浏览目录
一、pymysql介绍
1、介绍
PyMySQL 是在 Python3.x 版本中用于连接 MySQL 服务器的一个库,Python2中则使用mysqldb。
Django中也可以使用PyMySQL连接MySQL数据库。
2、安装
pip install pymysql
二、连接数据库
1、注意事项
在进行本文以下内容之前需要注意:
- 你有一个MySQL数据库,并且已经启动。
- 你有可以连接该数据库的用户名和密码
- 你有一个有权限操作的database
2、基本使用
# 导入pymysql模块 import pymysql # 连接database conn = pymysql.connect(host=“你的数据库地址”, user=“用户名”,password=“密码”,database=“数据库名”,charset=“utf8”) # 得到一个可以执行SQL语句的光标对象 cursor = conn.cursor() # 定义要执行的SQL语句 sql = """ CREATE TABLE USER1 ( id INT auto_increment PRIMARY KEY , name CHAR(10) NOT NULL UNIQUE, age TINYINT NOT NULL )ENGINE=innodb DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; """ # 执行SQL语句 cursor.execute(sql) # 关闭光标对象 cursor.close() # 关闭数据库连接 conn.close()
返回字典格式数据:
# 导入pymysql模块 import pymysql # 连接database conn = pymysql.connect(host=“你的数据库地址”, user=“用户名”,password=“密码”,database=“数据库名”,charset=“utf8”) # 得到一个可以执行SQL语句并且将结果作为字典返回的游标 cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 定义要执行的SQL语句 sql = """ CREATE TABLE USER1 ( id INT auto_increment PRIMARY KEY , name CHAR(10) NOT NULL UNIQUE, age TINYINT NOT NULL )ENGINE=innodb DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; """ # 执行SQL语句 cursor.execute(sql) # 关闭光标对象 cursor.close() # 关闭数据库连接 conn.close()
注意:
port端口为Int数据类型。
charset=“utf8”,编码不要写成"utf-8"。
三、execute( ) 之 sql 注入
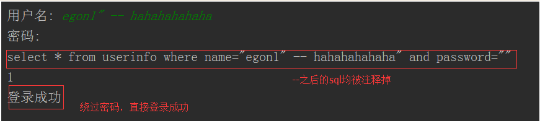
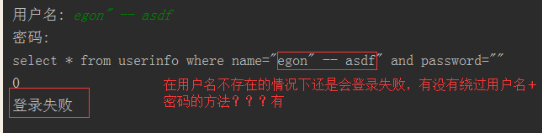
注意:符号--会注释掉它之后的sql,正确的语法:--后至少有一个任意字符
根本原理:就根据程序的字符串拼接name='%s',我们输入一个xxx' -- haha,用我们输入的xxx加'在程序中拼接成一个判断条件name='xxx' -- haha'
最后那一个空格,在一条sql语句中如果遇到select * from t1 where id > 3 -- and name='egon';则--之后的条件被注释掉了 #1、sql注入之:用户存在,绕过密码 egon' -- 任意字符 #2、sql注入之:用户不存在,绕过用户与密码 xxx' or 1=1 -- 任意字符

解决注入:
# 原来是我们对sql进行字符串拼接 # sql="select * from userinfo where name='%s' and password='%s'" %(user,pwd) # print(sql) # rows=cursor.execute(sql) #改写为(execute帮我们做字符串拼接,我们无需且一定不能再为%s加引号了) sql="select * from userinfo where name=%s and password=%s" #!!!注意%s需要去掉引号,因为pymysql会自动为我们加上 rows=cursor.execute(sql,[user,pwd]) #pymysql模块自动帮我们解决sql注入的问题,只要我们按照pymysql的规矩来。
四、增删改查操作
1、增
# 导入pymysql模块 import pymysql # 连接database conn = pymysql.connect(host=“你的数据库地址”, user=“用户名”,password=“密码”,database=“数据库名”,charset=“utf8”) # 得到一个可以执行SQL语句的光标对象 cursor = conn.cursor() sql = "INSERT INTO USER1(name, age) VALUES (%s, %s);" username = "Alex" age = 18 # 执行SQL语句 cursor.execute(sql, [username, age]) # 提交事务 conn.commit() cursor.close() conn.close()
插入数据回滚
# 导入pymysql模块
import pymysql
# 连接database
conn = pymysql.connect(host=“你的数据库地址”, user=“用户名”,password=“密码”,database=“数据库名”,charset=“utf8”)
# 得到一个可以执行SQL语句的光标对象
cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = "INSERT INTO USER1(name, age) VALUES (%s, %s);"
username = "Alex"
age = 18
try:
# 执行SQL语句
cursor.execute(sql, [username, age])
# 提交事务
conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
# 有异常,回滚事务
conn.rollback()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
获取插入数据的ID(关联操作时会用到)
# 导入pymysql模块
import pymysql
# 连接database
conn = pymysql.connect(host=“你的数据库地址”, user=“用户名”,password=“密码”,database=“数据库名”,charset=“utf8”)
# 得到一个可以执行SQL语句的光标对象
cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = "INSERT INTO USER1(name, age) VALUES (%s, %s);"
username = "Alex"
age = 18
try:
# 执行SQL语句
cursor.execute(sql, [username, age])
# 提交事务
conn.commit()
# 提交之后,获取刚插入的数据的ID
last_id = cursor.lastrowid
except Exception as e:
# 有异常,回滚事务
conn.rollback()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
批量执行
# 导入pymysql模块
import pymysql
# 连接database
conn = pymysql.connect(host=“你的数据库地址”, user=“用户名”,password=“密码”,database=“数据库名”,charset=“utf8”)
# 得到一个可以执行SQL语句的光标对象
cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = "INSERT INTO USER1(name, age) VALUES (%s, %s);"
data = [("Alex", 18), ("Egon", 20), ("Yuan", 21)]
try:
# 批量执行多条插入SQL语句
cursor.executemany(sql, data)
# 提交事务
conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
# 有异常,回滚事务
conn.rollback()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
2、删
# 导入pymysql模块
import pymysql
# 连接database
conn = pymysql.connect(host=“你的数据库地址”, user=“用户名”,password=“密码”,database=“数据库名”,charset=“utf8”)
# 得到一个可以执行SQL语句的光标对象
cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = "DELETE FROM USER1 WHERE id=%s;"
try:
cursor.execute(sql, [4])
# 提交事务
conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
# 有异常,回滚事务
conn.rollback()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
3、改
# 导入pymysql模块
import pymysql
# 连接database
conn = pymysql.connect(host=“你的数据库地址”, user=“用户名”,password=“密码”,database=“数据库名”,charset=“utf8”)
# 得到一个可以执行SQL语句的光标对象
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 修改数据的SQL语句
sql = "UPDATE USER1 SET age=%s WHERE name=%s;"
username = "Alex"
age = 80
try:
# 执行SQL语句
cursor.execute(sql, [age, username])
# 提交事务
conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
# 有异常,回滚事务
conn.rollback()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
4、查
查询单条数据
# 导入pymysql模块 import pymysql # 连接database conn = pymysql.connect(host=“你的数据库地址”, user=“用户名”,password=“密码”,database=“数据库名”,charset=“utf8”) # 得到一个可以执行SQL语句的光标对象 cursor = conn.cursor() # 查询数据的SQL语句 sql = "SELECT id,name,age from USER1 WHERE id=1;" # 执行SQL语句 cursor.execute(sql) # 获取单条查询数据 ret = cursor.fetchone() cursor.close() conn.close() # 打印下查询结果 print(ret)
查询多条数据
# 导入pymysql模块 import pymysql # 连接database conn = pymysql.connect(host=“你的数据库地址”, user=“用户名”,password=“密码”,database=“数据库名”,charset=“utf8”) # 得到一个可以执行SQL语句的光标对象 cursor = conn.cursor() # 查询数据的SQL语句 sql = "SELECT id,name,age from USER1;" # 执行SQL语句 cursor.execute(sql) # 获取多条查询数据 ret = cursor.fetchall() cursor.close() conn.close() # 打印下查询结果 print(ret)
进阶用法
# 可以获取指定数量的数据 cursor.fetchmany(3) # 光标按绝对位置移动1 cursor.scroll(1, mode="absolute") # 光标按照相对位置(当前位置)移动1 cursor.scroll(1, mode="relative")