一、静态联编与动态联编
看段代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 const double PI=3.1415; 5 6 class point 7 { 8 private: 9 int x,y; 10 11 public: 12 point(int x=0,int y=0) 13 { 14 this->x=x,this->y=y; 15 } 16 double Area() 17 { 18 return 0.0; 19 } 20 }; 21 class circle:public point 22 { 23 private: 24 double radius; 25 26 public: 27 circle(int x,int y,double r):point(x,y) 28 { 29 radius=r; 30 } 31 double Area() 32 { 33 return PI*radius*radius; 34 } 35 }; 36 37 int main() 38 { 39 point p1(10,10); 40 cout<<"p1.Area()="<<p1.Area()<<endl; 41 circle c1(10,10,20); 42 cout<<"c1.Area()="<<c1.Area()<<endl; 43 point *pp; 44 pp=&c1; 45 cout<<"pp->Area()="<<pp->Area()<<endl; 46 point &rp=c1; 47 cout<<"rp.Area()="<<rp.Area()<<endl; 48 return 0; 49 }
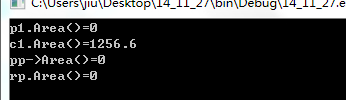
这里是静态联编,编译时调用体已与函数绑定好了。由于pp和rp都是基类指针,调用的是基类的Area()。但实际上我们用指针或者引用都是为了操作派生类,故而这里与我们的初衷不符。
继而我们需要用到虚函数来达到目的,实现动态联编在运行时才决定调用哪个函数。仅仅需要在把基类的Area()加个修饰符virtual即可。

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 const double PI=3.1415; 5 6 class point 7 { 8 private: 9 int x,y; 10 11 public: 12 point(int x=0,int y=0) 13 { 14 this->x=x,this->y=y; 15 } 16 virtual double Area()//仅仅修改这里 17 { 18 return 0.0; 19 } 20 }; 21 class circle:public point 22 { 23 private: 24 double radius; 25 26 public: 27 circle(int x,int y,double r):point(x,y) 28 { 29 radius=r; 30 } 31 double Area() 32 { 33 return PI*radius*radius; 34 } 35 }; 36 37 int main() 38 { 39 point p1(10,10); 40 cout<<"p1.Area()="<<p1.Area()<<endl; 41 circle c1(10,10,20); 42 cout<<"c1.Area()="<<c1.Area()<<endl; 43 point *pp; 44 pp=&c1; 45 cout<<"pp->Area()="<<pp->Area()<<endl; 46 point &rp=c1; 47 cout<<"rp.Area()="<<rp.Area()<<endl; 48 return 0; 49 }
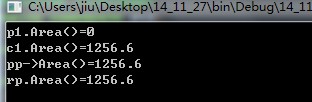
pp和rp调用的都是派生类的成员函数,达到目的。
二、虚函数
1.格式即在类成员函数的定义格式前加上virtual修饰符。
2.使用条件:
(1).应满足类型兼容规则。
(2).在基类中定义虚函数,并且在派生类中要重新定义虚函数。
(3).要由成员函数或者是通过指针、引用访问虚函数。
3.特点:如果基类的某个成员函数被说明为虚函数,则无论被公有继承多少层,它仍保持其虚函数特性。在正常情况下,对虚函数的访问与其他成员函数完全一样,只有通过基类指针或引用来调用虚函数时才体现虚函数与一般函数的不同。
4.注意:虚函数不能为静态成员函数、友元函数、内联函数、构造函数等,可以是析构函数,而且通常把析构函数声明为虚函数。
5.虚析构函数:

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class A 5 { 6 public: 7 virtual ~A() 8 { 9 cout<<"A.."<<endl; 10 } 11 }; 12 class B:public A 13 { 14 public: 15 ~B() 16 { 17 cout<<"B.."<<endl; 18 } 19 }; 20 class C:public B 21 { 22 public: 23 ~C() 24 { 25 cout<<"C.."<<endl; 26 } 27 }; 28 29 int main() 30 { 31 A* a=new C; 32 delete a; 33 return 0; 34 }
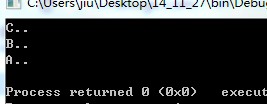
一旦基类的析构函数被声明为虚函数,则派生类的析构函数会自动成为虚函数。基类的虚析构函数可以确保使用基类类型的指针能够自动调用适当的析构函数对不同对象进行清理工作,保证每一层派生类都析构资源,每一层new的资源都逃脱不了,防止内存泄露。
三、抽象类
1.带有至少一个纯虚函数的类称作抽象类。纯虚函数用在基类中,没有具体实现,唯一作用是为派生类提供一个一致的接口。
2.纯虚函数定义的格式:virtual 函数类型 函数名(参数表)=0;
3.特性:
(1):抽象类不能实例化,即不能产生对象,只能通过继承机制生成没有纯虚函数的非抽象派生类,然后再实例化。
(2):派生类可以不给出基类纯虚函数的实现,则派生类本身也成了抽象类,无法实例化。
(3):抽象类不能用作参数类型、函数返回值或强制类型转换。
(4):可以定义一个抽象类的指针或引用,然后指向并访问各派生类成员。
4.来个例子:

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 const double PI=3.1415; 5 6 class point 7 { 8 private: 9 int x,y; 10 11 public: 12 point(int x=0,int y=0) 13 { 14 this->x=x,this->y=y; 15 } 16 virtual double Area() const=0;//纯虚函数 17 }; 18 class circle:public point 19 { 20 private: 21 double radius; 22 23 public: 24 circle(int x,int y,double r):point(x,y) 25 { 26 radius=r; 27 } 28 double Area() const 29 { 30 return PI*radius*radius; 31 } 32 }; 33 34 int main() 35 { 36 circle c1(10,10,20); 37 cout<<"c1.Area()="<<c1.Area()<<endl; 38 point *pp; 39 pp=&c1; 40 cout<<"pp->Area()="<<pp->Area()<<endl; 41 point &rp=c1; 42 cout<<"rp.Area()="<<rp.Area()<<endl; 43 return 0; 44 }
