在 http://flume.apache.org 上下载flume-1.6.0版本,将源码导入到Idea开发工具后如下图所示:
一、主要模块说明
-
flume-ng-channels 里面包含了filechannel,jdbcchannel,kafkachannel,memorychannel通道的实现。
-
flume-ng-clients 实现了log4j相关的几个Appender,使得log4j的日志输出可以直接发送给flume-agent;其中有一个LoadBalancingLog4jAppender的实现,提供了多个flume-agent的load balance和ha功能,采用flume作为日志收集的可以考虑将这个appender引入内部的log4j中。
-
flume-ng-configuration 这个主要就是Flume配置信息相关的类,包括载入flume-config.properties配置文件并解析。其中包括了Source的配置,Sink的配置,Channel的配置,在阅读源码前推荐先梳理这部分关系再看其他部分的。
-
flume-ng-core flume整个核心框架,包括了各个模块的接口以及逻辑关系实现。其中instrumentation是flume内部实现的一套metric机制,metric的变化和维护,其核心也就是在MonitoredCounterGroup中通过一个Map<key, AtomicLong>来实现metric的计量。ng-core下几乎大部分代码任然几种在channel、sink、source几个子目录下,其他目录基本完成一个util和辅助的功能。
-
flume-ng-node 实现启动flume的一些基本类,包括main函数的入口(Application.java中)。在理解configuration之后,从application的main函数入手,可以较快的了解整个flume的代码。
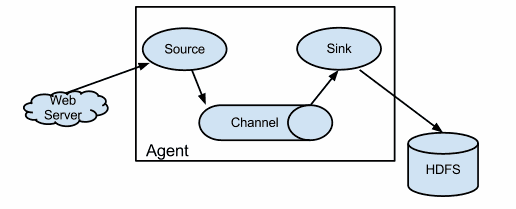
二、Flume逻辑结构图
三、flume-ng启动文件介绍
################################
# constants
################################
#设置常量值,主要是针对不同的参数执行相应的类,以启动Flume环境
FLUME_AGENT_CLASS="org.apache.flume.node.Application"
FLUME_AVRO_CLIENT_CLASS="org.apache.flume.client.avro.AvroCLIClient"
FLUME_VERSION_CLASS="org.apache.flume.tools.VersionInfo"
FLUME_TOOLS_CLASS="org.apache.flume.tools.FlumeToolsMain"
#真正启动Flume环境的方法
run_flume() {
local FLUME_APPLICATION_CLASS
if [ "$#" -gt 0 ]; then
FLUME_APPLICATION_CLASS=$1
shift
else
error "Must specify flume application class" 1
fi
if [ ${CLEAN_FLAG} -ne 0 ]; then
set -x
fi
#执行这一行命令,执行相应的启动类,比如org.apache.flume.node.Application
$EXEC $JAVA_HOME/bin/java $JAVA_OPTS $FLUME_JAVA_OPTS "${arr_java_props[@]}" -cp "$FLUME_CLASSPATH"
-Djava.library.path=$FLUME_JAVA_LIBRARY_PATH "$FLUME_APPLICATION_CLASS" $*
}
################################
# main
################################
# set default params
# 在启动的过程中使用到的参数
FLUME_CLASSPATH=""
FLUME_JAVA_LIBRARY_PATH=""
#默认占用堆空间大小,这一块都可以根据JVM进行重新设置
JAVA_OPTS="-Xmx20m"
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=""
opt_conf=""
opt_classpath=""
opt_plugins_dirs=""
arr_java_props=()
arr_java_props_ct=0
opt_dryrun=""
# 根据不同的参数,执行不同的启动类,每个常量所对应的类路径在代码前面有过介绍。
if [ -n "$opt_agent" ] ; then
run_flume $FLUME_AGENT_CLASS $args
elif [ -n "$opt_avro_client" ] ; then
run_flume $FLUME_AVRO_CLIENT_CLASS $args
elif [ -n "${opt_version}" ] ; then
run_flume $FLUME_VERSION_CLASS $args
elif [ -n "${opt_tool}" ] ; then
run_flume $FLUME_TOOLS_CLASS $args
else
error "This message should never appear" 1
fi
这是其中最主要的一部分flume-ng命令行,根据重要性摘取了一段,感兴趣的读者可以自己到bin目录下查看全部。
四、从Flume-NG启动过程开始说起
从bin/flume-ng这个shell脚本可以看到Flume的起始于org.apache.flume.node.Application类,这是flume的main函数所在。
main方法首先会先解析shell命令,如果指定的配置文件不存在就抛出异常。
代码如下所示:
Options options = new Options();
Option option = new Option("n", "name", true, "the name of this agent");
option.setRequired(true);
options.addOption(option);
option = new Option("f", "conf-file", true,
"specify a config file (required if -z missing)");
option.setRequired(false);
options.addOption(option);
option = new Option(null, "no-reload-conf", false,
"do not reload config file if changed");
options.addOption(option);
// Options for Zookeeper
option = new Option("z", "zkConnString", true,
"specify the ZooKeeper connection to use (required if -f missing)");
option.setRequired(false);
options.addOption(option);
option = new Option("p", "zkBasePath", true,
"specify the base path in ZooKeeper for agent configs");
option.setRequired(false);
options.addOption(option);
option = new Option("h", "help", false, "display help text");
options.addOption(option);
#命令行解析类
CommandLineParser parser = new GnuParser();
CommandLine commandLine = parser.parse(options, args);
if (commandLine.hasOption('h')) {
new HelpFormatter().printHelp("flume-ng agent", options, true);
return;
}
String agentName = commandLine.getOptionValue('n');
boolean reload = !commandLine.hasOption("no-reload-conf");
if (commandLine.hasOption('z') || commandLine.hasOption("zkConnString")) {
isZkConfigured = true;
}
以上代码是Application类中校验shell命令行的代码,举个例子在启动flume的时候,使用如下命令行:
./bin/flume-ng agent -n agent -c conf -f conf/hw.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
里面的-n -f等参数都是在上面代码中校验的。
再往下看main方法里的代码:
File configurationFile = new File(commandLine.getOptionValue('f'));
/*
* The following is to ensure that by default the agent will fail on
* startup if the file does not exist.
*/
if (!configurationFile.exists()) {
// If command line invocation, then need to fail fast
if (System.getProperty(Constants.SYSPROP_CALLED_FROM_SERVICE) ==
null) {
String path = configurationFile.getPath();
try {
path = configurationFile.getCanonicalPath();
} catch (IOException ex) {
logger.error("Failed to read canonical path for file: " + path,
ex);
}
throw new ParseException(
"The specified configuration file does not exist: " + path);
}
}
List<LifecycleAware> components = Lists.newArrayList();
if (reload) {
EventBus eventBus = new EventBus(agentName + "-event-bus");
PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider configurationProvider =
new PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider(
agentName, configurationFile, eventBus, 30);
components.add(configurationProvider);
application = new Application(components);
eventBus.register(application);
} else {
PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider configurationProvider =
new PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider(
agentName, configurationFile);
application = new Application();
application.handleConfigurationEvent(configurationProvider
.getConfiguration());
}
}
application.start();
说明:
根据命令中含有”no-reload-conf”参数,决定采用那种加载配置文件方式:
一、没有此参数,会动态加载配置文件,默认每30秒加载一次配置文件,因此可以动态修改配置文件;
二、有此参数,则只在启动时加载一次配置文件。实现动态加载功能采用了发布订阅模式,使用guava中的EventBus实现。
三、PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider这个类是配置文件加载类。
类图如下:
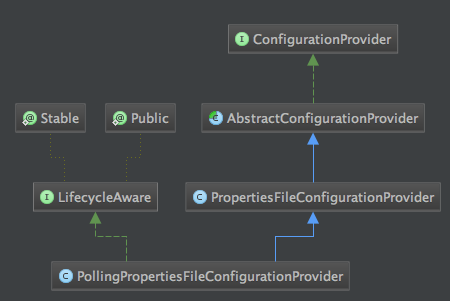
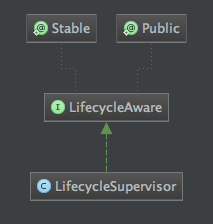
从图中可以看出在整个PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider类中,它实现了LifecycleAware接口,而这个接口是掌管整个Flume生命周期的一个核心接口,LifecycleSupervisor实现了这个接口,通过上面代码中application.start方法触发LifecyleAware的start方法,下面是这个接口的方法定义及相关类代码:
public interface LifecycleAware {
/**
* <p>
* Starts a service or component.
* </p>
* @throws LifecycleException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public void start();
/**
* <p>
* Stops a service or component.
* </p>
* @throws LifecycleException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public void stop();
/**
* <p>
* Return the current state of the service or component.
* </p>
*/
public LifecycleState getLifecycleState();
}
Application.start()方法内容:
public synchronized void start() {
for(LifecycleAware component : components) {
supervisor.supervise(component,
new SupervisorPolicy.AlwaysRestartPolicy(), LifecycleState.START);
}
}
LifecycleSupervisor.supervise方法内容如下:
public synchronized void supervise(LifecycleAware lifecycleAware,
SupervisorPolicy policy, LifecycleState desiredState) {
if(this.monitorService.isShutdown()
|| this.monitorService.isTerminated()
|| this.monitorService.isTerminating()){
throw new FlumeException("Supervise called on " + lifecycleAware + " " +
"after shutdown has been initiated. " + lifecycleAware + " will not" +
" be started");
}
Preconditions.checkState(!supervisedProcesses.containsKey(lifecycleAware),
"Refusing to supervise " + lifecycleAware + " more than once");
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Supervising service:{} policy:{} desiredState:{}",
new Object[] { lifecycleAware, policy, desiredState });
}
Supervisoree process = new Supervisoree();
process.status = new Status();
process.policy = policy;
process.status.desiredState = desiredState;
process.status.error = false;
MonitorRunnable monitorRunnable = new MonitorRunnable();
monitorRunnable.lifecycleAware = lifecycleAware;
monitorRunnable.supervisoree = process;
monitorRunnable.monitorService = monitorService;
supervisedProcesses.put(lifecycleAware, process);
ScheduledFuture<?> future = monitorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(
monitorRunnable, 0, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
monitorFutures.put(lifecycleAware, future);
}
在上面的代码中,会创建MonitorRunnable对象,这个对象是个定时对象,里面的run方法主要是根据supervisoree.status.desiredState的值执行对应的操作。
包括:START,STOP等状态, 大家注意scheduleWithFixedDelay这个方法,这是java线程池自带的,要求每次任务执行完以后再延迟3秒,而不是每隔3秒执行一次,大家注意这一点。
又有同学会问循环调用会不会有问题,这里回应大家其实也没问题,这么做是为了重试机制,看下面代码:
if (!lifecycleAware.getLifecycleState().equals( supervisoree.status.desiredState))
在MonitorRunnable内部有这样一个判断,当getLifecycleState与supervisoree.status.desiredState状态不相等的时候才会执行,而ifecycleAware.getLifecycleState()初始状态是IDLE。
时序调用图如下所示
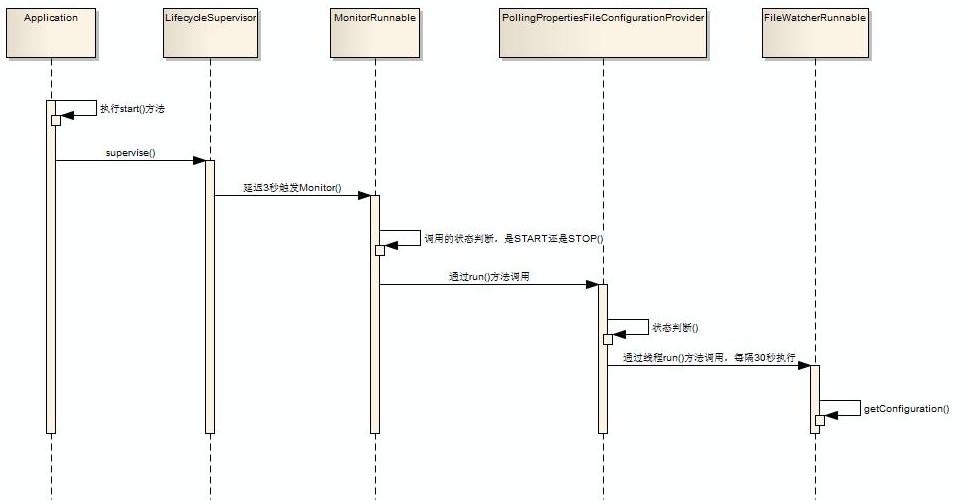
注:
PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider.start()方法会启动一个单线程FileWatcherRunnable每隔30s去加载一次配置文件:
eventBus.post(getConfiguration())。
getConfiguration()解析了配置文件并且获取所有组件及配置属性
五、配置文件加载详细分析
先看一下FileWatcherRunnable内部的代码:
public MaterializedConfiguration getConfiguration() {
//初始化三大组件的配置Map,source,channel,sink
MaterializedConfiguration conf = new SimpleMaterializedConfiguration();
FlumeConfiguration fconfig = getFlumeConfiguration();
AgentConfiguration agentConf = fconfig.getConfigurationFor(getAgentName());
if (agentConf != null) {
Map<String, ChannelComponent> channelComponentMap = Maps.newHashMap();
Map<String, SourceRunner> sourceRunnerMap = Maps.newHashMap();
Map<String, SinkRunner> sinkRunnerMap = Maps.newHashMap();
try {
loadChannels(agentConf, channelComponentMap);
loadSources(agentConf, channelComponentMap, sourceRunnerMap);
loadSinks(agentConf, channelComponentMap, sinkRunnerMap);
Set<String> channelNames =
new HashSet<String>(channelComponentMap.keySet());
for(String channelName : channelNames) {
ChannelComponent channelComponent = channelComponentMap.
get(channelName);
if(channelComponent.components.isEmpty()) {
LOGGER.warn(String.format("Channel %s has no components connected" +
" and has been removed.", channelName));
channelComponentMap.remove(channelName);
Map<String, Channel> nameChannelMap = channelCache.
get(channelComponent.channel.getClass());
if(nameChannelMap != null) {
nameChannelMap.remove(channelName);
}
} else {
LOGGER.info(String.format("Channel %s connected to %s",
channelName, channelComponent.components.toString()));
conf.addChannel(channelName, channelComponent.channel);
}
}
for(Map.Entry<String, SourceRunner> entry : sourceRunnerMap.entrySet()) {
conf.addSourceRunner(entry.getKey(),