansible/hacking/env-setup -q echo "[INFO] Current python version" python --version echo "[INFO] Current ansible version" ansible-playbook --version echo "[INFO] Remote system disk space" ssh root@test.example.com df -h echo "[INFO] Rmote system RAM" ssh root@test.example.com free -m else echo "Deployment user is incorrect, please check" fi set -x """ } } stage ("Anisble deployment") { steps { input "Do you approve the deployment?" dir("${env.WORKSPACE}/wordpress_playbooks"){ echo "[INFO] Start deployment" sh """ set +x source /home/deploy/.py3-a2.5-env/bin/activate source /home/deploy/.py3-a2.5-env/ansible/hacking/env-setup -q ansible-playbook -i inventory/$deploy_env ./deploy.yml -e project=wordpress -e branch=$branch -e env=$deploy_env set -x """ echo "[INFO] Deployment finished..." } } } } }
开始构建
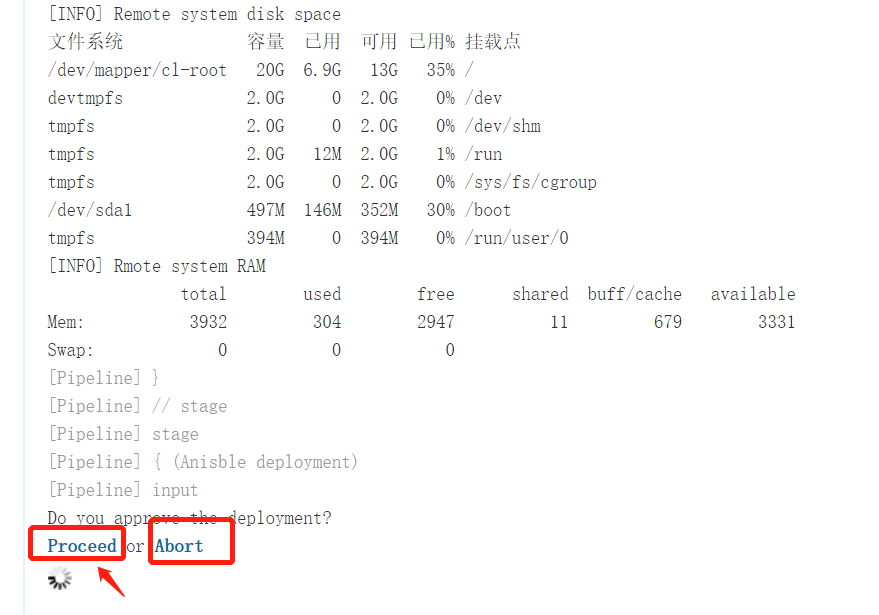

注意:由于需要拉取wordpress 源代码,所以最好将源代码上传到gitlab或者去github 拉取!构建才能成功。
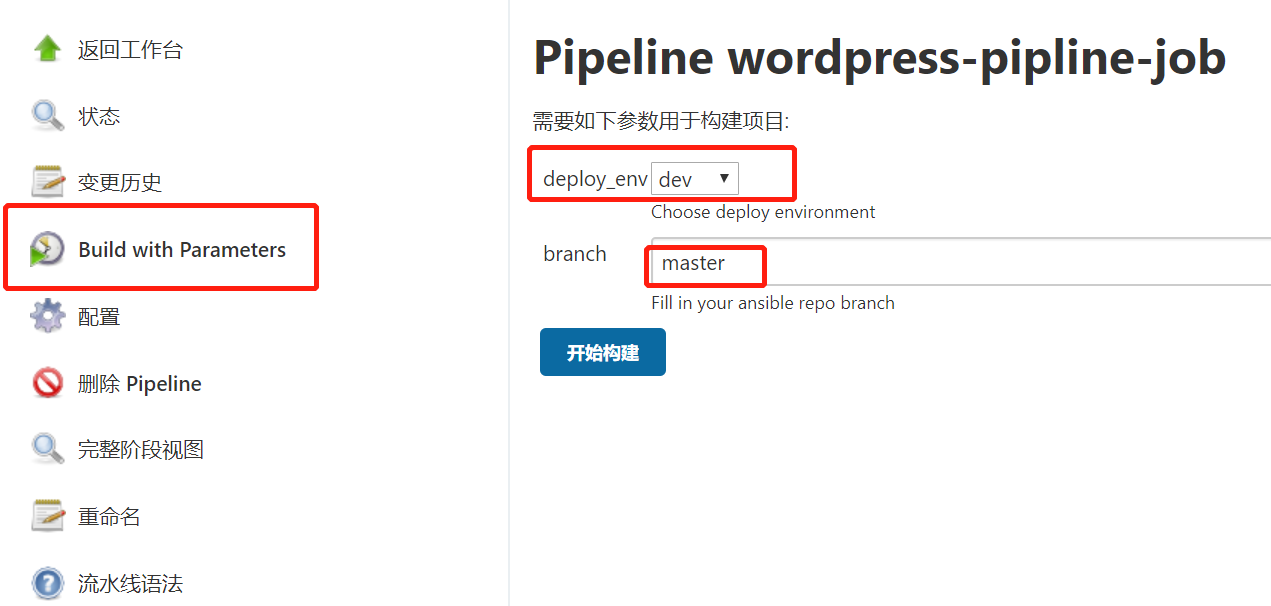

此时ansible 持续交付流程完成,由于mysql作为一个数据库系统,在线上平台,不能作为持续交付的部署流程,不能重复的进行初始化构建,否则会导致数据库出现问题,所以需要手动处理;
二、登录(目标)远程主机,进行数据库的初始化操作和设置管理员密码,最终完成wordpress 的初始化安装工作;
1.数据库操作
[root@testbox ~]# systemctl start mysqld [root@testbox ~]# mysql_secure_installation Securing the MySQL server deployment. Enter password for user root: #回车 ..... 省略过程 按照提示进行输入完成mysql的初始化工作 [root@testbox ~]# mysql -u root -p Enter password: 输入密码 mysql> create database wordpress character set utf8; #创建wordpress 数据库 Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
2.网页输入目标主机的主机名进行wordpress 的安装工作
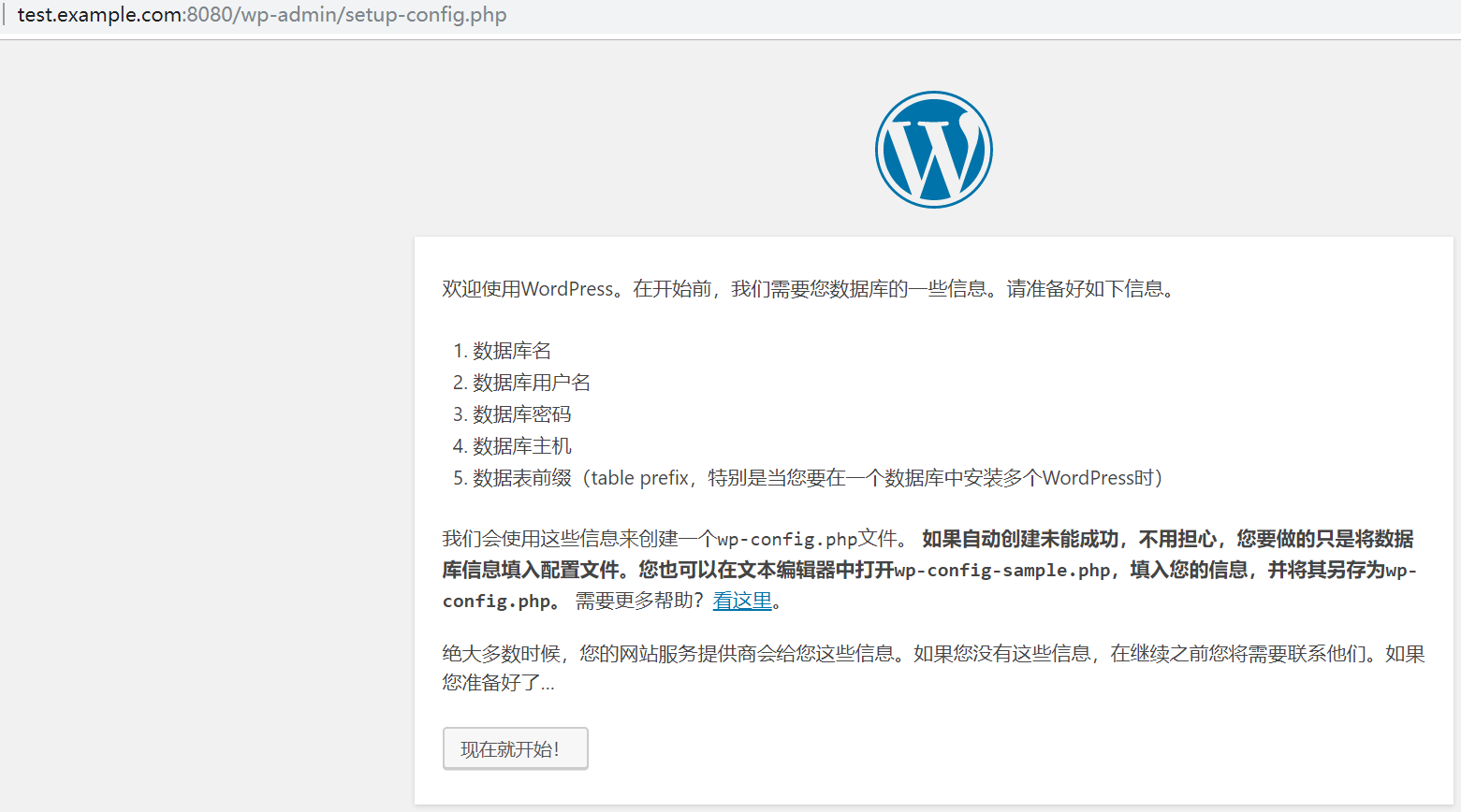
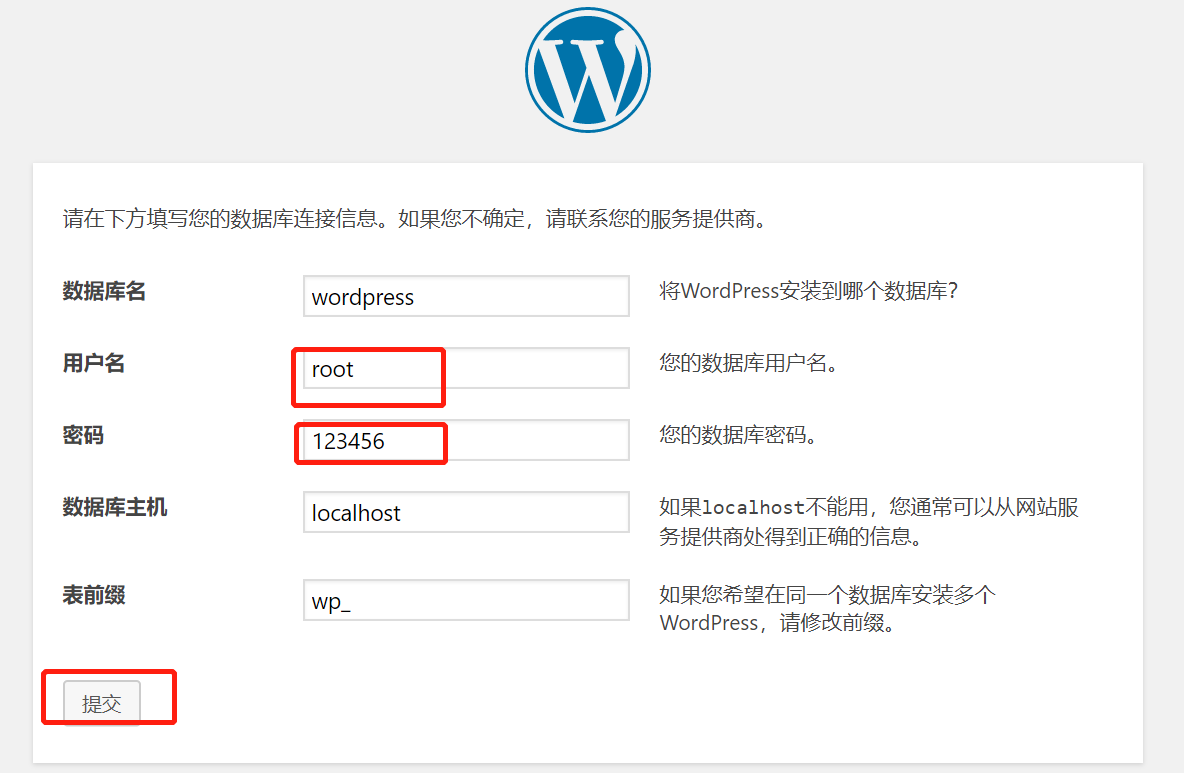
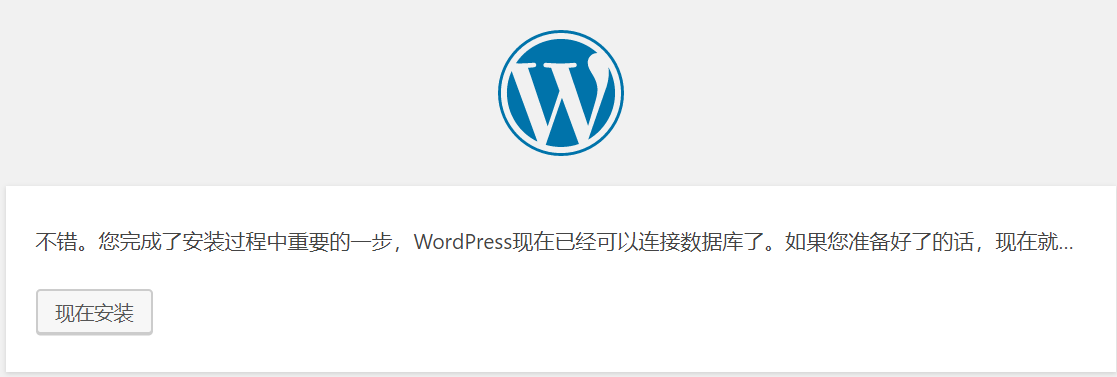
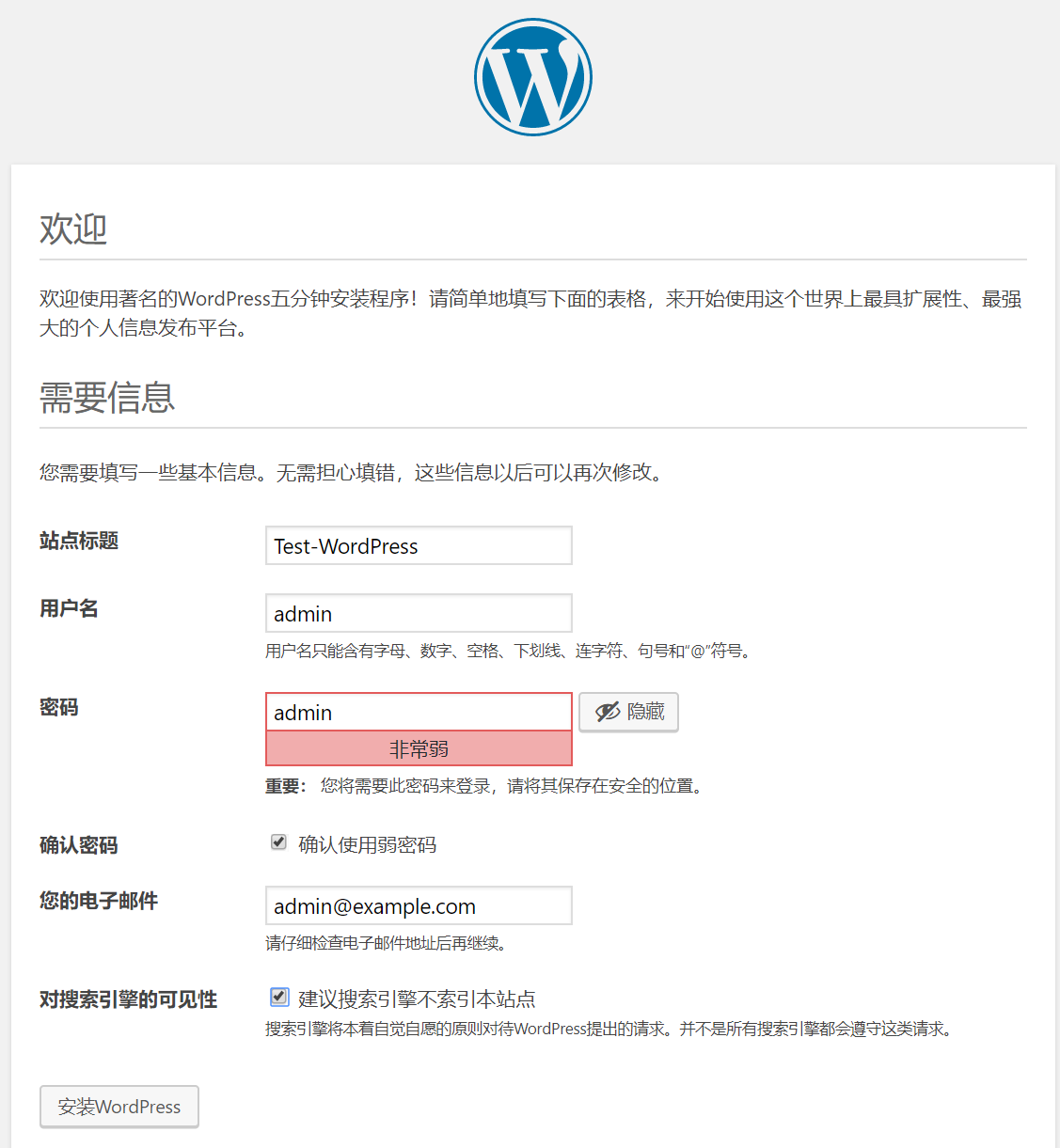
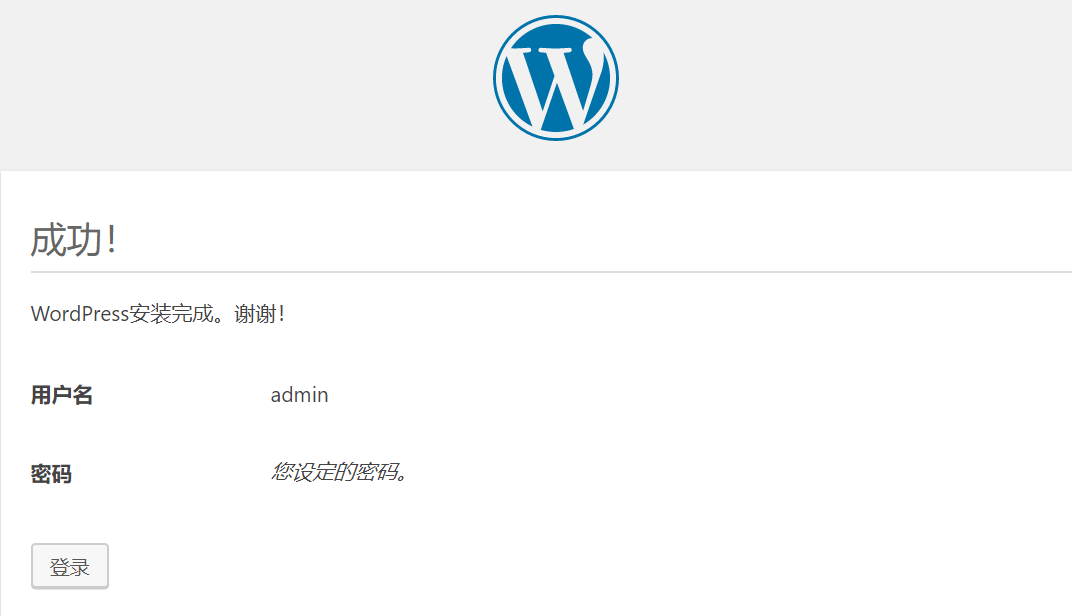
3.进入wordpress 的后台管理界面
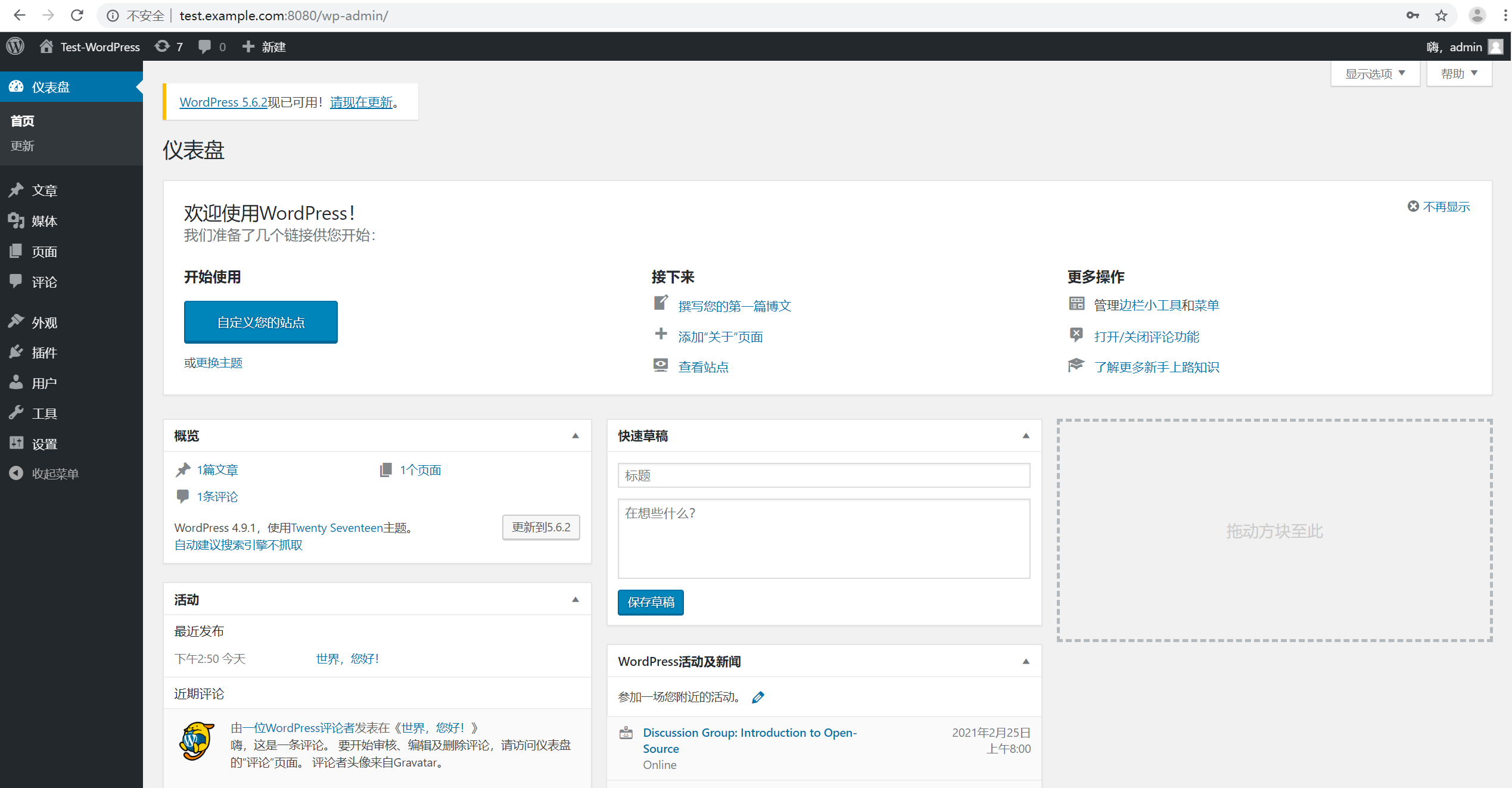
4.刷新url http://test.example.com:8080/
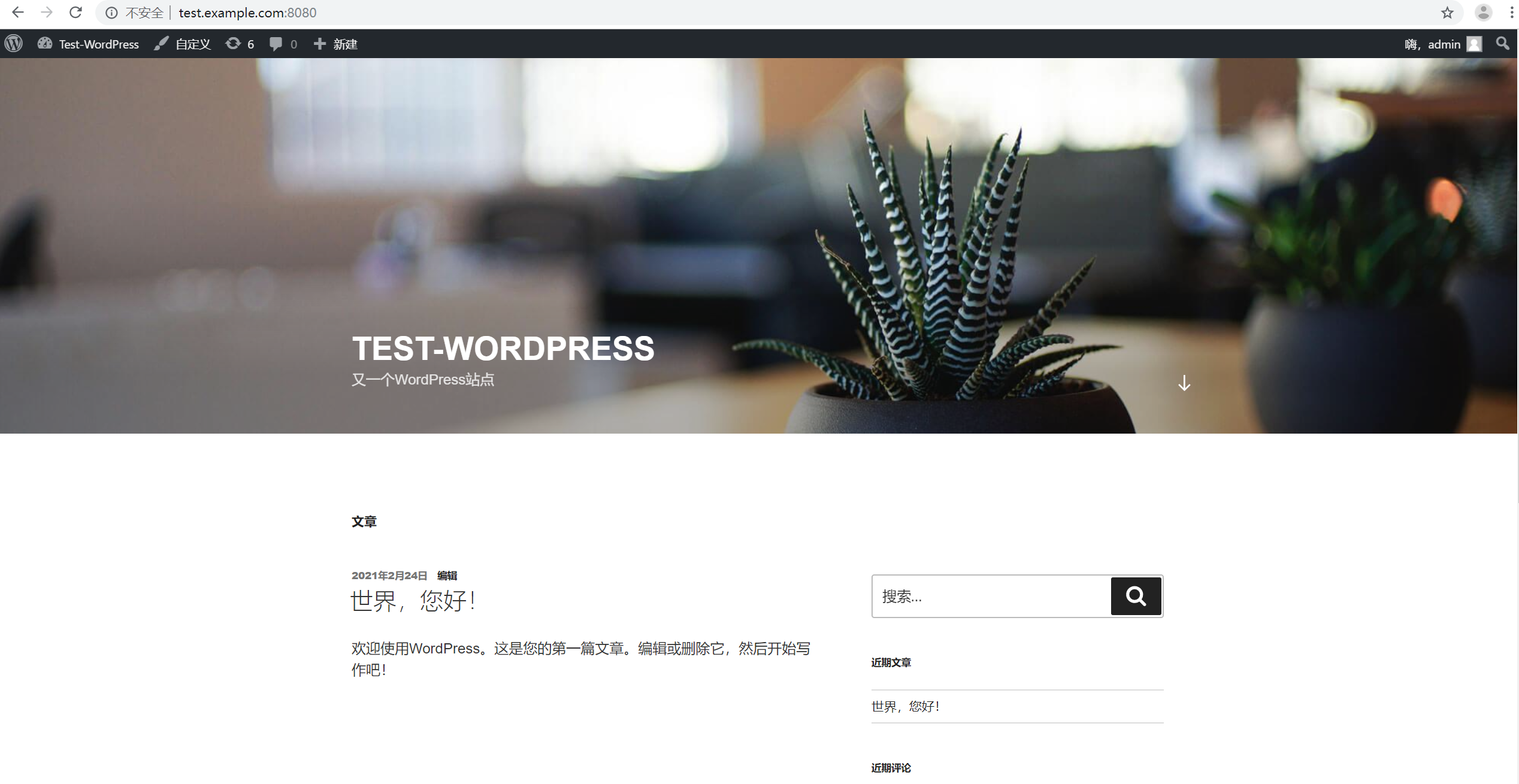
结论:可以看到 wordpress 站点已经成功的安装, 至此,利用Jenkins下的pipline job 编写工作流部署脚本,
配合gitlab 抓取 ansible部署脚本和wordpress 网站源码,以及ansible 的远程推送,实现nginx +mysql + php +wordpress
自动化部署交付,最终将wordpress 博客一键部署到远程主机上,实现产品持续交付的目的。
