牛客专题之DFS序
简介
dfs序: 每个节点在dfs深度优先遍历中的进出栈的时间序列,也就是tarjan算法中的dfn数组。
画个图理解一下:
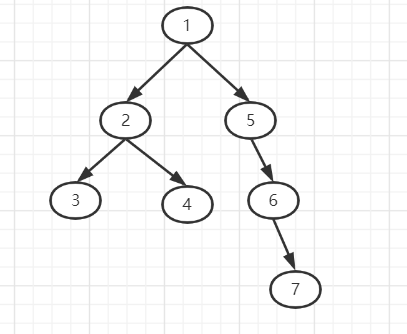
这棵树的dfs序:1 3 2 4 2 5 6 7 6 5 1。
那么这个序列有什么用呢?
通过观察,两个相同数字之间就是以它为根的子树, 也就是说,通过dfs序我们可以得到,这个节点第一次进入栈的时间戳(l_i)和第一次出栈的时间戳(r_i)。之后我们就可以通过(l_i)和(r_i)操纵这棵树了。
具体看题:
模板
Military Problem 原CF1006E
题意
你有一棵有(n)个节点的树,有(q)次询问,每次询问有((u,k)),指从以(u)为根的子树出发先序遍历到达的第(k)个点是哪一个?如果不存在,输出(-1)。
一道模板题。先预处理出每个点的dfs序, 即每个点的(l_i)和(r_i)。
询问的时候判断是否(l[u] + k - 1 > r[u]), 否则输出(a[l[u]+k-1])就好了。
/*
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/problem/112932
https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1006/E
*/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 10;
int a[maxn], cnt = 0;
int l[maxn], r[maxn];
vector<int> G[maxn];
void dfs(int u, int fa){
l[u] = ++cnt;
a[cnt] = u;
for(auto v : G[u]) {
if(fa == v) continue;
dfs(v, u);
}
r[u] = cnt;
}
int main(){
int n, q;
cin >> n >> q;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
int u; cin >> u;
G[i].push_back(u);
G[u].push_back(i);
}
dfs(1, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= q; i++){
int u, k;
cin >> u >> k;
if(l[u] + k - 1 > r[u]) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << a[l[u] + k - 1] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
选点
题意
有一棵(n)个节点的二叉树,每个节点有权值(w_i),要选尽量多的点,但是得满足以下限制:
对于任意一棵子树,都要满足:
- 如果选了根节点的话,在这棵子树内选的其他的点都要比根节点的值大
- 如果在左子树选了一个点,在右子树中选的其他点要比它小。
思路
读题后可以得到:根的值< 右子树的最大值 < 左子树的最大值, 如果要得到尽量多的点,只需要记录从根 -> 右子树 -> 左子树的dfs序(此处为入栈时间戳(l_i)), 在(l_i)上找最长上升子序列(没想到。。)即可。
代码
/*
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/problem/22494
*/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 10;
int a[maxn], tot = 0, cnt;
int l[maxn], r[maxn], w[maxn], ans[maxn];
vector<int> G[maxn];
void dfs(int u){
if(u == 0) return;
a[++tot] = w[u];
dfs(r[u]); dfs(l[u]);
}
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> w[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> l[i] >> r[i];
dfs(1);
ans[++cnt] = a[1];
// 最长上升子序列贪心O(nlogn)解法
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
if(a[i] > ans[cnt]) ans[++cnt] = a[i];
else{
int t = lower_bound(ans + 1, ans + 1 + cnt, a[i]) - ans;
ans[t] = a[i];
}
}
cout << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
dfs序+树状数组/线段树
求和
题意
一颗以(k)为根有 (n) 个节点的树,每个节点有一个点权(v_i)。有(m) 次操作
- 1 x y 表示将节点 (x)的权值加上 (y)
- 2 x 表示求以(x)为根的子树上所有节点(包括(x))的和
思路:
通过 dfs 序将一整棵子树上映射到序列中连续的一段上。问题就变成对数组进行:单点修改,区间查询。用树状数组维护就好了。
代码
/*
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/problem/204871
*/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pb push_back
const int maxn = 1e6 + 10;
int l[maxn], r[maxn];
int bits[maxn];
vector<int> G[maxn];
int n, m, k, cnt = 0;
int lowbit(int x){
return x & (-x);
}
void add(int x, int val){
while(x < maxn){
bits[x] += val;
x += lowbit(x);
}
}
int query(int x){
int res = 0;
while(x){
res += bits[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return res;
}
void dfs(int u, int fa){
l[u] = ++cnt;
for(auto v : G[u]){
if(v == fa) continue;
dfs(v, u);
}
r[u] = cnt;
}
int a[maxn], op[maxn], b[maxn], val[maxn];
int main(){
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
int u, v; cin >> u >> v;
G[u].push_back(v);
G[v].push_back(u);
}
dfs(k, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) add(l[i], a[i]);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int op; cin >> op;
if(op == 1){
int x, y; cin >> x >> y;
add(l[x], y);
}
else{
int x; cin >> x;
cout << (query(r[x]) - query(l[x]-1)) << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
Propagating tree 原CF383C
题意
一颗以(1)为根有 (n) 个节点的树,每个节点有一个点权(a_i)。有(m) 次操作
- 1 x y 表示将 (x) 结点权值 (+val) ,(x) 的儿子权值 (-val),(x) 的孙子们 (+val), 以此类推。
- 2 x 表示(x)的点权
思路
乍一看是树状数组差分,区间修改,单点查询。但是第一个操作搞不定,仔细观察后得到(1)操作和每个节点的深度奇偶有关。所以只需判断一下深度,决定修改的值的正负就可以(又没想到。。。)。
代码
/*
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/problem/110318
*/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pb push_back
const int maxn = 1e6 + 10;
int l[maxn], r[maxn];
int bits[maxn];
vector<int> G[maxn];
int n, m, k, cnt = 0;
int a[maxn], dep[maxn];
int lowbit(int x){
return x & (-x);
}
void add(int x, int val){
while(x < maxn){
bits[x] += val;
x += lowbit(x);
}
}
int query(int x){
int res = 0;
while(x){
res += bits[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return res;
}
void dfs(int u, int fa){
l[u] = ++cnt;
dep[u] = dep[fa] + 1;
for(auto v : G[u]){
if(v == fa) continue;
dfs(v, u);
}
r[u] = cnt;
}
int main(){
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
int u, v; cin >> u >> v;
G[u].pb(v);
G[v].pb(u);
}
dfs(1, 0);
// for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) add(l[i], a[i]);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int op; cin >> op;
if(op == 1){
int x, y; cin >> x >> y;
if(dep[x] & 1){
add(l[x], y);
add(r[x] + 1, -y);
} else {
add(l[x], -y);
add(r[x] + 1, y);
}
}
else{
int x; cin >> x;
int y = query(l[x]);
if(dep[x] & 1) cout << a[x] + y << endl;
else cout << a[x] - y << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
[华华和月月种树]https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/problem/23051)
题意
华华和月月一起维护了一棵动态有根树,每个点有一个权值。刚开存档的时候,树上只有 0 号节点,权值为 0 。接下来三种操作:
- (1) (i) 表示月月氪金使节点(i) 长出了一个新的儿子节点,权值为(0),编号为当前最大编号 (+1)(也可以理解为,当前是第几个操作 (1),新节点的编号就是多少)。
- (2) (i) (a) 表示华华上线做任务使节点 (i) 的子树中所有节点(即它和它的所有子孙节点)权值加 (a) 。
- (3) (i),华华需要给出 (i) 节点此时的权值。
思路
树状数组区间更新单点求值。
操作(1)可以将新加的点的减去它的父亲的权值来使得新加的点值为(0)。
代码
/*
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/problem/23051
https://blog.nowcoder.net/n/0055f19c0e49422786d7b7981a914709
*/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pb push_back
const int maxn = 1e6 + 10;
int l[maxn], r[maxn];
int bits[maxn];
vector<int> G[maxn];
int m, cnt = 0;
int lowbit(int x){
return x & (-x);
}
void add(int x, int val){
while(x <= cnt + 1){
bits[x] += val;
x += lowbit(x);
}
}
int query(int x){
int res = 0;
while(x){
res += bits[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return res;
}
void dfs(int u){
l[u] = ++cnt;
for(auto v : G[u]) dfs(v);
r[u] = cnt;
}
int a[maxn], op[maxn], b[maxn], val[maxn];
int main(){
cin >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
cin >> op[i] >> a[i];
if(op[i] == 2) cin >> b[i];
else if(op[i] == 1){
G[a[i]].pb(++cnt);
b[i] = cnt;
}
}
dfs(0);
// cout << cnt << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
if(op[i] == 1) val[l[b[i]]] -= query(l[a[i]]);
else if(op[i] == 2){
add(l[a[i]], b[i]);
add(r[a[i]] + 1, -b[i]);
}
else cout << val[l[a[i]]] + query(l[a[i]]) << endl;
}
return 0;
}