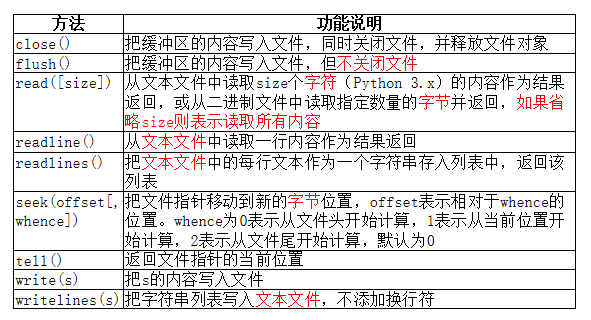
文件操作三步走:打开、读写、关闭。
open(file, mode='r', buffering=-1, encoding=None, errors=None, newline=None, closefd=True, opener=None)
file参数指定了被打开的文件名称。
mode参数指定了打开文件后的处理方式。
encoding参数指定对文本进行编码和解码的方式,只适用于文本模式,可以使用Python支持的任何格式,如GBK、utf8、CP936等等。
文件打开模式

例:向文本文件中写入内容,然后再读出
s = 'Hello world
文本文件的读取方法、文本文件的写入方法
'
with open('sample.txt','w') as fp: #默认使用cp936编码
fp.write(s*5)
#生成的文件放在.py文件所在文件夹
with open('sample.txt') as fp:
print(fp.read())
E:pytho_pycharmvenvScriptspython.exe E:/pytho_pycharm/prac.py
Hello world
文本文件的读取方法、文本文件的写入方法
Hello world
文本文件的读取方法、文本文件的写入方法
Hello world
文本文件的读取方法、文本文件的写入方法
Hello world
文本文件的读取方法、文本文件的写入方法
Hello world
文本文件的读取方法、文本文件的写入方法
Process finished with exit code 0
例:将一个CP936编码格式的文本文件中的内容全部复制到另一个使用UTF8编码的文本文件中。
#将一个CP936编码格式的文本文件中的内容全部复制到另一个使用UTF-8编码的文本文件中
def filecopy(srcc,dstt,srccEncoding,dsttEncoding):
with open(srcc,'r',encoding=srccEncoding) as srcfp:
with open(dstt,'w',encoding=dsttEncoding) as dstfp:
dstfp.write(srcfp.read())
filecopy('sample.txt','sample_new.txt','cp936','utf8')
#读取这两个文件
with open('sample.txt') as fp: #默认为CP936编码
print(fp.read())
print()
with open('sample_new.txt',encoding='utf-8') as fp: #如果是其他编码需要有(encoding = )
print(fp.read())
例:遍历并输出文本文件的所有行内容
with open('sample.txt') as fp:
for line in fp:
print(line,end='')
案例:
根据考试成绩,统计学科等级水平。 分析:某中学对学生的附加科目进行能力测试,并按以下标准统计学科等级水平。
(1)生物和科学两门课都达到60分,总分达到180分为及格;
(2)每门课达到85分,总分达到260分为优秀;
(3)总分不到180分或有任意一门课不到60分,为不及格。
学生成绩原始数据如图所示。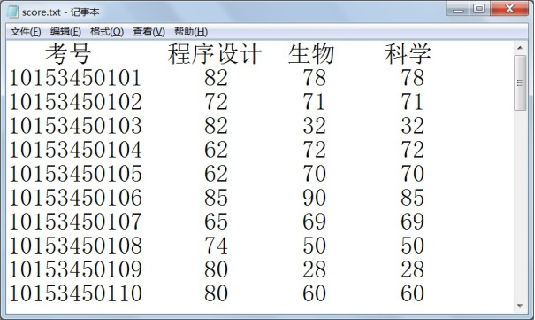
编程要求:从score.txt文件中读取学生成绩数据,判定等级并写入level.txt文件中。
L = list(open('score.txt')) #文件中的每一行都是列表的一个元素
f = open('level.txt','w') #新建level文件夹写入
flag = 1
for s in L:
x = s.split()
if flag:
flag = 0
f.write("%s %s %s %s 是否及格
" % (x[0], x[1], x[2], x[3]))
continue
for i in range(len(x)): #假如一行有多个类别就要用for循环
x[i] = int(x[i])
sum = x[1]+x[2]+x[3]
if x[1]>=85 and x[2]>=85 and x[3]>=85 and sum>=260 :
key = '优秀'
elif x[2]>=60 and x[3]>=60 and sum>=180:
key = '及格'
elif x[1]<60 or x[2]<60 or x[3]<60 or sum<180 :
key = '不及格'
f.write('%d %d %d %d %s
'%(x[0],x[1],x[2],x[3],key))
f.close()
f = open('level.txt')
print(f.read())
s=open('score.txt')
f=open('level.txt','w')
x = s.readline().split()
f.write()
while True:
x=s.readline().split()
if len(x)==0:
break
for i in range(1,len(x)):
x[i]=int(x[i])
sum=x[1]+x[2]+x[3]
if x[1]>=85 and x[2]>=85 and x[3]>=85 and sum>=260:
key = "优秀"
elif x[2]>=60 and x[3]>=60 and sum>=180:
key = "及格"
else:
key = "不及格"
f.write()
s.close()
f.close()