p1-p9
1: 注解
1.1 注解的概念
注解:能给人看,也能给机器看 ,机器会用反射机制进行访问。
如@Override都是注解,注解具有检查和约束的作用.如把S小写,override就报错了。

1.2 内置注解

package annotation;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* author liulei
* data 5.21
* since 1.8
* version 1.0
* Description 内置注解演示
*/
public class Demo01 {
//Override 重写的注释
@Override
public String toString(){
return super.toString();
}
//Deprecated 不推荐程序员使用,但是可以使用,或者存在更好的方式
@Deprecated
public static void test()
{
System.out.println("这是个不被推荐的方法");
}
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public void test02()
{
List list = new ArrayList();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test();
}
}
1.3 元注解
package annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* author liulei
* data 5.21
* since 1.8
* version 1.0
* Description 元注解演示
*/
@Myannotation
public class Demo02 {
@Myannotation
public void test()
{
}
@Myannotation2(age = 18,name = "liulei")
public void test1(){
}
@Myannotation3(value = "ll")
public void test2(){
}
}
//定义一个注解
//Target 表示注解可以用在哪些地方
//Retention 表示我们的注解在什么地方还有效,作用的范围
//runtime>class>source
//Documented 表示是否将注解生成在Javadoc中
//Inherited 子类可以继承父类的注解
@Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@interface Myannotation{
}
@interface Myannotation2{
//注解的参数:参数类型+参数名();
String name() default "";
int age();
int id() default -1;//如果默认为-1,代表不存在
String[] schools() default {"西部开源","清华大学"};
}
@interface Myannotation3{
String value();//如果只有一个参数,则参数为value
}

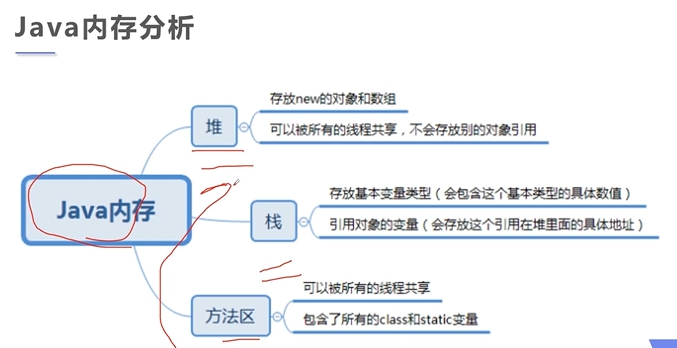
2:反射
2.1 反射介绍

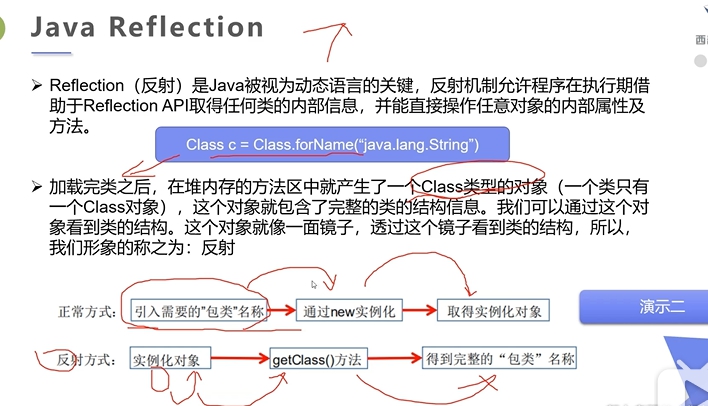


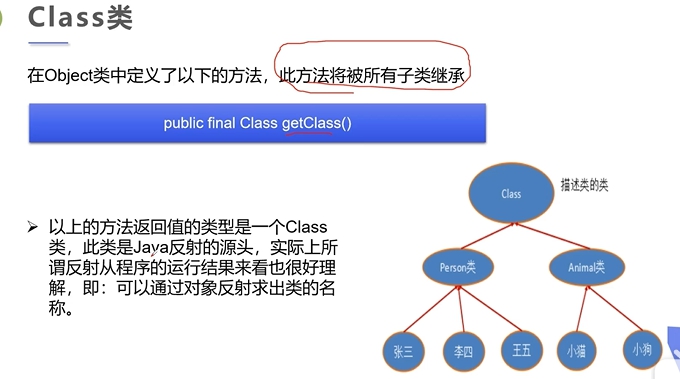
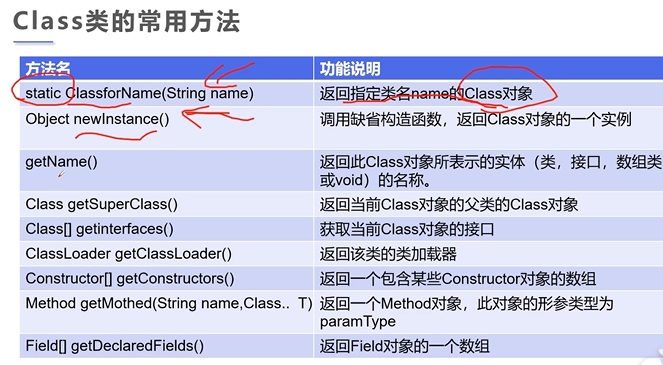
2.2 Class类

1 package Reflection; 2 3 /** 4 * author liulei 5 * data 5.21 6 * since 1.8 7 * version 1.0 8 * Description 获取类对象的Class对象的几种方法 9 */ 10 public class Test01 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { 12 Person p = new Student("abc"); 13 System.out.println("这个人是:"+p.name); 14 //方式一:通过对象获得 15 Class c1 = p.getClass(); 16 System.out.println(c1.hashCode()); 17 //方式二:forname获得 18 Class c2 = Class.forName("Reflection.Student"); 19 System.out.println(c2.hashCode()); 20 //方式三:通过类名.class获得 21 Class c3 = Student.class; 22 System.out.println(c3.hashCode()); 23 //方式四:基本内置类型都有一个Type属性 24 Class c4 = Integer.TYPE; 25 System.out.println(c4); 26 //获得父类类型 27 Class c5 = c1.getSuperclass(); 28 System.out.println(c5); 29 } 30 31 } 32 class Person{ 33 public String name; 34 35 public Person(String name) { 36 this.name = name; 37 } 38 public Person() { 39 } 40 41 } 42 class Student extends Person 43 { 44 public Student(String name) { 45 this.name = name; 46 } 47 } 48 class Teacher extends Person 49 { 50 public Teacher() { 51 } 52 53 public Teacher(String name) { 54 this.name = "老师"; 55 } 56 }

1 package Reflection; 2 3 import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; 4 5 /** 6 * author liulei 7 * data 8 * since 1.8 9 * version 1.0 10 * Description 11 */ 12 public class Test02 { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 Class c1 = Object.class;//类 15 Class c2 = Comparable.class;//接口 16 Class c3 = String[].class;//数组 17 Class c4 = int[][].class;//二维数组 18 Class c5 = Override.class;//注解 19 Class c6 = ElementType.class;//枚举 20 Class c7 = Integer.class;//基本数据类型 21 Class c8 = void.class;//void 22 Class c9 = Class.class;//Class 23 System.out.println(c1); 24 System.out.println(c2); 25 System.out.println(c3); 26 System.out.println(c4); 27 System.out.println(c5); 28 System.out.println(c6); 29 System.out.println(c7); 30 System.out.println(c8); 31 System.out.println(c9); 32 33 //只要元素类型与维度一致,就是同一个Class 34 int[] a = new int[10]; 35 int[] b =new int[100]; 36 System.out.println(a.getClass().hashCode()); 37 System.out.println(b.getClass().hashCode()); 38 39 } 40 }
2.3 类的加载
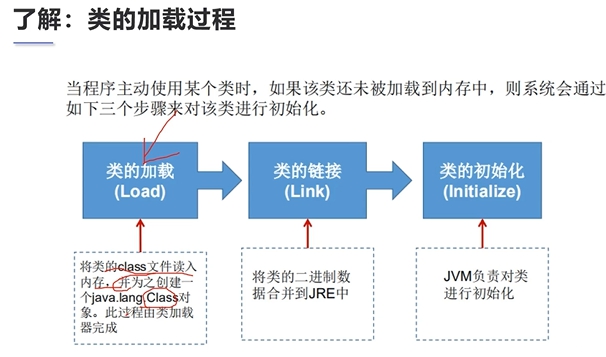

1 package Reflection; 2 3 /** 4 * author liulei 5 * data 6 * since 1.8 7 * version 1.0 8 * Description 9 */ 10 public class Test03 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 A a = new A(); 13 System.out.println(A.m); 14 } 15 } 16 /* 17 1 加载到内存,会产生一个类对应的Class对象 18 2 链接,链接结束后 m = 0 19 3 初始化 20 <clinit>() 21 { 22 System.out.println("A类静态代码块初始化"); 23 m = 300; 24 m = 100; 25 } 26 */ 27 class A{ 28 static { 29 System.out.println("A类静态代码块初始化"); 30 m = 300; 31 } 32 static int m = 100; 33 34 public A() { 35 System.out.println("A类的无参构造初始化"); 36 } 37 }