需求:在一个vue的项目中,我们需要从一个列表页面点击列表中的某一个详情页面,从详情页面返回不刷新列表,而从列表的上一个页面重新进入列表页面则需要刷新列表。
而浏览器的机制则是每一次的页面打开都会重新执行所有的程序,所以这个功能并不能直接实现。而vue-router给我们提供了一个叫scrollBehavior的回调函数,我门可以用这个方法结合keep-alive能很好的实现这个功能,下面第一步附上实现代码:
首先我们创建a,b,c,d四个页面,在路由的meta属性中添加需要缓存的页面标识(isKeepAlive):
import Vue from 'vue' import Router from 'vue-router' const HelloWorld = () => import('@/components/HelloWorld') const A = () => import('@/components/router-return/router-a') const B = () => import('@/components/router-return/router-b') const C = () => import('@/components/router-return/router-c') const D = () => import('@/components/router-return/router-d') Vue.use(Router) const routes = [ { path: '/', name: 'HelloWorld', component: HelloWorld }, { path: '/a', name: 'A', component: A }, { path: '/b', name: 'B', component: B, meta: { isKeepAlive: true } }, { path: '/c', name: 'C', component: C }, { path: '/d', name: 'D', component: D } ]
然后我们修改app.vue页面:
<template>
<div id="app">
<img src="./assets/logo.png">
<keep-alive>
<router-view v-if="$route.meta.isKeepAlive"/>
</keep-alive>
<router-view v-if="!$route.meta.isKeepAlive"/>
</div>
</template>
最后我们添加new Router方法的scrollBehavior的回调处理方法:
export default new Router({ routes, scrollBehavior (to, from, savedPosition) { // 从第二页返回首页时savedPosition为undefined if (savedPosition || typeof savedPosition === 'undefined') { // 只处理设置了路由元信息的组件 from.meta.isKeepAlive = typeof from.meta.isKeepAlive === 'undefined' ? undefined : false to.meta.isKeepAlive = typeof to.meta.isKeepAlive === 'undefined' ? undefined : true if (savedPosition) { return savedPosition } } else { from.meta.isKeepAlive = typeof from.meta.isKeepAlive === 'undefined' ? undefined : true to.meta.isKeepAlive = typeof to.meta.isKeepAlive === 'undefined' ? undefined : false } } })
在scrollBehavior方法中的savedPosition参数,每一次点击进去的值为null,而点击浏览器的前进与后退则会返回上一次该页面离开时候的pageXOffset与pageYOffset的值,然后我们可以根据这个返回的值来修改路由信息里面的isKeepAlive值来控制是否显示缓存。
我们来看下vue-router里面scrollBehavior执行的源码:
在vue-router.js的1547行发现:
function handleScroll ( router, to, from, isPop) { if (!router.app) { return } var behavior = router.options.scrollBehavior; if (!behavior) { return } { assert(typeof behavior === 'function', "scrollBehavior must be a function"); } // wait until re-render finishes before scrolling router.app.$nextTick(function () { // 得到该页面之前的position值,如果没有缓存则返回null var position = getScrollPosition(); var shouldScroll = behavior(to, from, isPop ? position : null); if (!shouldScroll) { return } if (typeof shouldScroll.then === 'function') { shouldScroll.then(function (shouldScroll) { // 移动页面到指定位置 scrollToPosition((shouldScroll), position); }).catch(function (err) { { assert(false, err.toString()); } }); } else { // 移动页面到指定位置 scrollToPosition(shouldScroll, position); } }); }
再看下上面方法中用到的几个主要方法的写法:
// getScrollPosition 得到移动的坐标 function getScrollPosition () { var key = getStateKey(); if (key) { return positionStore[key] } } // scrollToPosition 页面移动方法 function scrollToPosition (shouldScroll, position) { var isObject = typeof shouldScroll === 'object'; if (isObject && typeof shouldScroll.selector === 'string') { var el = document.querySelector(shouldScroll.selector); if (el) { var offset = shouldScroll.offset && typeof shouldScroll.offset === 'object' ? shouldScroll.offset : {}; offset = normalizeOffset(offset); position = getElementPosition(el, offset); } else if (isValidPosition(shouldScroll)) { position = normalizePosition(shouldScroll); } } else if (isObject && isValidPosition(shouldScroll)) { position = normalizePosition(shouldScroll); } if (position) { window.scrollTo(position.x, position.y); } }
然后我们看看vue-router是怎么缓存页面x,y的坐标的,上面的getScrollPosition是用来获取坐标的,那么肯定也有保存坐标的方法,在getScrollPosition的上面一个方法则是saveScrollPosition就是保存的方法:
// saveScrollPosition function saveScrollPosition () { var key = getStateKey(); if (key) { positionStore[key] = { x: window.pageXOffset, y: window.pageYOffset }; } }
而这个保存的方法会有一个key值是缓存的标识,继续查找getStateKey:
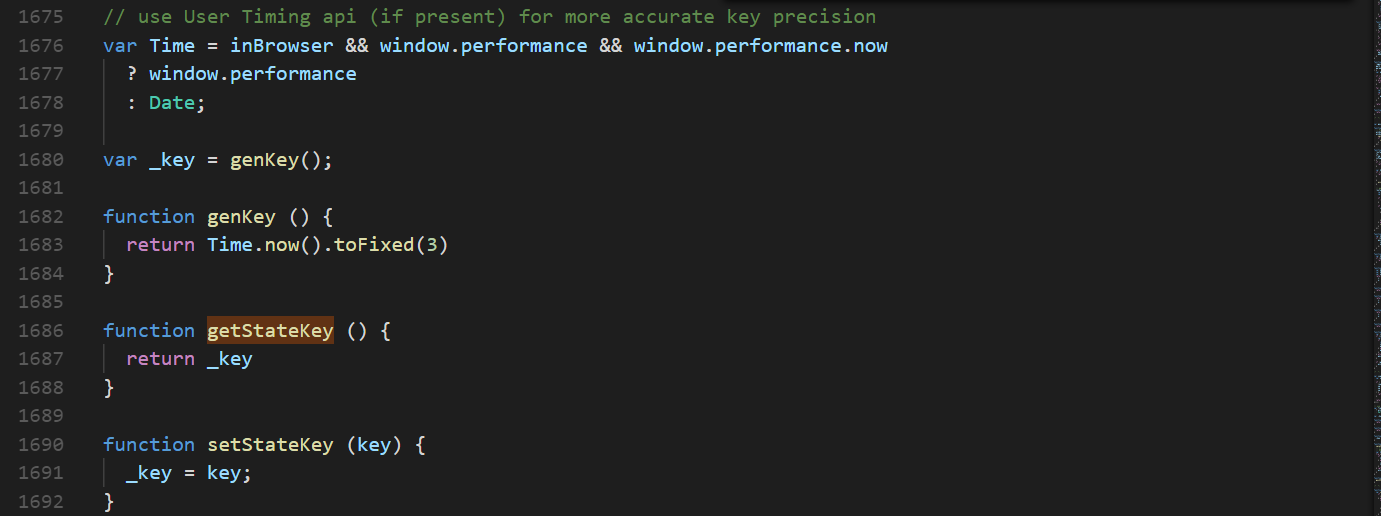
根据上面代码发现key值就是一个时间值。而setStateKey则是一个key值更新的方法,然后继续查找setStateKey执行的地方:
function setupScroll () { // Fix for #1585 for Firefox window.history.replaceState({ key: getStateKey() }, ''); window.addEventListener('popstate', function (e) { saveScrollPosition(); if (e.state && e.state.key) { setStateKey(e.state.key); } }); }
然后发现该方法执行的地方是popState执行的时候,而key的来源则是popState返回参数里面的state属性里面,而state值的设定则是pushstate执行的时候传进去的,所以我们继续查pushstate执行的方法:
function pushState (url, replace) { saveScrollPosition(); // try...catch the pushState call to get around Safari // DOM Exception 18 where it limits to 100 pushState calls var history = window.history; try { if (replace) { history.replaceState({ key: _key }, '', url); } else { _key = genKey(); history.pushState({ key: _key }, '', url); } } catch (e) { window.location[replace ? 'replace' : 'assign'](url); } }
根据上面代码发现,每次push的时候都会去生成一个当前时间的key值保存在state里面,作用于popstate时使用。
那么到此scrollBehavior方法的整个执行逻辑就清楚了:该方法最主要的是运用了浏览器的popstate方法只会在浏览器回退与前进才会执行的机制,在页面进入时生成一个唯一的key值保存在state里面,离开的时候将页面滚动位置保存在state里面的唯一key值上。每次pushstate的时候key值都是最新的,没有缓存所以返回null,而执行popstate的时候state里面的key都有缓存,则返回上次离开时候的滚动坐标。