【平衡树splay实现】
无注释代码

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef long long LL; 4 const int INF=1e9+7,MAXN=1e5+5; 5 int N; 6 int key[MAXN],cnt[MAXN],ch[MAXN][2],siz[MAXN],f[MAXN]; 7 int root,sz; 8 inline void clear(int x){ 9 key[x]=cnt[x]=ch[x][0]=ch[x][1]=siz[x]=f[x]=0; 10 } 11 inline int get(int x){ 12 return x==ch[f[x]][1]; 13 } 14 inline void upd(int x){ 15 if(x){ 16 siz[x]=cnt[x]; 17 if(ch[x][0]){ 18 siz[x]+=siz[ch[x][0]]; 19 } 20 if(ch[x][1]){ 21 siz[x]+=siz[ch[x][1]]; 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 inline void rotate(int x){ 26 int fa=f[x],gf=f[fa],which=get(x); 27 ch[fa][which]=ch[x][which^1]; 28 f[ch[fa][which]]=fa; 29 ch[x][which^1]=fa; 30 f[fa]=x; 31 f[x]=gf; 32 if(gf){ 33 ch[gf][ch[gf][1]==fa]=x; 34 } 35 upd(fa); 36 upd(x); 37 } 38 inline void splay(int x){ 39 for(int fa;(fa=f[x]);rotate(x)){ 40 if(f[fa]){ 41 rotate(get(x)==get(fa)?fa:x); 42 } 43 } 44 root=x; 45 } 46 inline void ins(int x){ 47 if(!root){ 48 sz++; 49 clear(sz); 50 root=sz; 51 cnt[sz]=siz[sz]=1; 52 key[sz]=x; 53 return; 54 } 55 int cur=root,fa=0; 56 while(1){ 57 if(x==key[cur]){ 58 cnt[cur]++; 59 upd(cur); 60 upd(fa); 61 splay(cur); 62 return; 63 } 64 fa=cur; 65 cur=ch[fa][key[fa]<x]; 66 if(!cur){ 67 clear(++sz); 68 f[sz]=fa; 69 cnt[sz]=siz[sz]=1; 70 ch[fa][key[fa]<x]=sz; 71 key[sz]=x; 72 upd(fa); 73 splay(sz); 74 return; 75 } 76 } 77 } 78 inline int find(int x){ 79 int cur=root,ret=0; 80 while(1){ 81 if(x<key[cur]){ 82 cur=ch[cur][0]; 83 }else{ 84 ret+=(ch[cur][0]?siz[ch[cur][0]]:0); 85 if(key[cur]==x){ 86 splay(cur); 87 return ret+1; 88 } 89 ret+=cnt[cur]; 90 cur=ch[cur][1]; 91 } 92 } 93 } 94 inline int findx(int x){ 95 int cur=root; 96 while(1){ 97 if(ch[cur][0]&&x<=siz[ch[cur][0]]){ 98 cur=ch[cur][0]; 99 }else{ 100 int tmp=(ch[cur][0]?siz[ch[cur][0]]:0)+cnt[cur]; 101 if(x<=tmp){ 102 return key[cur]; 103 } 104 x-=tmp; 105 cur=ch[cur][1]; 106 } 107 } 108 } 109 inline int pre(){ 110 int cur=ch[root][0]; 111 while(ch[cur][1]){ 112 cur=ch[cur][1]; 113 } 114 return cur; 115 } 116 inline int nxt(){ 117 int cur=ch[root][1]; 118 while(ch[cur][0]){ 119 cur=ch[cur][0]; 120 } 121 return cur; 122 } 123 inline void del(int x){ 124 find(x); 125 if(cnt[root]>1){ 126 cnt[root]--; 127 upd(root); 128 return; 129 } 130 if(!ch[root][0]&&!ch[root][1]){ 131 clear(root); 132 root=0; 133 return; 134 } 135 if(!ch[root][0]){ 136 int old=root; 137 root=ch[root][1]; 138 f[root]=0; 139 clear(old); 140 return; 141 } 142 if(!ch[root][1]){ 143 int old=root; 144 root=ch[root][0]; 145 f[root]=0; 146 clear(old); 147 return; 148 } 149 int old=root,p=pre(); 150 splay(p); 151 ch[root][1]=ch[old][1]; 152 f[ch[old][1]]=root; 153 clear(old); 154 upd(root); 155 } 156 int main(){ 157 scanf("%d",&N); 158 for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){ 159 int ii,jj; 160 scanf("%d%d",&ii,&jj); 161 switch(ii){ 162 case 1:{ 163 ins(jj); 164 break; 165 } 166 case 2:{ 167 del(jj); 168 break; 169 } 170 case 3:{ 171 printf("%d ",find(jj)); 172 break; 173 } 174 case 4:{ 175 printf("%d ",findx(jj)); 176 break; 177 } 178 case 5:{ 179 ins(jj); 180 printf("%d ",key[pre()]); 181 del(jj); 182 break; 183 } 184 case 6:{ 185 ins(jj); 186 printf("%d ",key[nxt()]); 187 del(jj); 188 break; 189 } 190 } 191 } 192 return 0; 193 }
变量声明:f[i]表示i的父结点,ch[i][0]表示i的左儿子,ch[i][1]表示i的右儿子,key[i]表示i的关键字(即结点i代表的那个数字),cnt[i]表示i结点的关键字出现的次数(相当于权值),size[i]表示包括i的这个子树的大小;sz为整棵树的大小,root为整棵树的根。
再介绍几个基本操作:
【clear操作】:将当前点的各项值都清0(用于删除之后)
inline void clear(int x){/*清空节点中的数据*/ key[x]=cnt[x]=ch[x][0]=ch[x][1]=siz[x]=f[x]=0; }
【get操作】:判断当前点是它父结点的左儿子还是右儿子
inline int get(int x){/*查询当前点是否为右孩子*/ return x==ch[f[x]][1]; }
【update操作】:更新当前点的size值(用于发生修改之后)
inline void upd(int x){/*更新cnt和siz数组*/ if(x){ siz[x]=cnt[x]; if(ch[x][0]){ siz[x]+=siz[ch[x][0]]; } if(ch[x][1]){ siz[x]+=siz[ch[x][1]]; } } }
【rotate操作】
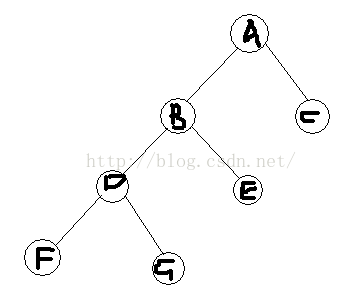
这是原来的树,假设我们现在要将D结点rotate到它的父亲的位置。
step 1:
找出D的父亲结点(B)以及父亲的父亲(A)并记录。判断D是B的左结点还是右结点。
step 2:
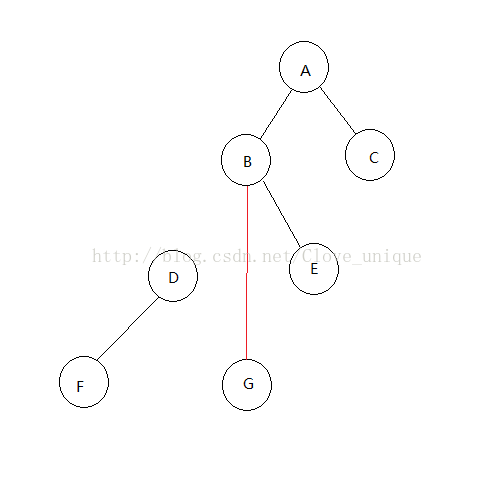
我们知道要将Drotate到B的位置,二叉树的大小关系不变的话,B就要成为D的右结点了没错吧?
咦?可是D已经有右结点了,这样不就冲突了吗?怎么解决这个冲突呢?
我们知道,D原来是B的左结点,那么rotate过后B就一定没有左结点了对吧,那么正好,我们把G接到B的左结点去,并且这样大小关系依然是不变的,就完美的解决了这个冲突。
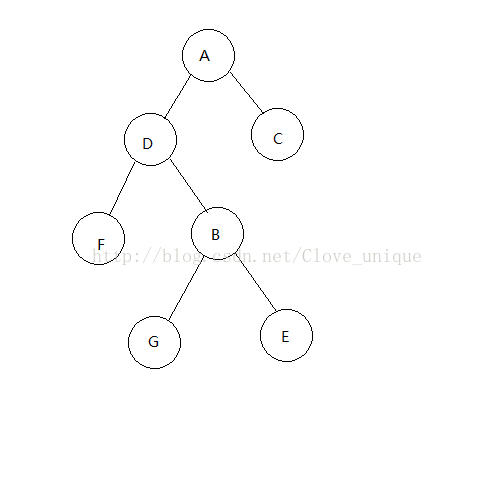
这样我们就完成了一次rotate,如果是右儿子的话同理。step 2的具体操作:
我们已经判断了D是B的左儿子还是右儿子,设这个关系为K;将D与K关系相反的儿子的父亲记为B与K关系相同的儿子(这里即为D的右儿子的父亲记为B的左儿子);将D与K关系相反的儿子的父亲即为B(这里即为把G的父亲记为B);将B的父亲即为D;将D与K关系相反的儿子记为B(这里即为把D的右儿子记为B);将D的父亲记为A。
最后要判断,如果A存在(即rotate到的位置不是根的话),要把A的儿子即为D。
显而易见,rotate之后所有牵涉到变化的父子关系都要改变。以上的树需要改变四对父子关系,BG DG BD AB,需要三个操作(BG BD AB)。
step 3:update一下当前点和各个父结点的各个值
inline void rotate(int x){ int fa=f[x]/*父亲*/,gf=f[fa]/*祖父*/,which=get(x); ch[fa][which]=ch[x][which^1]; f[ch[fa][which]]=fa; ch[x][which^1]=fa; f[fa]=x; f[x]=gf; if(gf){ ch[gf][ch[gf][1]==fa]=x; } upd(fa);/*先更新在下面的节点*/ upd(x); }
【splay操作】
其实splay只是rotate的发展。伸展操作只是在不停的rotate,一直到达到目标状态。如果有一个确定的目标状态,也可以传两个参。此代码直接splay到根。
splay的过程中需要分类讨论,如果是三点一线的话(x,x的父亲,x的祖父)需要先rotate x的父亲,否则需要先rotate x本身(否则会形成单旋使平衡树失衡)
inline void splay(int x){ for(int fa;(fa=f[x]);rotate(x)){ // printf("fa[%d]=%d ",fa,f[fa]); if(f[fa]){ rotate(get(x)==get(fa)?fa:x);/*三点一线先rotate父亲*/ } } root=x; }
【insert操作】
其实插入操作是比较简单的,和普通的二叉查找树基本一样。
step 1:如果root=0,即树为空的话,做一些特殊的处理,直接返回即可。
step 2:按照二叉查找树的方法一直向下找,其中:
如果遇到一个结点的关键字等于当前要插入的点的话,我们就等于把这个结点加了一个权值。因为在二叉搜索树中是不可能出现两个相同的点的。并且要将当前点和它父亲结点的各项值更新一下。做一下splay。
如果已经到了最底下了,那么就可以直接插入。整个树的大小要+1,新结点的左儿子右儿子(虽然是空)父亲还有各项值要一一对应。并且最后要做一下他父亲的update(做他自己的没有必要)。做一下splay。
inline void ins(int x){ if(!root){ sz++; clear(sz); root=sz; cnt[sz]=siz[sz]=1; key[sz]=x; return; } int cur=root,fa=0; while(1){ if(x==key[cur]){ cnt[cur]++; upd(cur); upd(fa); splay(cur); return; } fa=cur; cur=ch[fa][key[fa]<x]; if(!cur){ clear(++sz); f[sz]=fa; cnt[sz]=siz[sz]=1; ch[fa][key[fa]<x]=sz; key[sz]=x; upd(fa); splay(sz); return; } } }
【find操作】查询x的排名
初始化:ans=0,当前点=root
和其它二叉搜索树的操作基本一样。但是区别是:
如果x比当前结点小,即应该向左子树寻找,ans不用改变(设想一下,走到整棵树的最左端最底端排名不就是1吗)。
如果x比当前结点大,即应该向右子树寻找,ans需要加上左子树的大小以及根的大小(这里的大小指的是权值)。
不要忘记了再splay一下
inline int find(int x){ int cur=root,ret=0; while(1){ if(x<key[cur]){ cur=ch[cur][0]; }else{ ret+=(ch[cur][0]?siz[ch[cur][0]]:0); if(key[cur]==x){ splay(cur); return ret+1; } ret+=cnt[cur]; cur=ch[cur][1]; } } }
【findx操作】找到排名为x的点
初始化:当前点=root
和上面的思路基本相同:
如果当前点有左子树,并且x比左子树的大小小的话,即向左子树寻找;
否则,向右子树寻找:先判断是否有右子树,然后记录右子树的大小以及当前点的大小(都为权值),用于判断是否需要继续向右子树寻找。
inline int findx(int x){ int cur=root; while(1){ if(ch[cur][0]&&x<=siz[ch[cur][0]]){ cur=ch[cur][0]; }else{ int tmp=(ch[cur][0]?siz[ch[cur][0]]:0)+cnt[cur]; if(x<=tmp){ return key[cur]; } x-=tmp; cur=ch[cur][1]; } } }
【求x的前驱(后继),前驱(后继)定义为小于(大于)x,且最大(最小)的数】
这类问题可以转化为将x插入,求出树上的前驱(后继),再将x删除的问题。
其中insert操作上文已经提到。
【pre/next操作】
这个操作十分的简单,只需要理解一点:在我们做insert操作之后做了一遍splay。这就意味着我们把x已经splay到根了。求x的前驱其实就是求x的左子树的最右边的一个结点,后继是求x的右子树的左边一个结点(想一想为什么?)
inline int pre(){ int cur=ch[root][0]; while(ch[cur][1]){ cur=ch[cur][1]; } return cur; }
inline int nxt(){ int cur=ch[root][1]; while(ch[cur][0]){ cur=ch[cur][0]; } return cur; }
【del操作】
删除操作是最后一个稍微有点麻烦的操作。
step 1:随便find一下x。目的是:将x旋转到根。
step 2:那么现在x就是根了。如果cnt[root]>1,即不只有一个x的话,直接-1返回。
step 3:如果root并没有孩子,就说名树上只有一个x而已,直接clear返回。
step 4:如果root只有左儿子或者右儿子,那么直接clear root,然后把唯一的儿子当作根就可以了(f赋0,root赋为唯一的儿子)
剩下的就是它有两个儿子的情况。
step 5:我们找到新根,也就是x的前驱(x左子树最大的一个点),将它旋转到根。然后将原来x的右子树接到新根的右子树上(注意这个操作需要改变父子关系)。这实际上就把x删除了。不要忘了update新根。
inline void del(int x){ find(x); if(cnt[root]>1){ cnt[root]--; upd(root); return; } if(!ch[root][0]&&!ch[root][1]){ clear(root); root=0; return; } if(!ch[root][0]){ int old=root; root=ch[root][1]; f[root]=0; clear(old); return; } if(!ch[root][1]){ int old=root; root=ch[root][0]; f[root]=0; clear(old); return; } int old=root,p=pre(); splay(p); ch[root][1]=ch[old][1]; f[ch[old][1]]=root; clear(old); upd(root); }
【总结】
平衡树的本质其实是二叉搜索树,所以很多操作是基于二叉搜索树的操作。
splay的本质是rotate,旋转其实只是为了保证二叉搜索树的平衡性。
所有的操作一定都满足二叉搜索树的性质,所有改变父子关系的操作一定要update。
关键是理解rotate,splay的原理以及每一个操作的原理。
转载自原文
【完整代码】
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef long long LL; 4 const int INF=1e9+7,MAXN=1e5+5; 5 int N; 6 int key[MAXN]/*关键字|值*/,cnt[MAXN]/*关键字数量*/,ch[MAXN][2]/*儿子的下标*/,siz[MAXN],f[MAXN]; 7 int root/*根*/,sz/*节点栈顶*/;/*splay的数组空间不能重复利用*/ 8 inline void DEBUG(){ 9 printf("root=%d siz=%d ",root,sz); 10 for(int i=1;i<=sz;i++){ 11 printf("(idx=%d,cnt=%d,siz=%d,key=%d,f=%d,lc=%d,rc=%d) ",i,cnt[i],siz[i],key[i],f[i],ch[i][0],ch[i][1]); 12 } 13 puts("-------------------------------------------------------"); 14 } 15 inline void clear(int x){/*清除节点中的数据*/ 16 key[x]=cnt[x]=ch[x][0]=ch[x][1]=siz[x]=f[x]=0; 17 } 18 inline int get(int x){/*查询当前节点是否为右孩子*/ 19 return x==ch[f[x]][1]; 20 } 21 inline void upd(int x){ 22 if(x){ 23 siz[x]=cnt[x]; 24 if(ch[x][0]){ 25 siz[x]+=siz[ch[x][0]]; 26 } 27 if(ch[x][1]){ 28 siz[x]+=siz[ch[x][1]]; 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 inline void rotate(int x){ 33 int fa=f[x]/*父亲下标*/,gf=f[fa]/*祖父*/,which=get(x); 34 ch[fa][which]=ch[x][which^1]; 35 f[ch[fa][which]]=fa; 36 ch[x][which^1]=fa; 37 f[fa]=x; 38 f[x]=gf; 39 if(gf){ 40 ch[gf][ch[gf][1]==fa]=x; 41 } 42 upd(fa);/*先更新下方节点*/ 43 upd(x); 44 } 45 inline void splay(int x){ 46 for(int fa;(fa=f[x]);rotate(x)){ 47 if(f[fa]){ 48 rotate(get(x)==get(fa)?fa:x);/*三点一线先rotate父亲*/ 49 } 50 } 51 root=x; 52 } 53 inline void ins(int x){ 54 if(!root){ 55 sz++; 56 clear(sz); 57 root=sz; 58 cnt[sz]=siz[sz]=1; 59 key[sz]=x; 60 return; 61 } 62 int cur=root,fa=0; 63 while(1){ 64 if(x==key[cur]){ 65 cnt[cur]++; 66 upd(cur); 67 upd(fa); 68 splay(cur); 69 return; 70 } 71 fa=cur; 72 cur=ch[fa][key[fa]<x]; 73 if(!cur){ 74 clear(++sz); 75 f[sz]=fa; 76 cnt[sz]=siz[sz]=1; 77 ch[fa][key[fa]<x]=sz; 78 key[sz]=x; 79 upd(fa); 80 splay(sz); 81 return; 82 } 83 } 84 } 85 inline int find(int x){ 86 int cur=root,ret=0; 87 while(1){ 88 if(x<key[cur]){ 89 cur=ch[cur][0]; 90 }else{ 91 ret+=(ch[cur][0]?siz[ch[cur][0]]:0); 92 if(key[cur]==x){ 93 splay(cur); 94 return ret+1; 95 } 96 ret+=cnt[cur]; 97 cur=ch[cur][1]; 98 } 99 } 100 } 101 inline int findx(int x){ 102 int cur=root; 103 while(1){ 104 if(ch[cur][0]&&x<=siz[ch[cur][0]]){ 105 cur=ch[cur][0]; 106 }else{ 107 int tmp=(ch[cur][0]?siz[ch[cur][0]]:0)+cnt[cur]; 108 if(x<=tmp){ 109 return key[cur]; 110 } 111 x-=tmp; 112 cur=ch[cur][1]; 113 } 114 } 115 } 116 inline int pre(){ 117 int cur=ch[root][0]; 118 while(ch[cur][1]){ 119 cur=ch[cur][1]; 120 } 121 return cur; 122 } 123 inline int nxt(){ 124 int cur=ch[root][1]; 125 while(ch[cur][0]){ 126 cur=ch[cur][0]; 127 } 128 return cur; 129 } 130 inline void del(int x){ 131 find(x); 132 if(cnt[root]>1){ 133 cnt[root]--; 134 upd(root); 135 return; 136 } 137 if(!ch[root][0]&&!ch[root][1]){ 138 clear(root); 139 root=0; 140 return; 141 } 142 if(!ch[root][0]){ 143 int old=root; 144 root=ch[root][1]; 145 f[root]=0; 146 clear(old); 147 return; 148 } 149 if(!ch[root][1]){ 150 int old=root; 151 root=ch[root][0]; 152 f[root]=0; 153 clear(old); 154 return; 155 } 156 int old=root,p=pre(); 157 splay(p); 158 ch[root][1]=ch[old][1]; 159 f[ch[old][1]]=root; 160 clear(old); 161 upd(root); 162 } 163 int main(){ 164 scanf("%d",&N); 165 for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){ 166 int ii,jj; 167 scanf("%d%d",&ii,&jj); 168 switch(ii){ 169 case 1:{/*插入x数*/ 170 ins(jj); 171 break; 172 } 173 case 2:{/*删除x数*/ 174 del(jj); 175 break; 176 } 177 case 3:{/*查询x数的排名*/ 178 printf("%d ",find(jj)); 179 break; 180 } 181 case 4:{/*查询排名为x的数*/ 182 printf("%d ",findx(jj)); 183 break; 184 } 185 case 5:{/*求x的前驱*/ 186 ins(jj); 187 printf("%d ",key[pre()]); 188 del(jj); 189 break; 190 } 191 case 6:{/*求x的后继*/ 192 ins(jj); 193 printf("%d ",key[nxt()]); 194 del(jj); 195 break; 196 } 197 } 198 } 199 return 0; 200 }
无注释代码
 View Code
View Code