- OpenCV中的阈值(threshold)函数: threshold 的运用。
-
C++: double threshold(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, double thresh, double maxVal, int threshold-
Type)
Python: cv2.threshold(src, thresh, maxval, type[, dst ])! retval, dst
C: double cvThreshold(const CvArr* src, CvArr* dst, double threshold, double maxValue, int threshold-
Type)
Python: cv.Threshold(src, dst, threshold, maxValue, thresholdType) !None
Parameters
src – Source array (single-channel, 8-bit of 32-bit floating point).
dst – Destination array of the same size and type as src .
thresh – Threshold value.
maxVal – Maximum value to use with the THRESH_BINARY and THRESH_BINARY_INV
thresholding types.
thresholdType – Thresholding type (see the details below).
-
最简单的图像分割的方法。
-
应用举例:从一副图像中利用阈值分割出我们需要的物体部分(当然这里的物体可以是一部分或者整体)。这样的图像分割方法是基于图像中物体与背景之间的灰度差异,而且此分割属于像素级的分割。
-
为了从一副图像中提取出我们需要的部分,应该用图像中的每一个像素点的灰度值与选取的阈值进行比较,并作出相应的判断。(注意:阈值的选取依赖于具体的问题。即:物体在不同的图像中有可能会有不同的灰度值。
-
一旦找到了需要分割的物体的像素点,我们可以对这些像素点设定一些特定的值来表示。(例如:可以将该物体的像素点的灰度值设定为:‘0’(黑色),其他的像素点的灰度值为:‘255’(白色);当然像素点的灰度值可以任意,但最好设定的两种颜色对比度较强,方便观察结果)。
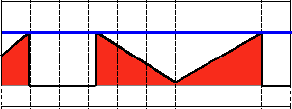
阈值类型1:二进制阈值化(THRESH_BINARY)
-
该阈值化类型如下式所示:
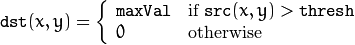
-
解释:在运用该阈值类型的时候,先要选定一个特定的阈值量,比如:125,这样,新的阈值产生规则可以解释为大于125的像素点的灰度值设定为最大值(如8位灰度值最大为255),灰度值小于125的像素点的灰度值设定为0。
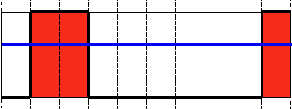
阈值类型2:反二进制阈值化(THRESH_BINARY_INV)
-
该阈值类型如下式所示:
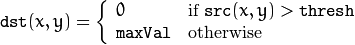
-
解释:该阈值化与二进制阈值化相似,先选定一个特定的灰度值作为阈值,不过最后的设定值相反。(在8位灰度图中,例如大于阈值的设定为0,而小于该阈值的设定为255)。
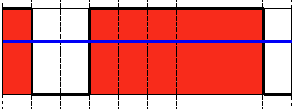
阈值类型3:截断阈值化(THRESH_TRUNC)
-
该阈值化类型如下式所示:
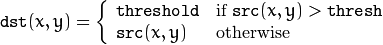
-
解释:同样首先需要选定一个阈值,图像中大于该阈值的像素点被设定为该阈值,小于该阈值的保持不变。(例如:阈值选取为125,那小于125的阈值不改变,大于125的灰度值(230)的像素点就设定为该阈值)。
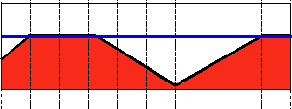
阈值类型4:阈值化为0(THRESH_TOZERO)
-
该阈值类型如下式所示:
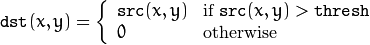
-
解释:先选定一个阈值,然后对图像做如下处理:1 像素点的灰度值大于该阈值的不进行任何改变;2 像素点的灰度值小于该阈值的,其灰度值全部变为0。
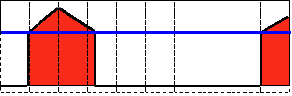
阈值类型5:反阈值化为0(THRESH_TOZERO_INV)
-
该阈值类型如下式所示:
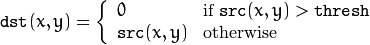
-
解释:原理类似于0阈值,但是在对图像做处理的时候相反,即:像素点的灰度值小于该阈值的不进行任何改变,而大于该阈值的部分,其灰度值全部变为0。