Python3 turtle安装和使用教程
Turtle库是Python语言中一个很流行的绘制图像的函数库,想象一个小乌龟,在一个横轴为x、纵轴为y的坐标系原点,(0,0)位置开始,它根据一组函数指令的控制,在这个平面坐标系中移动,从而在它爬行的路径上绘制了图形。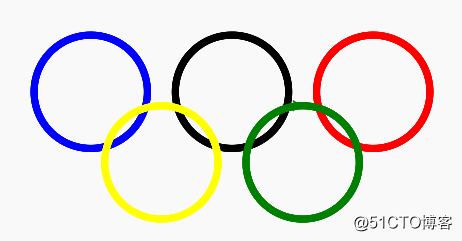
1 安装turtle
Python2安装命令:
pip install turtulePython3安装命令:
pip3 install turtle因为turtle库主要是在Python2中使用的,所以安装的时候可能会提示错误:
Command "python setup.py egg_info" failed with error code 1
解决方法请参考这里码客社区的《Python3安装turtle提示错误:Command "python setup.py egg_info" failed with error code 1》。
2 基础概念
2.1 画布(canvas)
画布就是turtle为我们展开用于绘图区域, 我们可以设置它的大小和初始位置。
常用的画布方法有两个:screensize()和setup()。
(1)turtle.screensize(canvwidth=None, canvheight=None, bg=None)
参数分别为画布的宽(单位像素), 高, 背景颜色
如:
turtle.screensize(800, 600, "green")
turtle.screensize() #返回默认大小(400, 300)(2)turtle.setup(width=0.5, height=0.75, startx=None, starty=None)
参数:
width, height:输入宽和高为整数时, 表示像素; 为小数时, 表示占据电脑屏幕的比例(startx, starty):这一坐标表示 矩形窗口左上角顶点的位置, 如果为空,则窗口位于屏幕中心
如:turtle.setup(width=0.6, height=0.6) turtle.setup(width=800, height=800, startx=100, starty=100)2.2 画笔
在画布上,默认有一个坐标原点为画布中心的坐标轴, 坐标原点上有一只面朝x轴正方向小乌龟。
这里我们描述小乌龟时使用了两个词语:标原点(位置),面朝x轴正方向(方向),turtle绘图中, 就是使用位置方向描述小乌龟(画笔)的状态
(1)画笔的属性
画笔有颜色、画线的宽度等属性。
1) turtle.pensize() :设置画笔的宽度;
2) turtle.pencolor():没有参数传入返回当前画笔颜色;传入参数设置画笔颜色,可以是字符串如"green", "red",也可以是RGB 3元组。
>>> pencolor('brown')
>>> tup = (0.2, 0.8, 0.55)
>>> pencolor(tup)
>>> pencolor()
'#33cc8c'3) turtle.speed(speed):设置画笔移动速度,画笔绘制的速度范围[0,10]整数, 数字越大越快
(2)绘图命令
操纵海龟绘图有着许多的命令,这些命令可以划分为3种:运动命令,画笔控制命令和全局控制命令
画笔运动命令:
命令 说明
turtle.forward(distance) 向当前画笔方向移动distance像素长
turtle.backward(distance) 向当前画笔相反方向移动distance像素长度
turtle.right(degree) 顺时针移动degree°
turtle.left(degree) 逆时针移动degree°
turtle.pendown() 移动时绘制图形,缺省时也为绘制
turtle.goto(x,y) 将画笔移动到坐标为x,y的位置
turtle.penup() 移动时不绘制图形,提起笔,用于另起一个地方绘制时用
turtle.speed(speed) 画笔绘制的速度范围[0,10]整数
turtle.circle() 画圆,半径为正(负),表示圆心在画笔的左边(右边)画圆
画笔控制命令:
命令 说明
turtle.pensize(width) 绘制图形时的宽度
turtle.pencolor() 画笔颜色
turtle.fillcolor(colorstring) 绘制图形的填充颜色
turtle.color(color1, color2) 同时设置pencolor=color1, fillcolor=color2
turtle.filling() 返回当前是否在填充状态
turtle.begin_fill() 准备开始填充图形
turtle.end_fill() 填充完成;
turtle.hideturtle() 隐藏箭头显示;
turtle.showturtle() 与hideturtle()函数对应
全局控制命令
命令 说明
turtle.clear() 清空turtle窗口,但是turtle的位置和状态不会改变
turtle.reset() 清空窗口,重置turtle状态为起始状态
turtle.undo() 撤销上一个turtle动作
turtle.isvisible() 返回当前turtle是否可见
stamp() 复制当前图形
turtle.write(s[,font=("font-name",font_size,"font_type")]) 写文本,s为文本内容,font是字体的参数,里面分别为字体名称,大小和类型;font为可选项, font的参数也是可选项
3 绘图举例
3.1 太阳花
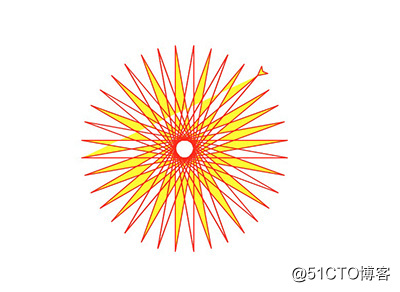
import turtle as t
import time
t.color("red", "yellow")
t.speed(10)
t.begin_fill()
for _ in range(50):
t.forward(200)
t.left(170)
end_fill()
time.sleep(1)3.2 绘制小蟒蛇
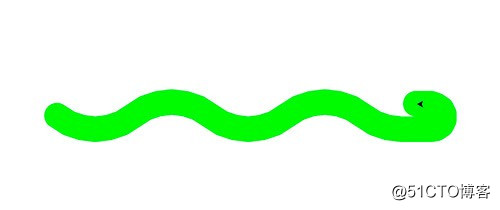
import turtle
def drawSnake(rad, angle, len, neckrad):
for _ in range(len):
turtle.circle(rad, angle)
turtle.circle(-rad, angle)
turtle.circle(rad, angle/2)
turtle.forward(rad/2) # 直线前进
turtle.circle(neckrad, 180)
turtle.forward(rad/4)
if __name__ == "__main__":
turtle.setup(1500, 1400, 0, 0)
turtle.pensize(30) # 画笔尺寸
turtle.pencolor("green")
turtle.seth(-40) # 前进的方向
drawSnake(70, 80, 2, 15)3.3 绘制五角星

import turtle
import time
turtle.pensize(5)
turtle.pencolor("yellow")
turtle.fillcolor("red")
turtle.begin_fill()
for _ in range(5):
turtle.forward(200)
turtle.right(144)
turtle.end_fill()
time.sleep(2)
turtle.penup()
turtle.goto(-150,-120)
turtle.color("violet")
turtle.write("Done", font=('Arial', 40, 'normal'))
time.sleep(1)3.4 绘制谢尔宾斯基三角形
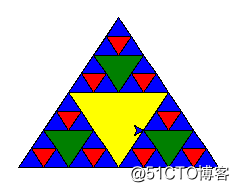
import turtle
def draw_triangle(points, color, t):
t.fillcolor(color)
t.up()
t.goto(points[0][0], points[0][1])
t.down()
t.begin_fill()
t.goto(points[1][0], points[1][1])
t.goto(points[2][0], points[2][1])
t.goto(points[0][0], points[0][1])
t.end_fill()
def get_mid(point1, point2):
return (point1[0] + point2[0]) / 2, (point1[1] + point2[1]) / 2
def sierpinski(points, degree, t):
color_map = ['blue', 'red', 'green', 'yellow', 'violet', 'orange', 'white',]
draw_triangle(points, color_map[degree], t)
if degree > 0:
sierpinski([points[0], get_mid(points[0], points[1]), get_mid(points[0], points[2])], degree - 1, t)
sierpinski([points[1], get_mid(points[0], points[1]), get_mid(points[1], points[2])], degree - 1, t)
sierpinski([points[2], get_mid(points[0], points[2]), get_mid(points[1], points[2])], degree - 1, t)
if __name__ == "__main__"
t = turtle.Turtle()
t.speed(5)
win = turtle.Screen()
points = [[-100, -50], [0, 100], [100, -50]]
sierpinski(points, 3, t)
win.exitonclick()
其它参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41084236/article/details/82218431?utm_source=blogxgwz1