前言
Spring MVC属于SpringFrameWork的后续产品,已经融合在Spring Web Flow里面。Spring 框架提供了构建 Web 应用程序的全功能 MVC 模块。使用 Spring 可插入的 MVC 架构,从而在使用Spring进行WEB开发时,可以选择使用Spring的Spring MVC框架或集成其他MVC开发框架,如Struts1(现在一般不用),Struts 2(一般老项目使用)等。
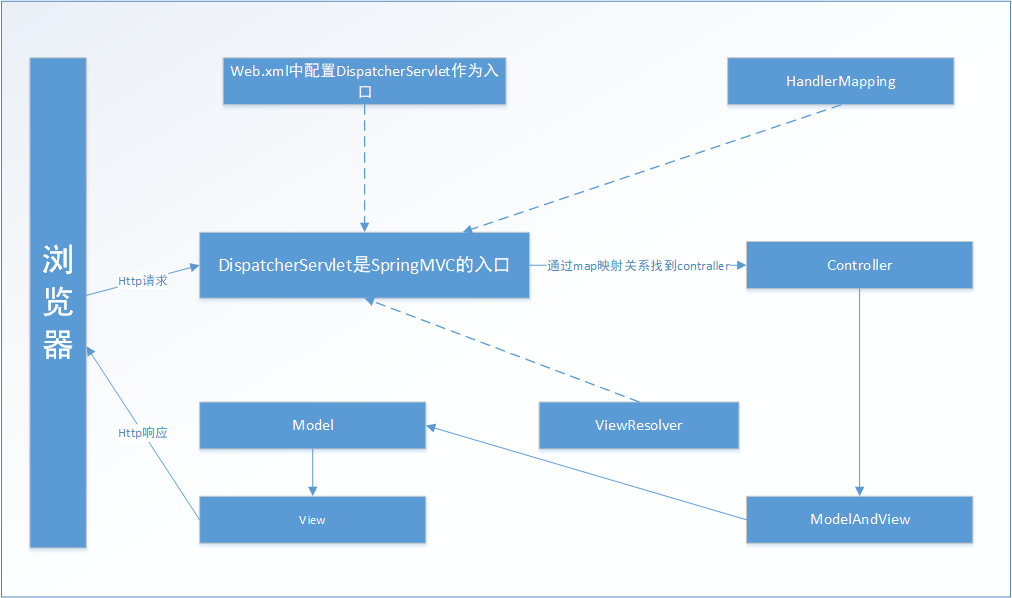
原理
SpringMVC 原理图
代码
创建一个web项目
准备两个jar包(dom4j-1.6.1.jar和javax.servlet-api-3.1.0.jar)
百度网盘下载地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1BjC34AYtjf17g5nZ2Hr4HA 提取码: 6yad
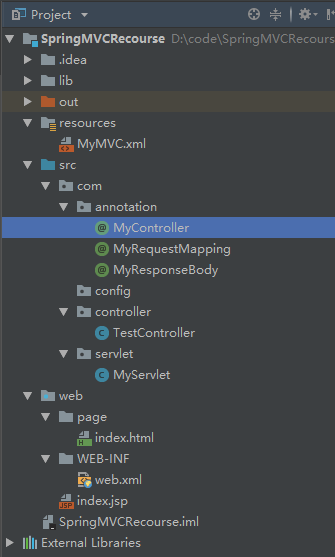
完整目录结构如下:
MyMVC.xml
<beans> <compentScan package="com"></compentScan> <view prefix = "/page/" suffix=".html"></view> </beans>
MyController
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyController { }
MyRequestMapping
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyRequestMapping { /** * url 的拦截地址 * @return */ String value() default ""; }
MyResponseBody
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyResponseBody { }
TestController
import com.annotation.MyController; import com.annotation.MyRequestMapping; import com.annotation.MyResponseBody; @MyController public class TestController { @MyRequestMapping(value = "/test.do") @MyResponseBody public Object test(String name){ return "hello world"; } @MyRequestMapping(value = "/test1.do") public Object test1(String name){ return "index"; } }
MyServlet
import com.annotation.MyController; import com.annotation.MyRequestMapping; import com.annotation.MyResponseBody; import org.dom4j.Document; import org.dom4j.DocumentException; import org.dom4j.Element; import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader; import javax.servlet.ServletConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Parameter; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet { private static String COMPENT_SCAN_ELEMENT_PACKAGE_NAME= "package"; private static String COMPENT_SCAN_ELEMENT_NAME = "compentScan"; private static String XML_PATH_LOCAL= "xmlPathLocal"; /** * 视图前缀 */ private static String prefix = ""; /** * 视图后缀 */ private static String suffix = ""; private static String projectPath = MyServlet.class.getResource("/").getPath(); private static Map<String,Method> methodMap = new HashMap<>(); /** * Tomcat容器会根据web.xml中的配置,执行init方法(类需要继承HttpServlet) * 第一步:通过tomcat解析web.xml的方式,获取xmlPathLocal对应的自定义XML。 * 第二步:解析自定义的xml(MyMVC.xml) * 第三步:根据MyMVC.xml,设置的规则扫描controller和视图文件,并将对应信息写入methodMap中 * @param config * @throws ServletException */ @Override public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { // 进行url转义会将空格变成%20,所以需要转化回来 projectPath = projectPath.replaceAll("%20"," "); String initParameter = config.getInitParameter(XML_PATH_LOCAL); // 解析xml文件 file:xml 文件对象 File file = new File(projectPath + "//" + initParameter); // 使用dom4j解析XML Document prase = prase(file); Element rootElement = prase.getRootElement(); Element view = rootElement.element("view"); prefix = view.attribute("prefix").getValue(); suffix = view.attribute("suffix").getValue(); Element compentScanEle = rootElement.element(COMPENT_SCAN_ELEMENT_NAME); String value = compentScanEle.attribute(COMPENT_SCAN_ELEMENT_PACKAGE_NAME).getValue(); // 根据解析后信息,扫描controller和视图文件 scanProjectByPath(projectPath+"\"+value); } /** * 扫描文件 * @param path */ public void scanProjectByPath(String path){ File file =new File(path); //递归解析项目所有文件 scanFile(file); } /** * 递归扫描 * @param file */ public void scanFile(File file){ //递归解析项目 if (file.isDirectory()){ for (File file1 : file.listFiles()) { scanFile(file1); } }else{ String filePath = file.getPath(); String suffix =filePath.substring(filePath.lastIndexOf(".")); if (suffix.equals(".class")){ String classPath = filePath.replace(new File(projectPath).getPath()+"\",""); classPath = classPath.replaceAll("\\","."); String className = classPath.substring(0,classPath.lastIndexOf(".")); try { Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className); if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)) { MyRequestMapping classRequestMapping = clazz.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class); String classRequestMappingUrl = ""; if (classRequestMapping!=null){ classRequestMappingUrl = classRequestMapping.value(); } for (Method method : clazz.getDeclaredMethods()) { if (!method.isSynthetic()) { MyRequestMapping annotation = method.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class); if (annotation != null) { String methodRequsetMappingUrl = ""; methodRequsetMappingUrl = annotation.value(); System.out.println("类:"+clazz.getName()+"的"+method.getName()+"方法被映射到了"+classRequestMappingUrl+methodRequsetMappingUrl+"上面"); methodMap.put(classRequestMappingUrl+methodRequsetMappingUrl,method); } } } } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } /** * 通过dom4j 将文件变成对象 * @param file * @return */ public Document prase(File file){ SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader(); try { return saxReader.read(file); } catch (DocumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doPost(req, resp); } /** * 获取请求,然后转发到对应controller中 * @param req * @param resp * @throws ServletException * @throws IOException */ @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { //拿到请求的URI String requestURI = req.getRequestURI(); Method method = methodMap.get(requestURI); if (method!=null){ //jdk8以前 直接拿参数名称 拿不到 Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); Object[] objects = new Object[parameters.length]; for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) { Parameter parameter = parameters[i]; String name = parameter.getName(); Class type = parameter.getType(); if (type.equals(String.class)){ objects[i] = req.getParameter(name); }else if(type.equals(HttpServletRequest.class)){ objects[i] = req; }else if(type.equals(HttpServletResponse.class)){ objects[i] = resp; }else{ try { Object o = type.newInstance(); for (Field field : type.getDeclaredFields()) { field.setAccessible(true); String fieldName = field.getName(); field.set(o,req.getParameter(fieldName)); } objects[i] = o; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } try { Object o= null; o = method.getDeclaringClass().newInstance(); Object invoke = method.invoke(o, objects); // 判断返回值是否是Void if (!method.getReturnType().equals(Void.class)){ MyResponseBody annotation = method.getAnnotation(MyResponseBody.class); if (annotation!=null){ //提供接口来做这个事情 resp.getWriter().write(String.valueOf(invoke)); }else { // 返回视图信息 req.getRequestDispatcher(prefix+String.valueOf(invoke)+suffix).forward(req,resp); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }else { resp.setStatus(404); } } }
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>这里是index.xml</h1> </body> </html>
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name> <servlet> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.servlet.MyServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <!-- contextConfigLocation 是参数名称,该参数的值包含 Spring MVC 的配置文件路径 --> <param-name>xmlPathLocal</param-name> <param-value>MyMVC.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
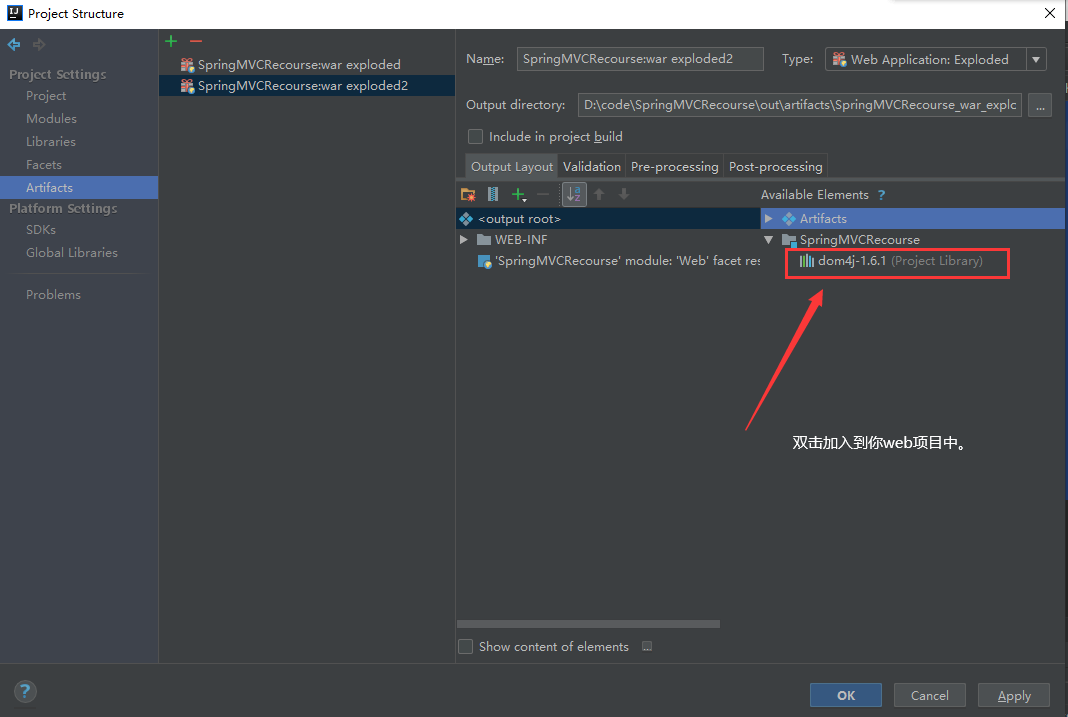
部署tomcat
直接部署会缺少jar包
总结
通过这方式可以让我们更好的理解SpringNVC的原理,遇到问题也可以帮助你更好去处理。以上案例只是简单的模拟,真正的SpringMVC是有很强的扩展性,这大概也是为什么大家都选择用的原因。