一、概述
1.是什么
简单说, Thymeleaf 是一个跟 Velocity、FreeMarker 类似的模板引擎,它可以完全替代 JSP 。
2.feature
1.Thymeleaf 在有网络和无网络的环境下皆可运行,即它可以让美工在浏览器查看页面的静态效果,也可以让程序员在服务器查看带数据的动态页面效果。这是由于它支持 html 原型,然后在 html 标签里增加额外的属性来达到模板+数据的展示方式。浏览器解释 html 时会忽略未定义的标签属性,所以 thymeleaf 的模板可以静态地运行;当有数据返回到页面时,Thymeleaf 标签会动态地替换掉静态内容,使页面动态显示。
2.Thymeleaf 开箱即用的特性。它提供标准和spring标准两种方言,可以直接套用模板实现JSTL、 OGNL表达式效果,避免每天套模板、该jstl、改标签的困扰。同时开发人员也可以扩展和创建自定义的方言。3. Thymeleaf 提供spring标准方言和一个与 SpringMVC 完美集成的可选模块,可以快速的实现表单绑定、属性编辑器、国际化等功能。
3.文档
官方教程:http://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/2.1/usingthymeleaf.html#what-is-thymeleaf
推荐教程:http://blog.didispace.com/springbootweb/
http://blog.csdn.net/u012706811/article/details/52185345
二、HelloWorld
1.引入依赖
springboot直接引入:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency>
非springboot项目使用如下依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4</version>
</dependency>
默认的模板映射路径是:src/main/resources/templates,
springboot1.4之后,可以使用thymeleaf3来提高效率,并且解决标签闭合问题,配置方式:
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<!-- set thymeleaf version -->
<thymeleaf.version>3.0.0.RELEASE</thymeleaf.version>
<thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>2.0.0</thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>
<!--set java version-->
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
之前的model/modelMap/modelAndView等页面数据传递参考之前随笔:点击查看
快速回顾:

package com.learndemo.controller; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; @Controller @RequestMapping(value = "/return") public class LearnReturnType { /** * Model本身不能设置页面跳转的url地址别名或者物理跳转地址,那么我们可以通过控制器方法的返回值来设置跳转url * 地址别名或者物理跳转地址 * * @param model * 一个接口, 其实现类为ExtendedModelMap,继承了ModelMap类 * @return 跳转url地址别名或者物理跳转地址 */ @RequestMapping(value = "/index1") public String index1(Model model) { model.addAttribute("result", "后台返回index1"); return "result"; } /** * ModelMap对象主要用于传递控制方法处理数据到结果页面,类似于request对象的setAttribute方法的作用。 用法等同于Model * * @param model * @return 跳转url地址别名或者物理跳转地址 */ @RequestMapping(value = "/index2") public String index2(ModelMap model) { model.addAttribute("result", "后台返回index2"); return "result"; } /** * ModelAndView主要有两个作用 设置转向地址和传递控制方法处理结果数据到结果页面 * @return 返回一个模板视图对象 */ @RequestMapping(value = "/index3") public ModelAndView index3() { ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView("result"); // ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView(); // mv.setViewName("result"); mv.addObject("result", "后台返回index3"); return mv; } /** * map用来存储递控制方法处理结果数据,通过ModelAndView方法返回。 * 当然Model,ModelMap也可以通过这种方法返回 * @return 返回一个模板视图对象 */ @RequestMapping(value = "/index4") public ModelAndView index4() { Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); map.put("result", "后台返回index4"); return new ModelAndView("result", map); } }
2.配置thymeleaf视图解析器
这点与springMVC是相类似的:
#thymeleaf start
spring.thymeleaf.mode=HTML5
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8
spring.thymeleaf.content-type=text/html
#开发时关闭缓存,不然没法看到实时页面
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
#thymeleaf end
实际项目中可能会有不太严格的HTML格式,此时设置mode=HTML5将会对非严格的报错,可以参考以下配置:
spring.thymeleaf.mode=LEGACYHTML5
你可能会发现在默认配置下,thymeleaf对.html的内容要求很严格,比如<meta charset="UTF-8" />,
如果少最后的标签封闭符号/,就会报错而转到错误页。也比如你在使用Vue.js这样的库,然后有<div v-cloak></div>这样的html代码,
也会被thymeleaf认为不符合要求而抛出错误。
因此,建议增加下面这段:
spring.thymeleaf.mode = LEGACYHTML5
spring.thymeleaf.mode的默认值是HTML5,其实是一个很严格的检查,改为LEGACYHTML5可以得到一个可能更友好亲切的格式要求。
需要注意的是,LEGACYHTML5需要搭配一个额外的库NekoHTML才可用。
- <dependency>
- <groupId>net.sourceforge.nekohtml</groupId>
- <artifactId>nekohtml</artifactId>
- <version>1.9.22</version>
- </dependency>
最后重启项目就可以感受到不那么严格的thymeleaf了。
这样,需要的配置项如下:
# 一项是非严格的HTML检查,一项是禁用缓存来获取实时页面数据,其他采用默认项即可
thymeleaf:
mode: LEGACYHTML5
cache: false
// 完整配置项参考类ThymeleafProperties
3。编写控制器
/**
* 测试demo的controller
*
* @author zcc ON 2018/2/8
**/
@Controller
public class HelloController {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloController.class);
@GetMapping(value = "/hello")
public String hello(Model model) {
String name = "jiangbei";
model.addAttribute("name", name);
return "hello";
}
}
4.编写模板html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>hello</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<!--/*@thymesVar id="name" type="java.lang.String"*/-->
<p th:text="'Hello!, ' + ${name} + '!'">3333</p>
</body>
</html>
其中,注释是通过alt+enter进行自动生成的,便于IDEA补全,如果不加,IDEA将会报错cannot reslove,
当然也可以通过如下方式解决,解决之前推荐在maven项目中reimport一下!(据说新版本的IDEA中已经修复此问题,待更新至2017.3以后)
5.测试

三、基础语法
1.创建HTML
由上文也可以知道需要在html中添加:
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
这样,下文才能正确使用th:*形式的标签!
2.获取变量值${...}
通过${…}进行取值,这点和ONGL表达式语法一致!
<!--/*@thymesVar id="name" type="java.lang.String"*/-->
<p th:text="'Hello!, ' + ${name} + '!'">3333</p>
选择变量表达式*{...}
<div th:object="${session.user}">
<p>Name: <span th:text="*{firstName}">Sebastian</span>.</p>
<p>Surname: <span th:text="*{lastName}">Pepper</span>.</p>
<p>Nationality: <span th:text={nationality}">Saturn</span>.</p>
</div>
等价于
<div>
<p>Name: <span th:text="${session.user.firstName}">Sebastian</span>.</p>
<p>Surname: <span th:text="${session.user.lastName}">Pepper</span>.</p>
<p>Nationality: <span th:text="${session.user.nationality}">Saturn</span>.</p>
</div>
至于p里面的原有的值只是为了给前端开发时做展示用的.这样的话很好的做到了前后端分离。
这也是Thymeleaf非常好的一个特性:在无网络的情况下也能运行,也就是完全可以前端先写出页面,模拟数据展现效果,后端人员再拿此模板修改即可!
3.链接表达式: @{…}
用来配合link src href使用的语法,类似的标签有:th:href和th:src
<!-- Will produce 'http://localhost:8080/gtvg/order/details?orderId=3' (plus rewriting) -->
<a href="details.html" th:href="@{http://localhost:8080/gtvg/order/details(orderId=${o.id})}">view</a> <!-- Will produce '/gtvg/order/details?orderId=3' (plus rewriting) --> <a href="details.html" th:href="@{/order/details(orderId=${o.id})}">view</a> <a href="details.html" th:href="@{order/{orderId}/details(orderId=${o.id})}">Content路径,默认访问static下的order文件夹</a>
4.文本替换
<span th:text="'Welcome to our application, ' + ${user.name} + '!'">
或者下面的表达方式:(只能包含表达式变量,而不能有条件判断等!)
<span th:text="|Welcome to our application, ${user.name}!|">
5.运算符
数学运算
- 二元操作:+, - , * , / , %
- 一元操作: - (负)
逻辑运算
- 一元 : and or
- 二元 : !,not
比较运算(为避免转义尴尬,可以使用括号中的英文进行比较运算!)
- 比较:> , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )
- 等于:== , != ( eq , ne )
条件运算
- If-then: (if) ? (then)
- If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
- Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
-
'User is of type ' + (${user.isAdmin()} ? 'Administrator' : (${user.type} ?: 'Unknown'))6.条件
if/unless
使用th:if和th:unless属性进行条件判断,th:unless于th:if恰好相反,只有表达式中的条件不成立,才会显示其内容。
<a th:href="@{/login}" th:unless=${session.user != null}>Login</a>
switch
<div th:switch="${user.role}">
<p th:case="'admin'">User is an administrator</p>
<p th:case="#{roles.manager}">User is a manager</p>
<p th:case="*">User is some other thing</p>
</div>
7.循环
通过th:each
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>hello</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 不存在则忽略,显示hello null!(可以通过默认值进行设置)-->
<p th:text="'Hello ' + (${name}?:'admin')">3333</p>
<table>
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>NAME</th>
<th>AGE</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="emp : ${empList}">
<td th:text="${emp.id}">1</td>
<td th:text="${emp.name}">海</td>
<td th:text="${emp.age}">18</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
后台:

@GetMapping(value = "/hello") public String hello(Model model) { List<Emp> empList = new ArrayList<>(); empList.add(new Emp(1, "校长", 24)); empList.add(new Emp(2, "书记", 28)); empList.add(new Emp(3, "小海", 25)); model.addAttribute("empList", empList); return "hello"; }
效果:
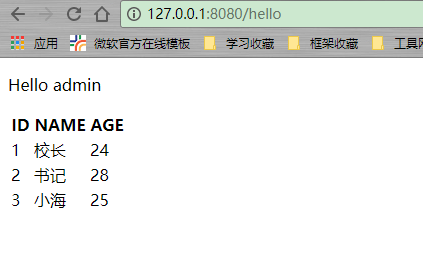
更多循环深入,iterStat等示例,参考:http://blog.csdn.net/sun_jy2011/article/details/40710429
8.内置对象Utilites
一般不推荐在前端进行这些处理,前端页面以减少逻辑为宜
#dates :
utility methods for java.util.Date objects: formatting, component extraction, etc. #calendars : analogous to #dates , but for java.util.Calendar objects.
#numbers :
utility methods for formatting numeric objects.
#strings :
utility methods for String objects: contains, startsWith, prepending/appending, etc. #objects : utility methods for objects in general.
#bools :
utility methods for boolean evaluation. #arrays : utility methods for arrays.
#lists :
utility methods for lists.
#sets :
utility methods for sets.
#maps :
utility methods for maps.
#aggregates :
utility methods for creating aggregates on arrays or collections.
#messages :
utility methods for obtaining externalized messages inside variables expressions, in the same way as they would be obtained using #{...} syntax.
#ids :
utility methods for dealing with id attributes that might be repeated (for example, as a result of an iteration).
常用示例:

/*
* Format date with the specified pattern
* Also works with arrays, lists or sets
*/
${#dates.format(date, 'dd/MMM/yyyy HH:mm')}
${#dates.arrayFormat(datesArray, 'dd/MMM/yyyy HH:mm')}
${#dates.listFormat(datesList, 'dd/MMM/yyyy HH:mm')}
${#dates.setFormat(datesSet, 'dd/MMM/yyyy HH:mm')}
/*
* Create a date (java.util.Date) object for the current date and time
*/
${#dates.createNow()}
/*
* Create a date (java.util.Date) object for the current date (time set to 00:00)
*/
${#dates.createToday()}

/*
* Check whether a String is empty (or null). Performs a trim() operation before check
* Also works with arrays, lists or sets
*/
${#strings.isEmpty(name)}
${#strings.arrayIsEmpty(nameArr)}
${#strings.listIsEmpty(nameList)}
${#strings.setIsEmpty(nameSet)}
/*
* Check whether a String starts or ends with a fragment
* Also works with arrays, lists or sets
*/
${#strings.startsWith(name,'Don')} // also array*, list* and set*
${#strings.endsWith(name,endingFragment)} // also array*, list* and set*
/*
* Compute length
* Also works with arrays, lists or sets
*/
${#strings.length(str)}
/*
* Null-safe comparison and concatenation
*/
${#strings.equals(str)}
${#strings.equalsIgnoreCase(str)}
${#strings.concat(str)}
${#strings.concatReplaceNulls(str)}
/*
* Random
*/
${#strings.randomAlphanumeric(count)}
完整参考:点击查看
四、常用标签

// 类似于th:object和th:field等进行表单参数绑定还是很有用的!使用与注意事项,参见:这里
参考博文:https://www.cnblogs.com/hjwublog/p/5051732.html
