与前面介绍的7种排序算法不同,基数排序(Radix Sort)是基于多关键字排序的一种排序算法。也就是说,前面介绍的7种排序算法是建立在对单关键字进行比较的基础之上,而基数排序则是采用"分配"与"收集"的办法,将单关键字按照一定策略拆分成多个关键字,进而对多个关键字进行排序,最终完成对单关键字的排序。
基数排序的典型例子当然就是扑克牌排序啦,几乎所有的数据结构教科书都会讲到,原因是形象易懂。每张扑克牌都有两个关键字:花色和面值。假定有序关系为:
- 花色: 黑桃 < 红桃 < 梅花 < 方块
- 面值: 2 < 3 < 4 < 5 < 6 < 7 < 8 < 9 < 10 < J < Q < K < A
如果把所有扑克牌排成下列次序:
- 黑桃2, ..., 黑桃A, 红桃2, ..., 红桃A, 梅花2, ..., 梅花A, 方块2, ..., 方块A。
那么这就是多关键字排序。排序后形成的有序序列叫做词典有序序列。 对于扑克牌排序,有两种方法。可以先按花色排序,之后再按面值排序;也可以先按面值排序,再按花色排序。
再举个对数字进行基数排序的例子,

利用visualgo.net创建一个动画演示(01)如下:
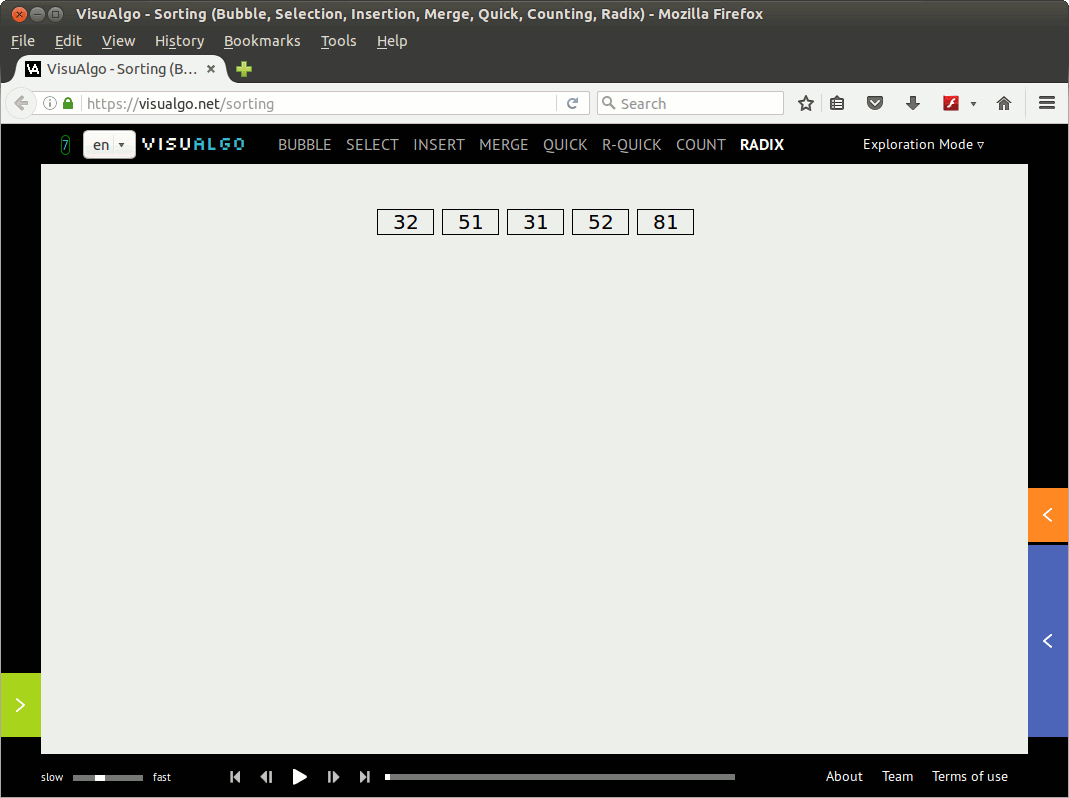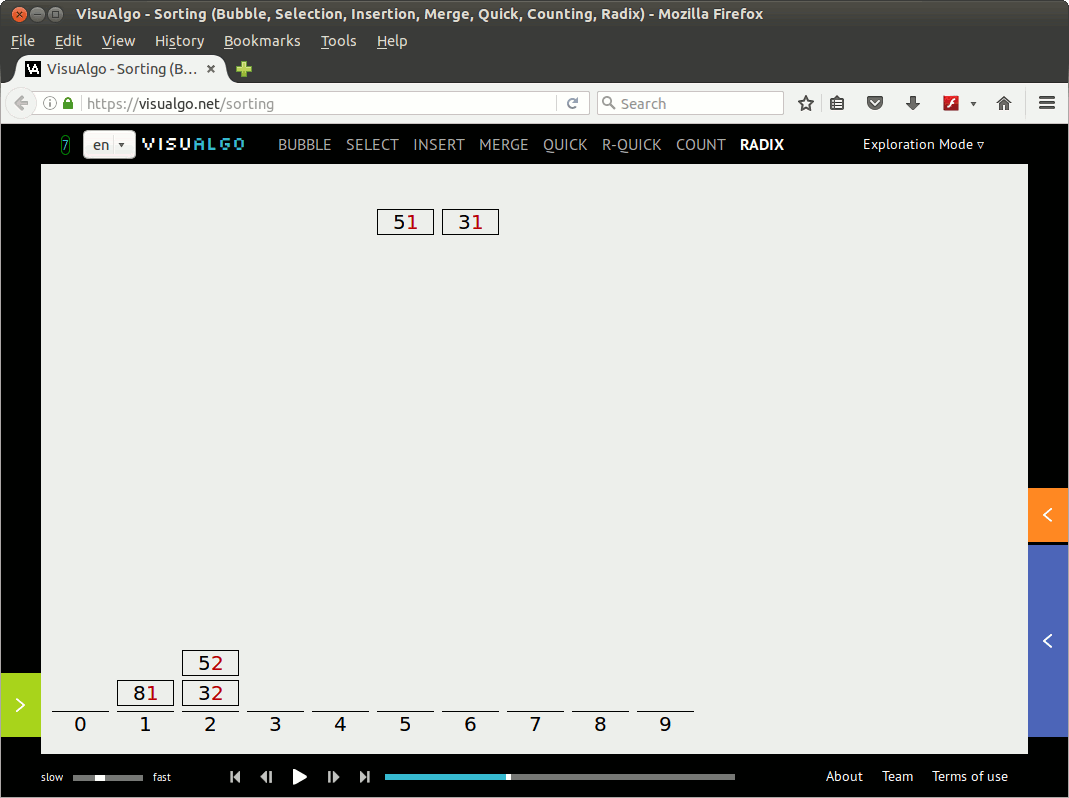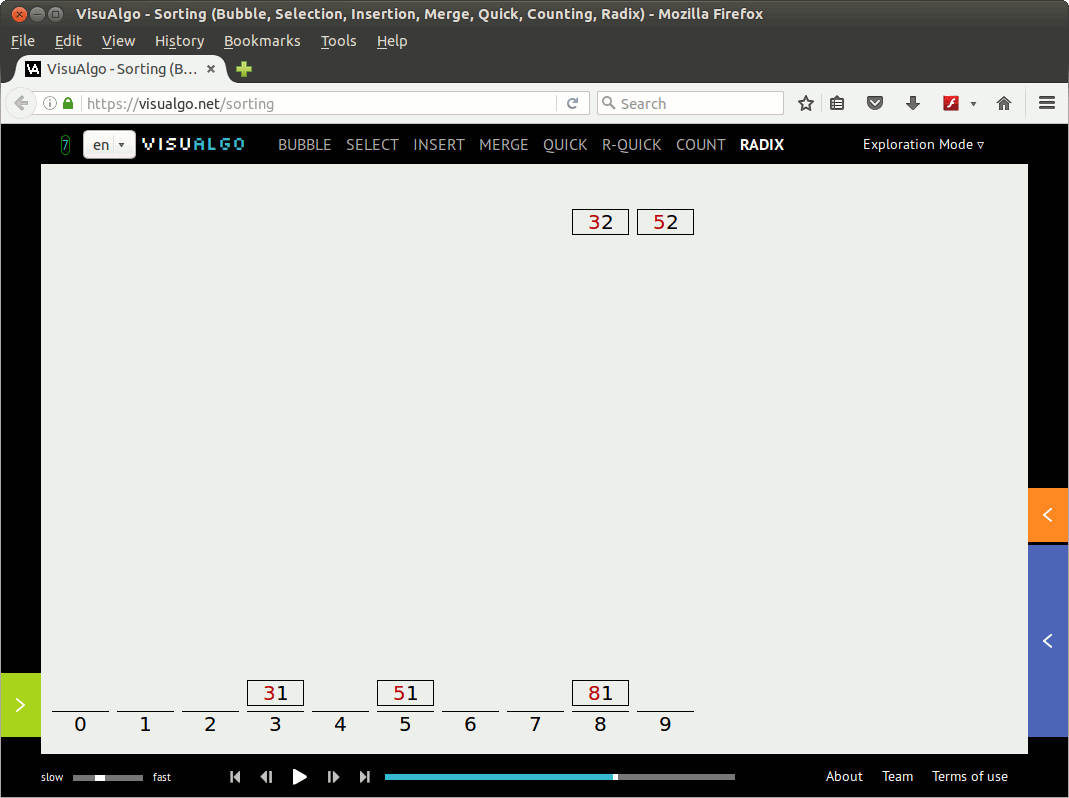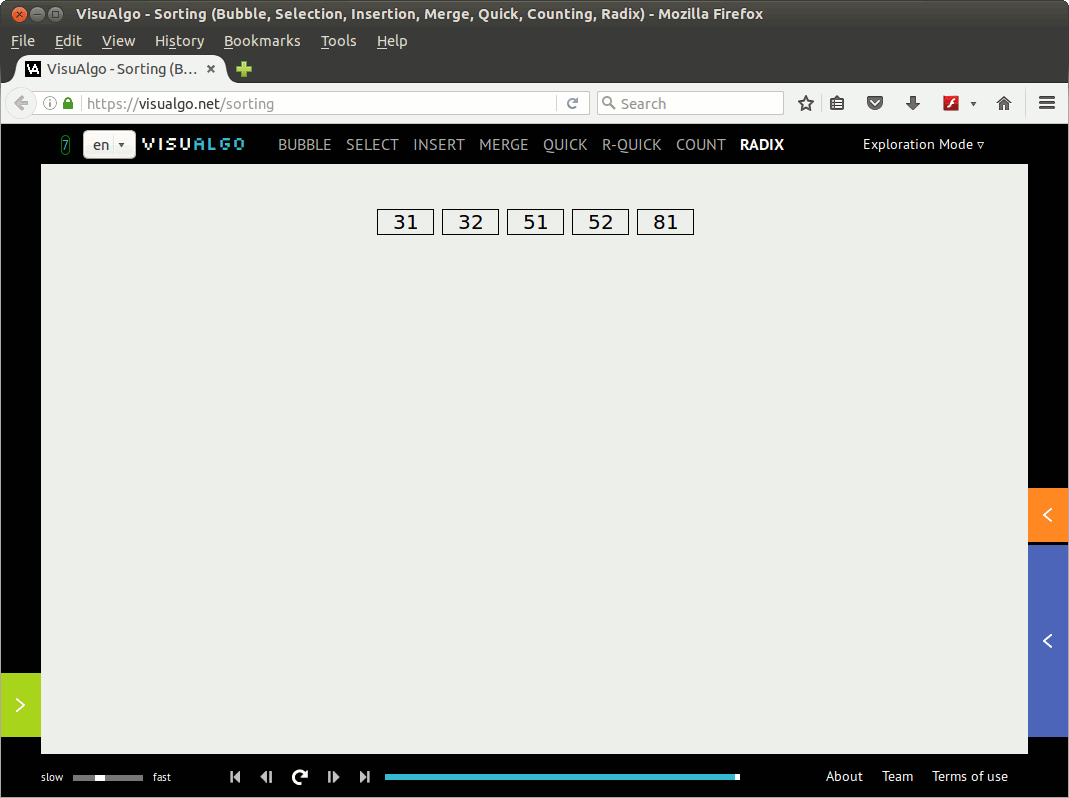
注意: 后面给出的第一个基数排序C代码实现(radixsort.c)并未完全基于上面的动画演示,而是基于David Galles在RadixSort上给出的动画演示(个人觉得David给出的组织bin[]的方法更酷一些,但是可读性稍差一些)。 补充说明中给出的代码实现radixsort2.c则是完全基于上面的动画演示。
基数排序的基本思想
设待排记录中的多个关键字为K1, K2, ..., Kr。K1第1关键字,Kr为第r关键字。由记录R1, R2, ..., Rn组成的表关于关键字K1, K2, ..., Kr有序,当且仅当对每一对记录Ri < Rj 都有(K1i, K2i, ..., Kri) <= (K1j, K2j, ..., Krj)。 排序方法如下:
- 首先按照关键字K1对R1, R2, ..., Rn进行排序,得到新的序列LIST1;
- 按照关键字K2对LIST1进行排序,得到新的序列LIST2; 如此循环往复直到完成对关键字Kr的排序为止。
为简单起见,我们只讨论非负数的整数序列(即a[i]>=0, i=0, 1, ..., N-1)的基数排序方法。(前面提到的扑克牌花色,完全可以按照黑红梅方的顺序编码为0, 1, 2, 3。于是,黑桃序列为: 002 < ... < 010 < 011(J) < 012(Q) < 013(K) < 014(A), 其他三种花色依次类推即可)
基数排序的分类
- 最高位优先MSD(Most Significant Digit first)
- 最低位优先LSD(Least Significant Digit fisrt)
最高位优先(MSD)
- 假设待排序列的最大整数的最高位为百位,先按照百位排,再按照十位排,最后按照个位排。
最低位优先(LSD)
- 假设待排序列的最大整数的最高位为百位,先按照个位排,再按照十位排,最后按照百位排。
基于LSD实现的基数排序相对简单,本文将给出这种基数排序的代码实现。(P.S. 在观看了Radix Sort Visualization之后,我大约花了15分钟就完成了代码实现,比啃数据结构的书容易多了。)
1. 获取整数的某个特定位的数字
1 /* 2 * Get the digit of number by index(= 0, 1, 2, ...) 3 * 4 * e.g. 5 * num = 6543210 6 * ------+------ 7 * index | digit 8 * ------+------ 9 * 0 | 0 10 * 1 | 1 11 * 2 | 2 12 * 3 | 3 13 * 4 | 4 14 * 5 | 5 15 * 6 | 6 16 * 7 | 0 17 * .. | .. 18 * ------+------ 19 */ 20 static unsigned char 21 get_digit_byindex(int num, unsigned int index) 22 { 23 int q = 0; /* quotient */ 24 int r = 0; /* remainder */ 25 for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--) { 26 r = num % 10; 27 q = num / 10; 28 num = q; 29 } 30 return (unsigned char)r; 31 }
2. 获取整数的宽度
1 /* 2 * Get width of a number 3 * e.g. 4 * for i in [ 0 .. 9 ] // width = 1 5 * for i in [ 10 .. 99 ] // width = 2 6 * for i in [100 .. 999] // width = 3 7 * ... 8 */ 9 static int 10 get_width_of_num(int num) 11 { 12 int w = 1; 13 for (int q = num / 10; q != 0; q /= 10) 14 w++; 15 return w; 16 }
3. 构造10个容器bin[],bin[i]存数字i的个数,i = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
1 /* 2 * Build bin[] by index(=0, 1, ..., N-1) (N is the max width of num in a[]) 3 * 4 * NOTE: This is the core function to understand radix sorting based on LSD 5 */ 6 static void 7 build_bin_byindex(int bin[], size_t nb, int a[], size_t na, int index) 8 { 9 /* 1. always reset bin[] */ 10 for (int i = 0; i < nb; i++) 11 bin[i] = 0; 12 13 /* 2. init bin[] by walking a[] */ 14 for (int i = 0; i < na; i++) { 15 unsigned char d = get_digit_byindex(a[i], index); 16 bin[d]++; 17 } 18 19 /* 3. build bin[] */ 20 for (int i = 1; i < nb; i++) 21 bin[i] += bin[i-1]; 22 }
4. 基于LSD的基数排序
1 void 2 radixsort(int a[], int n) 3 { 4 /* get the max width of num in a[] */ 5 int max = a[0]; 6 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 7 if (a[i] > max) 8 max = a[i]; 9 } 10 int maxwidth = get_width_of_num(max); 11 12 /* alloc bin[] to store the number of per digit */ 13 int bin[10] = { 0 }; 14 15 /* alloc aux[] to save a[] while rebuilding a[] */ 16 int *aux = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * n); 17 if (aux == NULL) /* error */ 18 return; 19 20 /* LSD (Least Significant Digit first) */ 21 for (int index = 0; index < maxwidth; index++) { 22 /* 1. build bin[] */ 23 build_bin_byindex(bin, 10, a, n, index); 24 25 /* 2. copy a[] to aux[] */ 26 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 27 aux[i] = a[i]; 28 29 /* 3. rebuild a[] */ 30 for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) { 31 unsigned char d = get_digit_byindex(aux[i], index); 32 a[--bin[d]] = aux[i]; 33 } 34 } 35 36 free(aux); 37 }
5. 完整的C代码实现
o radixsort.c
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 5 typedef enum bool_s {false, true} bool_t; 6 7 bool_t g_isint = true; 8 9 static void 10 show(int a[], size_t n) 11 { 12 if (g_isint) { 13 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 14 printf("%-2d ", a[i]); 15 } else { 16 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 17 printf("%-2c ", a[i]); 18 } 19 printf(" "); 20 } 21 22 /* 23 * Get the digit of number by index(= 0, 1, 2, ...) 24 * 25 * e.g. 26 * num = 6543210 27 * ------+------ 28 * index | digit 29 * ------+------ 30 * 0 | 0 31 * 1 | 1 32 * 2 | 2 33 * 3 | 3 34 * 4 | 4 35 * 5 | 5 36 * 6 | 6 37 * 7 | 0 38 * .. | .. 39 * ------+------ 40 */ 41 static unsigned char 42 get_digit_byindex(int num, unsigned int index) 43 { 44 int q = 0; /* quotient */ 45 int r = 0; /* remainder */ 46 for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--) { 47 r = num % 10; 48 q = num / 10; 49 num = q; 50 } 51 return (unsigned char)r; 52 } 53 54 /* 55 * Get width of a number 56 * e.g. 57 * for i in [ 0 .. 9 ] // width = 1 58 * for i in [ 10 .. 99 ] // width = 2 59 * for i in [100 .. 999] // width = 3 60 * ... 61 */ 62 static int 63 get_width_of_num(int num) 64 { 65 int w = 1; 66 for (int q = num / 10; q != 0; q /= 10) 67 w++; 68 return w; 69 } 70 71 /* 72 * Build bin[] by index(=0, 1, ..., N-1) (N is the max width of num in a[]) 73 * 74 * NOTE: This is the core function to understand radix sorting based on LSD 75 */ 76 static void 77 build_bin_byindex(int bin[], size_t nb, int a[], size_t na, int index) 78 { 79 /* 1. always reset bin[] */ 80 for (int i = 0; i < nb; i++) 81 bin[i] = 0; 82 83 /* 2. init bin[] by walking a[] */ 84 for (int i = 0; i < na; i++) { 85 unsigned char d = get_digit_byindex(a[i], index); 86 bin[d]++; 87 } 88 89 /* NOTE: dump bin[] just for visual observation */ 90 printf("1#bin[]: "); show(bin, nb); 91 92 /* 3. build bin[] */ 93 for (int i = 1; i < nb; i++) 94 bin[i] += bin[i-1]; 95 96 /* NOTE: dump bin[] just for visual observation */ 97 printf("2#bin[]: "); show(bin, nb); 98 } 99 100 void 101 radixsort(int a[], int n) 102 { 103 /* get the max width of num in a[] */ 104 int max = a[0]; 105 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 106 if (a[i] > max) 107 max = a[i]; 108 } 109 int maxwidth = get_width_of_num(max); 110 111 /* alloc bin[] to store the number of per digit */ 112 int bin[10] = { 0 }; 113 114 /* alloc aux[] to save a[] while rebuilding a[] */ 115 int *aux = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * n); 116 if (aux == NULL) /* error */ 117 return; 118 119 /* LSD (Least Significant Digit first) */ 120 for (int index = 0; index < maxwidth; index++) { 121 /* 1. build bin[] */ 122 build_bin_byindex(bin, 10, a, n, index); 123 124 /* 2. copy a[] to aux[] */ 125 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 126 aux[i] = a[i]; 127 128 /* 3. rebuild a[] */ 129 for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) { 130 unsigned char d = get_digit_byindex(aux[i], index); 131 a[--bin[d]] = aux[i]; 132 } 133 134 /* NOTE: dump a[] for visual observation */ 135 printf("%dth bit(done): ", index); show(a, n); 136 } 137 138 free(aux); 139 } 140 141 int 142 main(int argc, char *argv[]) 143 { 144 if (argc < 2) { 145 fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <C1> [C2] ... ", argv[0]); 146 return -1; 147 } 148 149 argc--; 150 argv++; 151 152 int n = argc; 153 int *a = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * n); 154 #define VALIDATE(p) do { if (p == NULL) return -1; } while (0) 155 VALIDATE(a); 156 157 char *s = getenv("ISINT"); 158 if (s != NULL && strncmp(s, "true", 4) == 0) 159 g_isint = true; 160 else if (s != NULL && strncmp(s, "false", 4) == 0) 161 g_isint = false; 162 163 if (g_isint) { 164 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 165 *(a+i) = atoi(argv[i]); 166 } else { 167 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 168 *(a+i) = argv[i][0]; 169 } 170 171 printf(" "); 172 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 173 printf("%-2x ", i); 174 printf(" "); 175 176 printf("Before sorting: "); show(a, n); 177 radixsort(a, n); 178 printf("After sorting: "); show(a, n); 179 180 #define FREE(p) do { free(p); p = NULL; } while (0) 181 FREE(a); 182 return 0; 183 }
o 编译并测试
$ gcc -g -Wall -std=gnu99 -m32 -o radixsort radixsort.c $ ./radixsort 32 51 31 52 81 0 1 2 3 4 Before sorting: 32 51 31 52 81 1#bin[]: 0 3 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2#bin[]: 0 3 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 0th bit(done): 51 31 81 32 52 1#bin[]: 0 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 1 0 2#bin[]: 0 0 0 2 2 4 4 4 5 5 1th bit(done): 31 32 51 52 81 After sorting: 31 32 51 52 81
基数排序(Radix Sort)是一种稳定的排序算法。设待排对象的个数为N,关键字个数为w,则时间复杂度和空间复杂度为:
Worst-case performance O(w*N)
Worst-case space complexity O(w+N)
在上面给出的C代码实现中:
- w=10, 即有10个容器(bin),辅助存储aux[]的长度为N,所以空间复杂度为O(10+N);
- 对每个数字(0..9)都要处理N次,所以最坏时间复杂度为O(10*N)。
参考资料:
- Radix Sort Visualization
- Radix sort
- https://visualgo.net/sorting
补充说明: 鉴于在本文开始的动画演示中,实现bin[]和重构a[]的过程可读性好,于是本人在阅读了Robert Sedgewick的算法第3版第10章 基数排序之后,给出如下C代码实现。该实现是基于按最低位优先(LSD)的方法,针对大小为32位的非负整数,遍历处理每一个二进制位。为简单起见,我在将a[N]的元素放置到bin[i](i=0,1)中去的时候,没有使用链式存储,而是一次性malloc大小为2*N的顺序存储空间aux[],将aux[0:N]分配给bin[0]使用,将aux[N:]分配给bin[1]使用(代码行: L108-121)。 (PS: 遍历处理每一个二进制位的思路是很酷的,读大师的书,总是会有新发现,大师就是大师,always膜拜ing...)
o radixsort2.c
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 5 typedef enum bool_s {false, true} bool_t; 6 7 bool_t g_isint = true; 8 9 typedef struct bin_unit_s { 10 size_t len; 11 int *unit; 12 } bin_unit_t; 13 14 static void 15 show(int a[], size_t n) 16 { 17 if (g_isint) { 18 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 19 printf("%-2d ", a[i]); 20 } else { 21 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 22 printf("%-2c ", a[i]); 23 } 24 printf(" "); 25 } 26 27 static bool_t 28 is_sorted(int a[], size_t n) 29 { 30 for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) 31 if (a[i] < a[i-1]) 32 return false; 33 return true; 34 } 35 36 /* 37 * Get the digit of number by index(= 0, 1, 2, ...) 38 */ 39 static unsigned char 40 get_digit_byindex(int num, unsigned int index) 41 { 42 return ((unsigned int)num >> index) & 0x1; 43 } 44 45 /* 46 * Build bin[] by index(=0, 1, ..., N-1) (N is the max width of num in a[]) 47 * 48 * NOTE: This is the core function to understand radix sorting based on LSD 49 */ 50 static void 51 build_bin_byindex(bin_unit_t *bin[], size_t nb, int a[], size_t na, int index) 52 { 53 /* 1. always reset bin[][] */ 54 for (int i = 0; i < nb; i++) { 55 bin[i]->len = 0; 56 for (int j = 0; j < na; j++) 57 (bin[i]->unit)[j] = 0x0; 58 } 59 60 /* 2. init bin[][] by walking a[] */ 61 for (int i = 0; i < na; i++) { 62 unsigned char d = get_digit_byindex(a[i], index); 63 (bin[d]->unit)[bin[d]->len] = a[i]; 64 (bin[d]->len)++; 65 66 /* NOTE: print a[i] and Xth bit just for visual observation */ 67 printf("%dth bit of %d is %d ", index, a[i], d); 68 } 69 70 /* NOTE: dump bin[] just for visual observation */ 71 for (int i = 0; i < nb; i++) { 72 printf("bin[%d]: ", i); 73 show(bin[i]->unit, bin[i]->len); 74 } 75 } 76 77 /* 78 * Rebuild a[] by walking numbers saved in (bin[0]->unit)[] and 79 * (bin[1]->unit)[] 80 * 81 * e.g. 82 * bin[0] = { .len = 2, .unit = {4, 2} } 83 * bin[1] = { .len = 3, .unit = {5, 3, 1} } 84 * a[5] = { 4, 2, 5, 3, 1 } 85 * 86 * bin[0] bin[1] ===> a[5] 87 * 88 * 1 89 * 3 90 * 1 5 91 * 2 3 2 92 * 4 5 ===> 4 93 * ----- ----- ----- 94 * 0 1 95 */ 96 static void 97 rebuild(int a[], size_t na, bin_unit_t *bin[], size_t nb) 98 { 99 int k = 0; 100 for (int i = 0; i < nb; i++) 101 for (int j = 0; j < bin[i]->len; j++) 102 a[k++] = (bin[i]->unit)[j]; 103 } 104 105 void 106 radixsort(int a[], int n) 107 { 108 /* alloc aux[] for puting a[] to (bin[i]->unit)[] (i= 0, 1) */ 109 int *aux = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * n * 2); 110 if (aux == NULL) /* error */ 111 return; 112 113 /* 114 * alloc bin[2], (hence, worst space complexity is O(n*2 + 2)) 115 * if number M of a[] whose Xth digit is 0, save M to (bin[0]->unit)[] 116 * else save M to (bin[1]->unit)[] 117 * where X = 0, 1, ..., 31 118 */ 119 bin_unit_t bin0 = {.len = 0, .unit = aux + 0}; 120 bin_unit_t bin1 = {.len = 0, .unit = aux + n}; 121 bin_unit_t *bin[2] = {&bin0, &bin1}; 122 123 /* LSD (Least Significant Digit first) */ 124 for (int index = 0; index < 32; index++) { 125 /* 0. break if a[] is in order */ 126 if (is_sorted(a, n)) 127 break; 128 129 /* 1. build bin[] */ 130 build_bin_byindex(bin, 2, a, n, index); 131 132 /* 2. rebuild a[] by walking bin[] */ 133 rebuild(a, n, bin, 2); 134 135 /* NOTE: dump a[] for visual observation */ 136 printf("%dth bit(done): ", index); show(a, n); 137 } 138 139 free(aux); 140 } 141 142 int 143 main(int argc, char *argv[]) 144 { 145 if (argc < 2) { 146 fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <C1> [C2] ... ", argv[0]); 147 return -1; 148 } 149 150 argc--; 151 argv++; 152 153 int n = argc; 154 int *a = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * n); 155 #define VALIDATE(p) do { if (p == NULL) return -1; } while (0) 156 VALIDATE(a); 157 158 char *s = getenv("ISINT"); 159 if (s != NULL && strncmp(s, "true", 4) == 0) 160 g_isint = true; 161 else if (s != NULL && strncmp(s, "false", 4) == 0) 162 g_isint = false; 163 164 if (g_isint) { 165 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 166 *(a+i) = atoi(argv[i]); 167 } else { 168 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 169 *(a+i) = argv[i][0]; 170 } 171 172 printf(" "); 173 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 174 printf("%-2x ", i); 175 printf(" "); 176 177 printf("Before sorting: "); show(a, n); 178 radixsort(a, n); 179 printf("After sorting: "); show(a, n); 180 181 #define FREE(p) do { free(p); p = NULL; } while (0) 182 FREE(a); 183 return 0; 184 }
o 编译并测试
$ gcc -g -Wall -m32 -std=c99 -o radixsort2 radixsort2.c $ ISINT=true ./radixsort2 > 4 2 1 8 0 1 2 3 Before sorting: 4 2 1 8 0th bit of 4 is 0 0th bit of 2 is 0 0th bit of 1 is 1 0th bit of 8 is 0 bin[0]: 4 2 8 bin[1]: 1 0th bit(done): 4 2 8 1 1th bit of 4 is 0 1th bit of 2 is 1 1th bit of 8 is 0 1th bit of 1 is 0 bin[0]: 4 8 1 bin[1]: 2 1th bit(done): 4 8 1 2 2th bit of 4 is 1 2th bit of 8 is 0 2th bit of 1 is 0 2th bit of 2 is 0 bin[0]: 8 1 2 bin[1]: 4 2th bit(done): 8 1 2 4 3th bit of 8 is 1 3th bit of 1 is 0 3th bit of 2 is 0 3th bit of 4 is 0 bin[0]: 1 2 4 bin[1]: 8 3th bit(done): 1 2 4 8 After sorting: 1 2 4 8
小结:
基数排序(Radix Sort)是一种非比较型整数(non-comparative integer)排序算法,也是一种分布式(distributed)排序算法,其本质是多关键字排序,既可以使用LSD(最低位优先)方法,也可以使用MSD(最高位优先)方法。 下一节将介绍另一种分布式排序算法 - 桶排序。