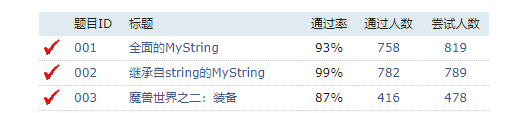
第五章 测验
1) 如果多种事物,有一些共同的特点,又有一些各自不同的特点,如何编写类来代表这些事物比较合适?
-
A.
B) 写一个类代表其中一种事物,代表其他事物的类,都从这个类派生出来
-
B.
C) 概括所有事物的共同特点,写一个基类。然后为每种事物写一个类,都从基类派生而来
-
C.
D) 一共就写一个类,包含所有事物的所有特点,然后用一个成员变量作为标记来区分不同种类的事物
-
D.
A) 为每种事物独立编写一个类,各类之间互相无关
2) 以下哪种派生关系是合理的
-
A.
B) 从“点”类派生出“圆”类
-
B.
D) 从“爬行动物”类派生出“哺乳动物”类
-
C.
A) 从“虫子”类派生出“飞虫”类
-
D.
C) 从“狼”类派生出“狗”类
3) 派生类和基类有同名同参数表的成员函数,这种现象:
-
A.
C) 叫覆盖。在派生类中基类的同名函数就没用了
-
B.
D) 叫覆盖。体现了派生类对从基类继承得到的特点的修改
-
C.
B) 叫函数的重载
-
D.
A) 叫重复定义,是不允许的
4) 以下说法正确的是:
-
A.
C) 派生类和基类的同名成员函数必须参数表不同,否则就是重复定义
-
B.
D) 派生类和基类的同名成员变量存放在相同的存储空间
-
C.
B) 派生类的成员函数中,可以调用基类的同名同参数表的成员函数
-
D.
A) 派生类可以和基类有同名成员函数,但是不能有同名成员变量
5) 以下说法正确的是:
-
A.
A) 派生类对象生成时,派生类的构造函数先于基类的构造函数执行
-
B.
B) 派生类对象消亡时,基类的析构函数先于派生类的析构函数执行
-
C.
D) 在派生类的构造函数中部可以访问基类的成员变量
-
D.
C) 如果基类有无参构造函数,则派生类的构造函数就可以不带初始化列表
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 求字符串的长度
int strlen(const char * s)
{
int i = 0;
for (; s[i]; ++i);
return i;
}
// 拷贝字符串
void strcpy(char * d, const char * s)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; s[i]; ++i)
d[i] = s[i];
d[i] = 0;
}
// 比较字符串的字典序
int strcmp(const char * s1, const char * s2)
{
for (int i = 0; s1[i] && s2[i]; ++i) {
if (s1[i] < s2[i])
return -1;
else if (s1[i] > s2[i])
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// 拼接字符串
void strcat(char * d, const char * s)
{
int len = strlen(d);
strcpy(d + len, s);
}
class MyString
{
private:
char* p; // 字符串指针 动态分配空间
int len; // 字符串长度
public:
// 字符串构造函数
MyString(const char* a)
{
len = strlen(a);
p = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(p, a);
}
// 无参数构造函数
MyString()
{
len = 1;
p = new char[1];
strcpy(p, "");
}
// 拷贝构造函数
MyString(const MyString& a)
{
len = strlen(a.p);
p = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(p, a.p);
}
// 输出运算符重载
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& o, const MyString& a)
{
o << a.p;
return o;
}
// 赋值运算符重载
MyString& operator=(const MyString& a)
{
if (p == a.p)
{
return *this;
}
if (p)
delete p;
len = strlen(a.p);
p = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(p, a.p);
return *this;
}
// [] 运算符重载
char& operator[](int i)
{
return p[i];
}
// 字符串+的重载
friend MyString operator+(const MyString& a, const MyString& b)
{
int l = b.len + a.len;
char *c = new char[l + 1];
strcpy(c, a.p);
int i;
int j = 0;
for (i = a.len; i <= l - 1; ++i, ++j)
c[i] = b.p[j];
c[i] = 0;
return MyString(c);
}
// 字符串+=的重载
void operator +=(const char *a)
{
// 注意,不能直接拼接的原因是空间不够,需要先删除p
// 申请一个更大的空间,在拼接
int i = len;
char *b = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(b, p);
delete p;
len = len + strlen(a);
p = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(p, b);
int j = 0;
for (; i <= len - 1; i++, j++) {
p[i] = a[j];
}
p[i] = 0;
}
// 比较字典序的重载
friend bool operator<(const MyString& a, const MyString& b)
{
if (strcmp(b.p, a.p) == 1) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// 比较字典序的重载
friend bool operator>(const MyString& a, const MyString& b) {
if (strcmp(a.p, b.p) == 1) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// 比较字典序的重载
friend bool operator==(const MyString& a, const MyString& b) {
if (strcmp(a.p, b.p) == 0) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// ()运算符的重载,取出字典字串
char* operator()(int a, int l) {
char* c = new char[l + 1];
int j = 0;
for (int i = a; i<a + l; i++, j++) {
c[j] = p[i];
}
c[j] = 0;
return c;
}
};
int CompareString(const void * e1, const void * e2)
{
MyString * s1 = (MyString *)e1;
MyString * s2 = (MyString *)e2;
if (*s1 < *s2)
return -1;
else if (*s1 == *s2)
return 0;
else if (*s1 > *s2)
return 1;
}
int main()
{
MyString s1("abcd-"), s2, s3("efgh-"), s4(s1);
MyString SArray[4] = { "big","me","about","take" };
cout << "1. " << s1 << s2 << s3 << s4 << endl;
s4 = s3;
s3 = s1 + s3;
cout << "2. " << s1 << endl;
cout << "3. " << s2 << endl;
cout << "4. " << s3 << endl;
cout << "5. " << s4 << endl;
cout << "6. " << s1[2] << endl;
s2 = s1;
s1 = "ijkl-";
s1[2] = 'A';
cout << "7. " << s2 << endl;
cout << "8. " << s1 << endl;
s1 += "mnop";
cout << "9. " << s1 << endl;
s4 = "qrst-" + s2;
cout << "10. " << s4 << endl;
s1 = s2 + s4 + " uvw " + "xyz";
cout << "11. " << s1 << endl;
qsort(SArray, 4, sizeof(MyString), CompareString);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
cout << SArray[i] << endl;
//s1的从下标0开始长度为4的子串
cout << s1(0, 4) << endl;
//s1的从下标5开始长度为10的子串
cout << s1(5, 10) << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class MyString :public string
{
// 在此处补充你的代码
public:
MyString():string() {}
MyString(const char *s):string(s) {}
MyString(const MyString & s):string(s){}
MyString(const string & s):string(s) {}
MyString operator()(int start, int end)
{
return substr(start, end);
}
};
int main()
{
MyString s1("abcd-"), s2, s3("efgh-"), s4(s1);
MyString SArray[4] = { "big","me","about","take" };
cout << "1. " << s1 << s2 << s3 << s4 << endl;
s4 = s3;
s3 = s1 + s3;
cout << "2. " << s1 << endl;
cout << "3. " << s2 << endl;
cout << "4. " << s3 << endl;
cout << "5. " << s4 << endl;
cout << "6. " << s1[2] << endl;
s2 = s1;
s1 = "ijkl-";
s1[2] = 'A';
cout << "7. " << s2 << endl;
cout << "8. " << s1 << endl;
s1 += "mnop";
cout << "9. " << s1 << endl;
s4 = "qrst-" + s2;
cout << "10. " << s4 << endl;
s1 = s2 + s4 + " uvw " + "xyz";
cout << "11. " << s1 << endl;
sort(SArray, SArray + 4);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
cout << SArray[i] << endl;
//s1的从下标0开始长度为4的子串
cout << s1(0, 4) << endl;
//s1的从下标5开始长度为10的子串
cout << s1(5, 10) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int M;//两大阵营开始都有M个生命元
int r_maker[5] = {2,3,4,1,0};
int b_maker[5] = {3,0,1,2,4};
string weapon[3] = {"sword","bomb","arrow"};
int HP[5];
/*
dragon: 0
ninja : 1
iceman: 2
lion : 3
wolf : 4
*/
/*
red :0
blue:1
*/
class Warrior {
private:
int num;//勇士编号
int hp;//勇士生命值
public:
Warrior(int from,int name,int warrior_t,int left_t);
};
Warrior::Warrior(int from,int name,int warrior_t,int left_t)
{
//阵营名
string camp_name;
if(from == 0)
camp_name = "red";
else
camp_name = "blue";
//武士名
string warrior_name;
switch (name)
{
case 0:warrior_name = "dragon";break;
case 1:warrior_name = "ninja";break;
case 2:warrior_name = "iceman";break;
case 3:warrior_name = "lion";break;
case 4:warrior_name = "wolf";break;
}
//武士编号
int warrior_num = warrior_t;
//生命值
int life = HP[name];
//各自阵营left
int left = left_t;
//输出所有的信息
cout<<camp_name<<' '<<warrior_name<<' '<<warrior_num<<' ';
cout<<"born with strength "<<life<<','<<left<<' '<<warrior_name;
cout<<" in "<<camp_name<<" headquarter"<<endl;
//最后设置该warrior的参数
num = warrior_num;
hp = life;
}
class Dragon : public Warrior
{
private:
double morale;
int weapon_num;
string weapon_name;