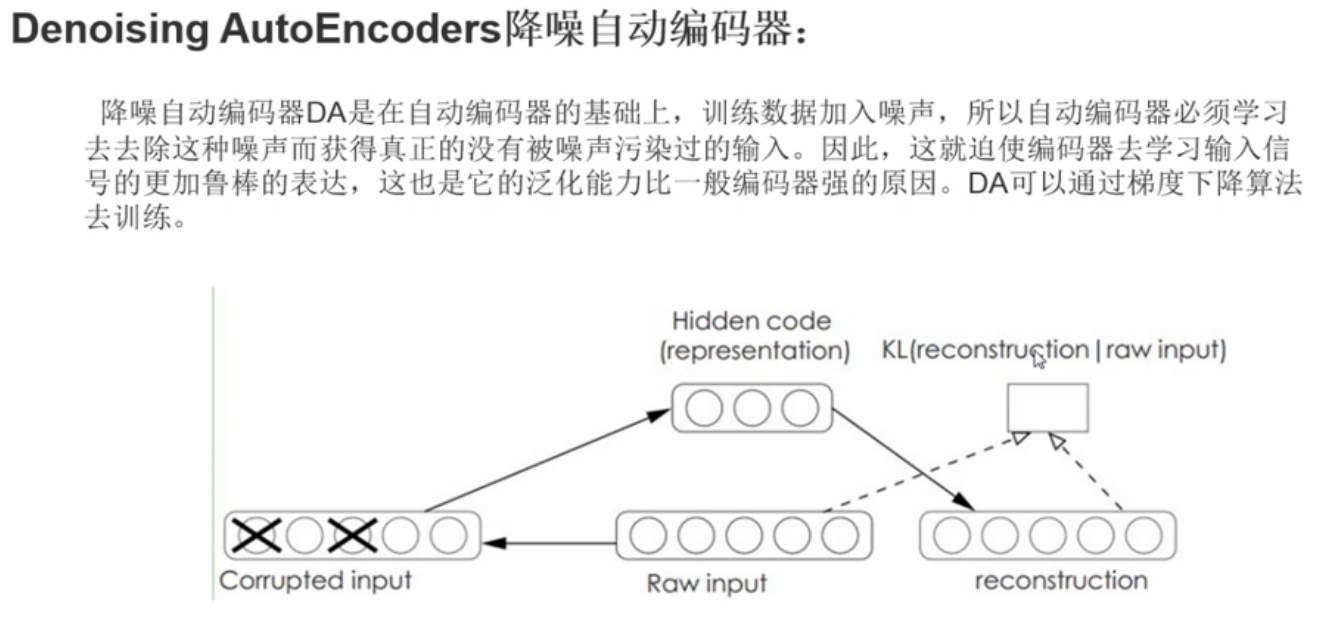
背景简介
TensorFlow实现讲解
设计新思路:
1.使用类来记录整个网络:
使用_init_()属性来记录 网络超参数 & 网络框架 & 训练过程
使用一个隐式方法初始化网络参数
2.使用字典存储初始化的各个参数(w&b)
参数初始化新思路:


主程序:



图结构实际实现
Version1:
导入包:
import numpy as np import sklearn.preprocessing as prep import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data import os
关闭日志警告:
级别2是警告信息忽略,级别3是错误信息忽略
# 关闭tensorflow的警告信息 os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
均匀分布参数生成函数:
# 标准均匀分布
def xavier_init(fan_in,fan_out,constant = 1):
low = -constant * np.sqrt(6.0/(fan_in+fan_out))
hight = constant * np.sqrt(6.0/(fan_in+fan_out))
return tf.random_uniform((fan_in,fan_out),maxval=hight,minval=low,dtype=tf.float32)
网络类:
class AdditiveGuassianNoiseAutoencoder():
def __init__(self,n_input,n_hidden,transfer_function=tf.nn.softplus,
optimzer=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(),scale=0.1):
# 网络参数
self.n_input = n_input
self.n_hidden = n_hidden
self.transfer = transfer_function # 激活函数
self.training_scale = scale # 噪声水平
network_weights = self._initialize_weights()
self.weights = network_weights
# 网络结构
self.x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_input])
self.hidden = self.transfer(
tf.add(tf.matmul(self.x + scale * tf.random_normal((n_input,)),
self.weights['w1']), self.weights['b1']))
self.reconstruction = tf.add(tf.matmul(self.hidden, self.weights['w2']),
self.weights['b2'])
# 训练部分
self.cost = 0.5 * tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow(tf.subtract(self.reconstruction, self.x), 2))
self.optimizer = optimzer.minimize(self.cost)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
self.sess = tf.Session()
self.sess.run(init)
print('begin to run session... ...')
def _initialize_weights(self):
all_weights = dict()
all_weights['w1'] = tf.Variable(xavier_init(self.n_input, self.n_hidden))
all_weights['b1'] = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([self.n_hidden], dtype=tf.float32))
all_weights['w2'] = tf.Variable(xavier_init(self.n_hidden, self.n_input))
all_weights['b2'] = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([self.n_input], dtype=tf.float32))
return all_weights
主函数:
AGN_AC = AdditiveGuassianNoiseAutoencoder(n_input=784, n_hidden=200,
transfer_function=tf.nn.softplus,
optimzer=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01),
scale=0.01)
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logdir='logs', graph=AGN_AC.sess.graph)
writer.close()
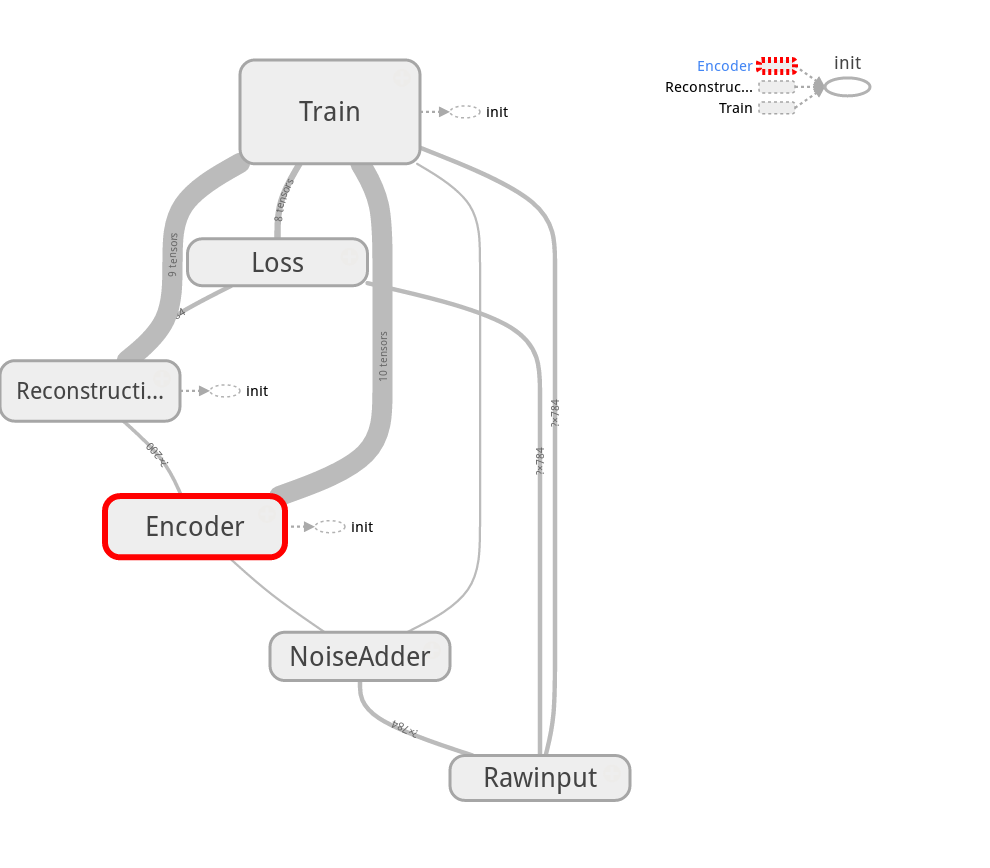
图:

VersionV2
添加了命名空间,使节点更为清晰,但实际图结构显得凌乱,由于W&b的节点没有被划归到层节点下的关系
import numpy as np
import sklearn.preprocessing as prep
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import os
# 关闭tensorflow的警告信息
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
# 标准均匀分布
def xavier_init(fan_in,fan_out,constant = 1):
low = -constant * np.sqrt(6.0/(fan_in+fan_out))
hight = constant * np.sqrt(6.0/(fan_in+fan_out))
return tf.random_uniform((fan_in,fan_out),maxval=hight,minval=low,dtype=tf.float32)
class AdditiveGuassianNoiseAutoencoder():
def __init__(self,n_input,n_hidden,transfer_function=tf.nn.softplus,
optimzer=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(),scale=0.1):
# 网络参数
self.n_input = n_input
self.n_hidden = n_hidden
self.transfer = transfer_function # 激活函数
self.training_scale = scale # 噪声水平
network_weights = self._initialize_weights()
self.weights = network_weights
# 网络结构
with tf.name_scope('Rawinput'): #<---
self.x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_input])
with tf.name_scope('NoiseAdder'): #<---
self.scale = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32) #<---使用占位符取代了固定的scale,增加了feed量
self.noise_x = self.x + self.scale * tf.random_normal((n_input,)) #<---
with tf.name_scope('Encoder'): #<---
self.hidden = self.transfer(
tf.add(tf.matmul(self.noise_x, self.weights['w1']), self.weights['b1']))
with tf.name_scope('Reconstruction'): #<---
self.reconstruction = tf.add(
tf.matmul(self.hidden, self.weights['w2']), self.weights['b2'])
# 训练部分
with tf.name_scope('Loss'): #<---
self.cost = 0.5 * tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow(tf.subtract(self.reconstruction, self.x), 2))
with tf.name_scope('Train'):
self.optimizer = optimzer.minimize(self.cost)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
self.sess = tf.Session()
self.sess.run(init)
print('begin to run session... ...')
def _initialize_weights(self):
all_weights = dict()
all_weights['w1'] = tf.Variable(xavier_init(self.n_input, self.n_hidden) ,name='weight1') #<---
all_weights['b1'] = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([self.n_hidden], dtype=tf.float32), name='bias1')
all_weights['w2'] = tf.Variable(xavier_init(self.n_hidden, self.n_input), name='weight2')
all_weights['b2'] = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([self.n_input], dtype=tf.float32), name='bias2')
return all_weights
AGN_AC = AdditiveGuassianNoiseAutoencoder(n_input=784, n_hidden=200,
transfer_function=tf.nn.softplus,
optimzer=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01),
scale=0.01)
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logdir='logs', graph=AGN_AC.sess.graph)
writer.close()
图:

Version3
保留字典结构存储W&b
但是把字典key&value生成拆开放在了每一层中
import numpy as np
import sklearn.preprocessing as prep
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import os
# 关闭tensorflow的警告信息
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
# 标准均匀分布
def xavier_init(fan_in,fan_out,constant = 1):
low = -constant * np.sqrt(6.0/(fan_in+fan_out))
hight = constant * np.sqrt(6.0/(fan_in+fan_out))
return tf.random_uniform((fan_in,fan_out),maxval=hight,minval=low,dtype=tf.float32)
class AdditiveGuassianNoiseAutoencoder():
def __init__(self,n_input,n_hidden,transfer_function=tf.nn.softplus,
optimzer=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(),scale=0.1):
# 网络参数
self.n_input = n_input
self.n_hidden = n_hidden
self.transfer = transfer_function # 激活函数
self.training_scale = scale # 噪声水平
self.weights = dict() #<---
# network_weights = self._initialize_weights()
# self.weights = network_weights
# 网络结构
with tf.name_scope('Rawinput'):
self.x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_input])
with tf.name_scope('NoiseAdder'):
self.scale = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
self.noise_x = self.x + self.scale * tf.random_normal((n_input,))
with tf.name_scope('Encoder'):
self.weights['w1'] = tf.Variable(xavier_init(self.n_input, self.n_hidden), name='weight1') #<---
self.weights['b1'] = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([self.n_hidden], dtype=tf.float32), name='bias1') #<---
self.hidden = self.transfer(
tf.add(tf.matmul(self.noise_x, self.weights['w1']), self.weights['b1']))
with tf.name_scope('Reconstruction'):
self.weights['w2'] = tf.Variable(xavier_init(self.n_hidden, self.n_input), name='weight2') #<---
self.weights['b2'] = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([self.n_input], dtype=tf.float32), name='bias2') #<---
self.reconstruction = tf.add(
tf.matmul(self.hidden, self.weights['w2']), self.weights['b2'])
# 训练部分
with tf.name_scope('Loss'):
self.cost = 0.5 * tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow(tf.subtract(self.reconstruction, self.x), 2))
with tf.name_scope('Train'):
self.optimizer = optimzer.minimize(self.cost)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
self.sess = tf.Session()
self.sess.run(init)
print('begin to run session... ...')
# def _initialize_weights(self):
# all_weights = dict()
# all_weights['w1'] = tf.Variable(xavier_init(self.n_input, self.n_hidden) ,name='weight1')
# all_weights['b1'] = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([self.n_hidden], dtype=tf.float32), name='bias1')
# all_weights['w2'] = tf.Variable(xavier_init(self.n_hidden, self.n_input), name='weight2')
# all_weights['b2'] = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([self.n_input], dtype=tf.float32), name='bias2')
# return all_weights
AGN_AC = AdditiveGuassianNoiseAutoencoder(n_input=784, n_hidden=200,
transfer_function=tf.nn.softplus,
optimzer=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01),
scale=0.01)
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logdir='logs', graph=AGN_AC.sess.graph)
writer.close()
图:
总结:
1.参数变量使用字典保存提升规整性;
2.参数变量生成仍然要放在层中,可视化效果更好。
降噪自编码器完整程序
import numpy as np
import sklearn.preprocessing as prep
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import os
# 关闭tensorflow的警告信息
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
# 标准均匀分布
def xavier_init(fan_in,fan_out,constant = 1):
low = -constant * np.sqrt(6.0/(fan_in+fan_out))
hight = constant * np.sqrt(6.0/(fan_in+fan_out))
return tf.random_uniform((fan_in,fan_out),maxval=hight,minval=low,dtype=tf.float32)
class AdditiveGuassianNoiseAutoencoder():
def __init__(self,n_input,n_hidden,transfer_function=tf.nn.softplus,
optimzer=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(),scale=0.1):
# 网络参数
self.n_input = n_input
self.n_hidden = n_hidden
self.transfer = transfer_function # 激活函数
self.training_scale = scale # 噪声水平
self.weights = dict()
# network_weights = self._initialize_weights()
# self.weights = network_weights
# 网络结构
with tf.name_scope('Rawinput'):
self.x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_input])
with tf.name_scope('NoiseAdder'):
self.scale = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
self.noise_x = self.x + self.scale * tf.random_normal((n_input,))
with tf.name_scope('Encoder'):
self.weights['w1'] = tf.Variable(xavier_init(self.n_input, self.n_hidden), name='weight1') # <---
self.weights['b1'] = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([self.n_hidden], dtype=tf.float32), name='bias1')
self.hidden = self.transfer(
tf.add(tf.matmul(self.noise_x, self.weights['w1']), self.weights['b1']))
with tf.name_scope('Reconstruction'):
self.weights['w2'] = tf.Variable(xavier_init(self.n_hidden, self.n_input), name='weight2') # <---
self.weights['b2'] = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([self.n_input], dtype=tf.float32), name='bias2')
self.reconstruction = tf.add(
tf.matmul(self.hidden, self.weights['w2']), self.weights['b2'])
# 训练部分
with tf.name_scope('Loss'):
self.cost = 0.5 * tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow(tf.subtract(self.reconstruction, self.x), 2))
with tf.name_scope('Train'):
self.optimizer = optimzer.minimize(self.cost)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
self.sess = tf.Session()
self.sess.run(init)
print('begin to run session... ...')
def partial_fit(self, X):
'''
训练并计算cost
:param X:
:return:
'''
cost, opt = self.sess.run([self.cost, self.optimizer],
feed_dict={self.x:X, self.scale:self.training_scale})
return cost
def calc_cost(self, X):
'''
不训练,只计算cost
:param X:
:return:
'''
return self.sess.run(self.cost, feed_dict={self.x: X, self.scale: self.training_scale})
# 数据集预处理
def standard_scale(X_train, X_test): #<-----数据集预处理部分
'''
0均值,1标准差
:param X_train:
:param X_test:
:return:
'''
# 根据预估的训练集的参数生成预处理器
preprocessor = prep.StandardScaler().fit(X_train)
X_train = preprocessor.transform(X_train)
X_test = preprocessor.transform(X_test)
return X_train, X_test
def get_random_block_from_data(data, batch_size):
'''
随机取一个batch的数据
:param data:
:param batch_size:
:return:
'''
start_index = np.random.randint(0, len(data) - batch_size)
return data[start_index:(start_index+batch_size)]
# 展示计算图
AGN_AC = AdditiveGuassianNoiseAutoencoder(n_input=784, n_hidden=200,
transfer_function=tf.nn.softplus,
optimzer=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01),
scale=0.01)
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logdir='logs', graph=AGN_AC.sess.graph)
writer.close()
# 读取数据
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('../Mnist_data/', one_hot=True)
X_train, X_test = standard_scale(mnist.train.images, mnist.test.images)
n_samples = int(mnist.train.num_examples) # 训练样本总数
training_epochs = 20 # 训练轮数,1轮等于n_samples/batch_size
batch_size = 128 # batch容量
display_step = 1 # 展示间隔
# 训练
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0 # 平均损失
total_batch = int(n_samples/batch_size) # 每一轮中step总数
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs = get_random_block_from_data(X_train, batch_size)
cost = AGN_AC.partial_fit(batch_xs)
avg_cost += cost / batch_size
avg_cost /= total_batch
if epoch % display_step == 0:
print('epoch : %04d, cost = %.9f' % (epoch+1, avg_cost))
# 计算测试集上的cost
print('Total coat:', str(AGN_AC.calc_cost(X_test)))
引入了数据预处理机制:
import sklearn.preprocessing as prep
# 数据集预处理
def standard_scale(X_train, X_test): #<-----一个新的尝试
'''
0均值,1标准差
:param X_train:
:param X_test:
:return:
'''
# 根据预估的训练集的参数生成预处理器
preprocessor = prep.StandardScaler().fit(X_train)
X_train = preprocessor.transform(X_train)
X_test = preprocessor.transform(X_test)
return X_train, X_test
因为就是个范例而已,所以并没有加入更多的步骤。
输出:
Python 3.6.0 |Anaconda 4.3.1 (64-bit)| (default, Dec 23 2016, 12:22:00)
Type "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
IPython 5.1.0 -- An enhanced Interactive Python.
? -> Introduction and overview of IPython's features.
%quickref -> Quick reference.
help -> Python's own help system.
object? -> Details about 'object', use 'object??' for extra details.
PyDev console: using IPython 5.1.0
Running /home/hellcat/PycharmProjects/data_analysis/TensorFlow/autoencodes/denoise.py
Backend Qt5Agg is interactive backend. Turning interactive mode on.
begin to run session... ...
Extracting ../Mnist_data/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
Extracting ../Mnist_data/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
Extracting ../Mnist_data/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
Extracting ../Mnist_data/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
epoch : 0001, cost = 172728.840323210
epoch : 0002, cost = 384090.340043217
epoch : 0003, cost = 1424137.733514817
epoch : 0004, cost = 252195.476644165
epoch : 0005, cost = 1989602.406287275
epoch : 0006, cost = 82078.567135613
epoch : 0007, cost = 4571607.288953234
epoch : 0008, cost = 12936386.999440582
epoch : 0009, cost = 192551.124642752
epoch : 0010, cost = 40848.185927740
epoch : 0011, cost = 2998.114711095
epoch : 0012, cost = 15210.583374379
epoch : 0013, cost = 38411.792979990
epoch : 0014, cost = 5556.733809144
epoch : 0015, cost = 35625.806443790
epoch : 0016, cost = 1274942.135287910
epoch : 0017, cost = 214436.171889868
epoch : 0018, cost = 29740.634501637
epoch : 0019, cost = 1136.356513888
epoch : 0020, cost = 2248.695473340
Total coat: 4.2886e+06