作者:finallyly 出处 :博客园(转载请注明作者和出处)
衡量字符串的相似度有多种方法,比如:检验两个字符串之间是否具有子串关系;在某个给定操作集合中定义一个串变化到另一个串所经历的操作数(如编辑距离公式);寻找另一个子串,该子串中的字符在两个待比较的串中都有出现,而且出现的前后顺序相同,另外我们不要求子串中的字符在待比较的串中是连续出现的,这个子串就被定义为common sequence。最长的子串被称作(longest common sequence)。
最近做的一个项目中需要实现一个基于LCS,以LCS为核心的算法,所以参照了《算法导论》上面的介绍,自己实现了LCS。并在此博文中进行介绍,旨在给后续介绍项目算法做铺垫。
此处给出全部实现代码和注释,供有计算文本字符串相似度(尤其是汉语字符串相似度)需求的童鞋参考。
此处设计一个类别stringprocess来完成对两个待比较的字符串的LCS的求解.
 stringprocess.h
stringprocess.h
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class stringprocess
{
public:
stringprocess(void);
~stringprocess(void);
//计算最大公共子序列的长度,同时填写result表格
int CalculateLongestCommonSequenceLen(const wchar_t* xpart,const wchar_t*ypart);
//void CreateEmptyIndexes();//生成一个空的Indexes组
void GetIndexesInfo(int* xpartInfo,int* ypartInfo );//分别返回最长公共子序列在x字符串和字符串中出现的下标。
wstring GetLongestCommonSequence();
private:
int **indexes;//声明指向指针的指针,保存两个字符串中的最长公共序列中的字符分别出现的位置。//它指向一个二维指针数组,指针数组的每个成员变量都指向一个长度为len(result)整型数组
char**resultbuffer;//此结构用于存放LCS算法运行过程的相关信息
int xpart_len;//x串的长度
int ypart_len;//y串的长度
wstring result;//最大公共子序列
};
类的成员函数实现文件:
 stringprocess.cpp
stringprocess.cpp
#include "stringprocess.h"
stringprocess::stringprocess(void)
{
indexes=NULL;
resultbuffer=NULL;
}
stringprocess::~stringprocess(void)
{
if (indexes!=NULL)
{
cout<<"indexes指针成员变量已经被分配了堆内存,需要以delete模式释放"<<endl;
for (int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
delete[]indexes[i];
}
delete []indexes;
cout<<"indexes释放完毕"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"指针成员变量为被分配堆内存,不需要以delete模式释放"<<endl;
}
if (resultbuffer!=NULL)
{ cout<<"resultbuffer指针成员变量已经被分配了堆内存,需要以delete模式释放"<<endl;
for (int i=0;i<xpart_len+2;i++)
{
delete resultbuffer[i];
}
delete resultbuffer;
cout<<"resultbuffer释放完毕"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"resultbuffer指针成员变量为被分配堆内存,不需要以delete模式释放"<<endl;
}
cout<<"destructor"<<endl;
}
/************************************************************************/
/* 返回最长公共子序列 */
/************************************************************************/
wstring stringprocess::GetLongestCommonSequence()
{
return result;
}
/************************************************************************/
/* 建立下标数组,用于保存最长公共子序列中的元素在原序列中的下标 */
/************************************************************************/
/*void stringprocess::CreateEmptyIndexes()
{
if (result.size()>0)
{
//indexes指向一个二维指针数组indexes[0]储存最大公共子序列中元素在xpart中的下标;
//indexes[1]储存最大公共子序列中元素在ypart中的下标
indexes=new int*[2];
for (int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
indexes[i]=new int[result.size()];
memset(indexes[i],0,sizeof(int)*result.size());
}
}
}*/
/************************************************************************/
/* 获取最长公共子序列在原字符串中的位置 */
/************************************************************************/
void stringprocess::GetIndexesInfo(int *xpartInfo, int *ypartInfo)
{
for (int i=0;i<result.size();i++)
{
xpartInfo[i]=indexes[0][i];
ypartInfo[i]=indexes[1][i];
}
}
/************************************************************************/
/* 求序列x和序列y的最大公共字串 */
/************************************************************************/
int stringprocess:: CalculateLongestCommonSequenceLen(const wchar_t* x,const wchar_t* y)
{
int resultlen=0;
//字符数组的实际维度要比字符串的长度多一,最后一位为'\0'元素,所以数组维度应该+1,
xpart_len=wcslen(x);
ypart_len=wcslen(y);
int lenx=xpart_len+1;
int leny=ypart_len+1;
int lenxx=lenx+1;//存储结果的维度把空字符串的位置算上
int lenyy=leny+1;
int**LCSlen=new int*[lenxx];
for (int i=0;i<lenxx;i++)
{
LCSlen[i]=new int[lenyy];
memset(LCSlen[i],0,lenyy*sizeof(int));
}
resultbuffer=new char*[lenxx];
for (int i=0;i<lenxx;i++)
{
resultbuffer[i]=new char[lenyy];
memset(resultbuffer[i],0,lenyy*sizeof(char));
}
//填充resultbuffer
//注意字符数组的下标最小值为零,临时储存数组的最小下标为1,0位对应为空字串
for (int i=0;i<lenx;i++)
{
for (int j=0;j<leny;j++)
{
if (x[i]==y[j])
{
LCSlen[i+1][j+1]=LCSlen[i][j]+1;
resultbuffer[i+1][j+1]='a';
}
else
{
if (LCSlen[i][j+1]>=LCSlen[i+1][j])
{
LCSlen[i+1][j+1]=LCSlen[i][j+1];
resultbuffer[i+1][j+1]='b';
}
else
{
LCSlen[i+1][j+1]=LCSlen[i+1][j];
resultbuffer[i+1][j+1]='c';
}
}
}
}
resultlen=LCSlen[lenx][leny]-1;
//释放对内存
for (int i=0;i<lenxx;i++)
{
delete LCSlen[i];
}
if (resultlen>0)//非空字符串
{
//indexes指向一个二维指针数组indexes[0]储存最大公共子序列中元素在xpart中的下标;
//indexes[1]储存最大公共子序列中元素在ypart中的下标
indexes=new int*[2];
for (int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
indexes[i]=new int[resultlen];
memset(indexes[i],0,sizeof(int)*resultlen);
}
wchar_t *resultchar=new wchar_t[resultlen+1];//类似一个栈
int workindex_i=lenx;
int workindex_j=leny;
int workindex_rst=resultlen;
while(workindex_i!=0&&workindex_j!=0)
{
if (resultbuffer[workindex_i][workindex_j]=='a')
{
resultchar[workindex_rst]=x[workindex_i-1];
if (x[workindex_i-1]!=0)
{
indexes[0][workindex_rst]=workindex_i-1;
indexes[1][workindex_rst]=workindex_j-1;
}
workindex_i--;
workindex_j--;
workindex_rst--;
}
else
{
if (resultbuffer[workindex_i][workindex_j]=='b')
{
workindex_i--;
}
else
{
workindex_j--;
}
}
}
result.assign(resultchar,resultlen);
}
delete LCSlen;
return resultlen;
}
此处需要注意的地方有该类的构造函数和析构函数的写法(该类并不在构造函数中给指针型数据成员动态申请内存)参考资料见《新手初学C++:带有指针型数据成员的类》以及如何申请高维数组的堆空间。参考资料见《c++声明二维变长数组并用memset赋0值》
另外要注意函数:CalculateLongestCommonSequenceLen,该函数计算LCS的长度,求出lcs串,并且保存LCS串中的每个字符在两个父串(待比较的字符串)中的下标。我们要注意到,将一个string转换成char数组的时候,char数组的维度应该为string的长度加1,因为char数组的最后一个元素为'\0'。另外注意到LCSLen和resultbuffer的维度要比char数组多1,这里设置0下标对应于空串。
下面给出算法运行结果图:
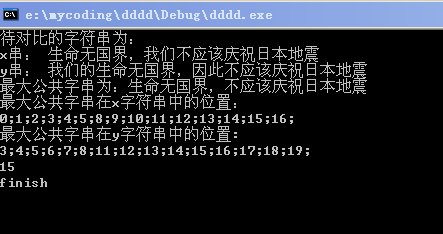
附: 主函数测试代码见《LCS算法示例的主函数调用 》
